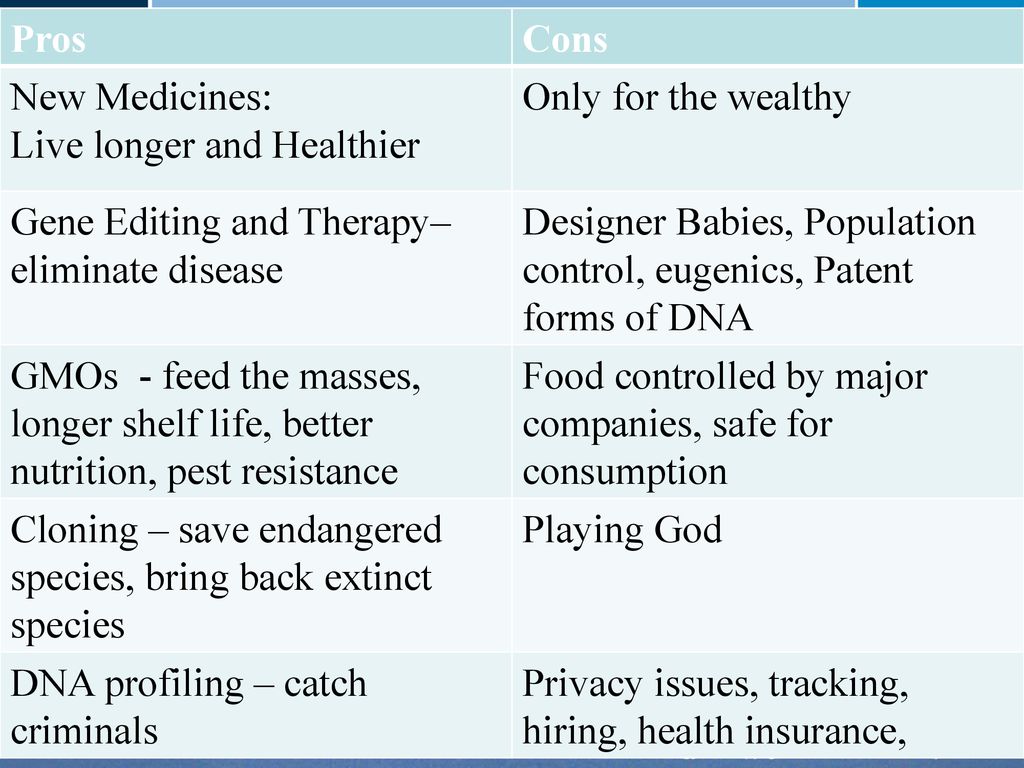
Designer babies, also known as genetically modified babies, refer to the use of genetic engineering techniques to select and alter the traits of an unborn child. This technology has the potential to eliminate certain genetic disorders and diseases, as well as enhance physical and mental abilities. However, the prospect of designer babies also raises numerous ethical and social concerns.
One pro of designer babies is the potential to eliminate inherited diseases and disorders. Genetic engineering techniques can be used to identify and prevent the transmission of genetic conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease. This could improve the quality of life for individuals and their families, as well as reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Another potential benefit of designer babies is the ability to enhance physical and mental abilities. For example, parents may be able to select traits such as intelligence, athletic ability, and physical attractiveness for their children. This could lead to a more diverse and highly skilled population, potentially leading to advancements in fields such as science, technology, and athletics.
However, there are also several significant cons to consider when it comes to designer babies. One concern is the ethical implications of selecting and altering the traits of a person. Some argue that this technology could lead to a society where individuals are judged and valued based on their genetic makeup, rather than their individual qualities and actions. This could lead to discrimination and inequality, as well as the devaluation of people with disabilities or those who do not possess certain desirable traits.
Another concern is the potential for misuse of this technology. There is a risk that designer babies could be used to create a new class of "elite" individuals, or that the technology could be used to further existing social and economic divides. There is also a risk that genetic engineering could be used to create weapons or other harmful uses.
In conclusion, the potential benefits and drawbacks of designer babies must be carefully considered. While the technology has the potential to eliminate inherited diseases and enhance physical and mental abilities, it also raises significant ethical and social concerns. It is important to carefully examine the potential impacts of this technology and to ensure that it is used in a responsible and ethical manner.
Network analysis is a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing complex systems, but it is not without its limitations. Here are some key limitations of network analysis:
Complexity: Network analysis can be very complex, particularly when dealing with large and highly interconnected systems. This can make it difficult for analysts to fully understand and interpret the results of their analysis.
Data quality: The quality of the data used in network analysis is crucial to the accuracy and reliability of the results. Poor quality data, such as incomplete or incorrect data, can lead to flawed conclusions and incorrect recommendations.
Limited scope: Network analysis is typically focused on understanding the relationships between individual entities within a system. It may not always be possible to capture the full context or broader environmental factors that may be influencing the system.
Assumptions: Network analysis often relies on assumptions about the relationships between entities in the system. These assumptions may not always hold true, which can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Limited predictive power: While network analysis can be useful for understanding and explaining past events, it may have limited predictive power when it comes to predicting future outcomes. This is because networks are often dynamic and can change over time, making it difficult to accurately forecast future events.
Overall, network analysis is a useful tool for understanding complex systems, but it is important to recognize its limitations and to use it in conjunction with other analytical techniques to get a complete understanding of the system being studied.