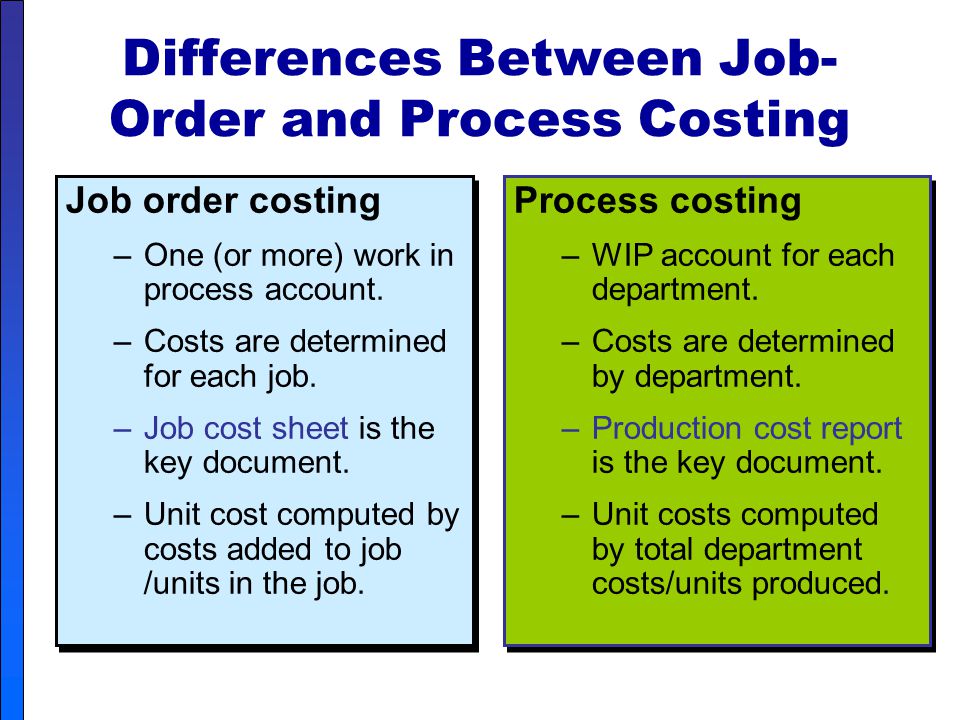
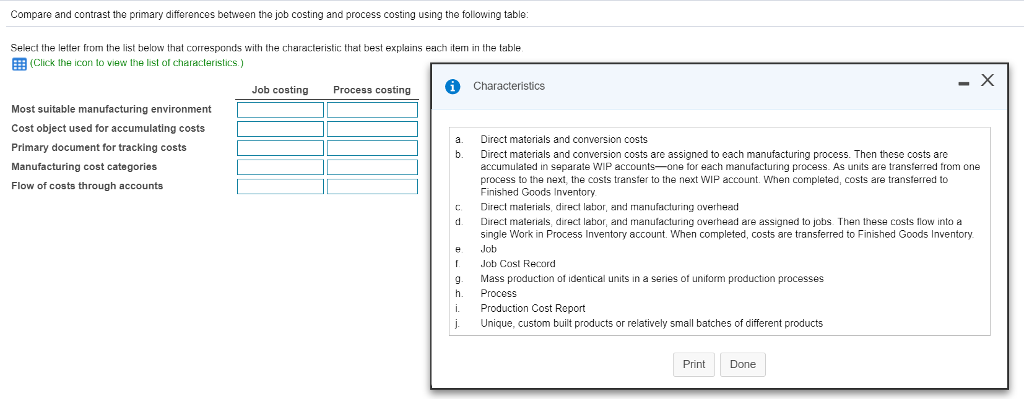
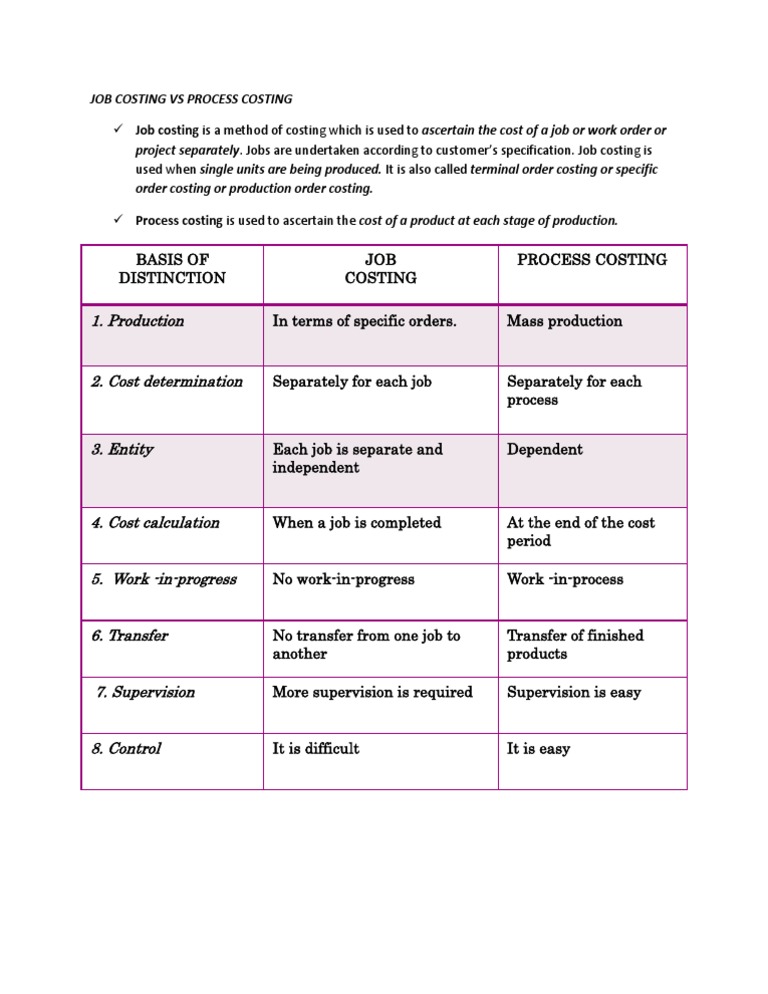
Job costing and process costing are two methods of cost accounting that are used to assign costs to products or services. While they may seem similar at first glance, they are actually quite different in terms of their approach and the types of industries they are best suited for.
Job costing is a method that is used when each product or service produced is unique and requires a specific set of resources. This method is commonly used in industries such as construction, custom manufacturing, and professional services, where each job or project is distinct from others. In job costing, the costs of each job are tracked separately and allocated to the specific product or service being produced. This allows the company to accurately determine the cost of each job, as well as the profit or loss associated with it.
On the other hand, process costing is a method that is used when products or services are produced in a continuous and repetitive manner, using a consistent set of resources. This method is commonly used in industries such as mass manufacturing, chemical production, and oil refining, where the same process is used to produce a large volume of similar products or services. In process costing, the costs of the production process are averaged out over the total number of units produced, and are then allocated to each unit. This allows the company to determine the average cost of production, as well as the profit or loss associated with each unit.
One key difference between job costing and process costing is the level of detail involved in tracking costs. In job costing, the costs of each job are tracked separately and in detail, while in process costing, the costs are averaged out over a larger volume of production. This means that job costing is more suitable for industries where each job is unique and requires a specific set of resources, while process costing is better suited for industries where the production process is more standardized and repetitive.
Another difference between the two methods is the way in which costs are allocated to products or services. In job costing, the costs are directly allocated to the specific job or project being produced, while in process costing, the costs are averaged out over a larger volume of production and then allocated to each unit. This means that the cost of each unit produced using process costing may be less accurate than the cost of each job produced using job costing, as it is based on an average rather than a specific set of resources.
In conclusion, while both job costing and process costing are methods of cost accounting used to assign costs to products or services, they are different in terms of their approach and the types of industries they are best suited for. Job costing is more detailed and suitable for industries where each job is unique, while process costing is more suited for industries where the production process is more standardized and repetitive. Understanding the differences between these two methods is important for businesses to choose the most appropriate method for their industry and to accurately determine the costs and profitability of their products or services.