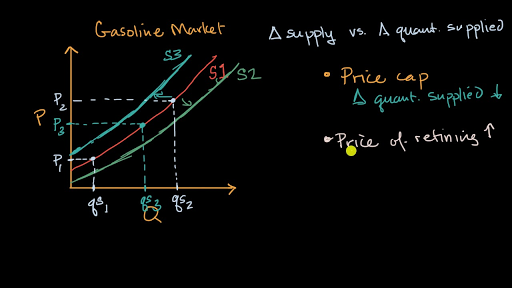
Change in supply refers to a shift in the entire supply curve for a good or service, while quantity supplied refers to the amount of a good or service that is being offered for sale at a particular price. These two concepts are closely related, but they are not the same thing.
Change in supply occurs when there is a change in the factors that affect the production of a good or service. This could be due to changes in the cost of production, changes in technology, or changes in the availability of resources. When the supply of a good or service increases, the supply curve shifts to the right, while a decrease in supply shifts the curve to the left.
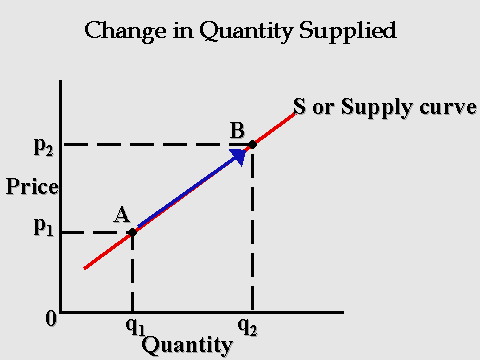
Quantity supplied, on the other hand, refers to the amount of a good or service that a producer is willing and able to sell at a particular price. This is represented by a point on the supply curve. If the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied will also increase, as producers are willing to produce and sell more at a higher price. Conversely, if the price decreases, the quantity supplied will also decrease, as producers are less willing to produce and sell at a lower price.
It is important to note that change in supply and quantity supplied are not the same thing, and they can have different effects on the market. For example, if there is a change in the cost of production that leads to an increase in the supply of a good or service, the entire supply curve will shift to the right, and the quantity supplied at each price will increase. However, if the price of the good or service increases, the quantity supplied will also increase, but the supply curve will not shift.
In summary, change in supply refers to a shift in the entire supply curve for a good or service, while quantity supplied refers to the amount of a good or service that is being offered for sale at a particular price. These two concepts are closely related, but they are not the same thing, and understanding the difference between them is important for analyzing market conditions and making informed decisions.
Difference Between Supply and Quantity Supplied (with Law of Supply and Comparison Chart)
.jpg)
What are the two types of shifts in supply curve? By joining these various points, A, B, C, D, E and F, we get curve S, which is known as the supply curve. Now our new equilibrium is going to be right here where S2 the new supply curve intersects with the demand curve and now we're going to have Q2 and we're going to have P2. Answer based on downward movement is also correct "Change in Supply'' means change in supplydue to change in any factor other than the own price of the good. This would be a change in quantity supplied. You want to determine the optimal number of driver partners to induct in a city. Price: Refers to the main factor that influences the supply of a product to a greater extent. Dagrimmatically, it means shift of supply curvewhen producermoves from A to B, the price remains unchanged at OP while the SupplyCurve shift from S1 to S2.
Change in supply and a change in quantity supplied
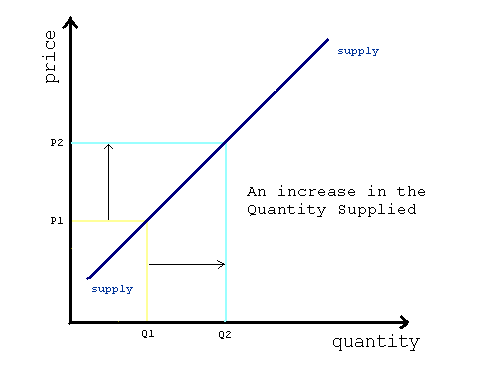
Understanding the quantity supplied is essential to understanding how markets work and how prices are determined. Other factors are: prices of commodities, production costs which includes an increase or decrease in production, resources, labor, and other related items , price of related goods in relation to market competition and other sellers , Movement in the quantity supplied is characterized as from one point of quantity supplied to another point. For example, if a farmer instead of traditional seeds utilizes hybrid varieties of seeds then his per hectare output would increase thus shifting his supply to the right. Example With the help of this supply schedule, we will plot the supply curve A functional relationship exists between the quantity supplied and the price of a commodity. Represents How much the market can offer. The difference between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied is that a change in the quantity supplied is due to a change in the own price. What is the difference between supply and quantity supplied? What are the 8 determinants of supply? Now if you were to ask "Well, what is going to happen now to the price of coffee? By contrast, changes in quantity supplied are caused by changes in price, causing producers to sell more or less at a different price.
Difference Between Change In Supply And Quantity Supplied

For example, if wages or cost of raw material or of fuel or power goes up it would increase cost of production and this would affect supply as less would be supplied at various given prices, this would shift supply curve to the left. It is due to this direct relationship between price of a commodity and its quantity supplied that the supply curve slopes upward as shown in the below figure -: Price S P1 P P2 0 Q2 Q Q1 Quantity suppliedWith increase in price from P2 to P to P1, quantity supplied increase from 0Q2 to 0Q to 0Q1 thus making upward sloping supply curve S. For example, if a farmer grows two crops, wheat and pulses and any rise in prices of pulses will induce the farmer to cultivate more pulses and less of wheat. Now if I were to ask you what would happen if the price decreased? The term quantity supplied means that the supply at a particular price and particular quantity. It is because due to a decrease in the inputs, it becomes more profitable to sign-up and drive and hence, more and more drivers are willing to sign-up. It is usually measured in units. Supply Schedule of a Firm A supply schedule is presented in the above table.
Changes in Quantity Supplied vs Shift in Supply

The world today is dominated by a continuous flow of information. But when there is a fall in the market price of the commodity, this results in contraction of supply. Movement along the supply curve or change in quanity supplied: When the supply of a good rises due to rise in the price of the good alone, it is termed as an expansion of supply. Mark each transaction as affecting owner's investment I , owner's drawings D , revenue R , expense E , or … not affecting owner's equity NOE. Also, high prices encourage a firm to produce or sell more. You conducted a survey to find out the number of people who are willing to sign-up as driver partners at different levels of fare per kilometer.

.jpg)