Science and pseudoscience are often confused, as both involve the exploration of the natural world and the search for knowledge. However, there are several key differences between the two that can help distinguish one from the other.
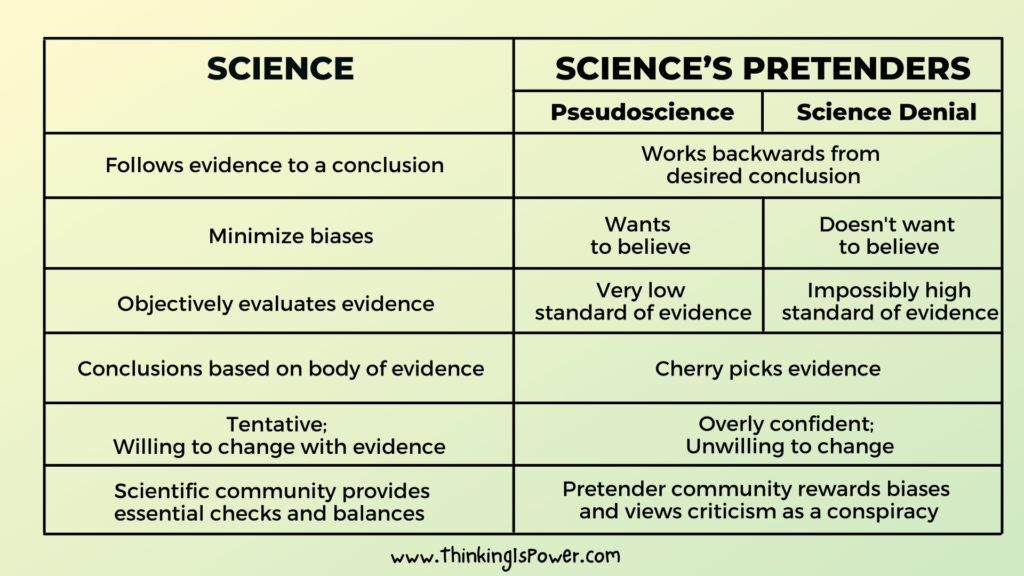
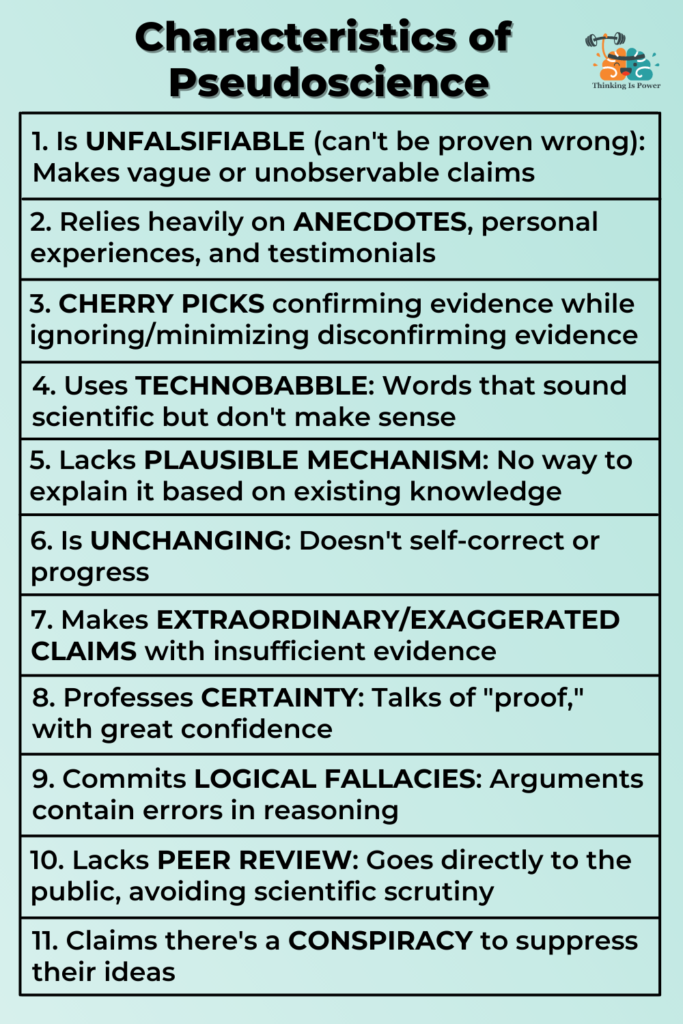
First, science is based on empirical evidence and the scientific method. This means that scientists collect data through observation and experimentation, and then use this data to form and test hypotheses. Pseudoscience, on the other hand, relies on untested or untestable claims, often based on personal beliefs or anecdotal evidence rather than objective, verifiable data.
Second, science is subject to peer review and is constantly tested and refined. When scientists publish their research, it is reviewed by other experts in the field, who will check the data and methods used to ensure that the conclusions are supported by the evidence. In contrast, pseudoscience is not subject to the same level of scrutiny and is often not backed up by any evidence at all.
Third, science is transparent and open to criticism. Scientists are expected to be clear and transparent about their methods and data, and they are open to criticism and discussion. Pseudoscience, on the other hand, is often shrouded in secrecy or presented as a set of facts that cannot be questioned.
Finally, science is self-correcting, meaning that new data or discoveries can lead to the revision or even rejection of previous theories. Pseudoscience, on the other hand, is resistant to change and often clings to outdated or incorrect ideas even in the face of new evidence.
In summary, the main difference between science and pseudoscience is that science is based on empirical evidence, subject to peer review and criticism, and transparent, while pseudoscience relies on untested or untestable claims, is not subject to the same level of scrutiny, and is resistant to change.
Discerning Between Science and Pseudoscience

If Newton and Einstein are wrong, I inquired of EU proponent Wallace Thornhill, can you generate spacecraft flight paths that are more accurate than those based on gravitational theory? Non-science, pseudoscience, quasi-science and bad science; is there a difference? You need a brain to be conscious, but consciousness exists elsewhere. It seemed like a fake documentary designed to make a quick buck off of fear. But it is even more concerning that when people believe such theories, serious harm may occur to the sufferer. The most common, and probably weakest, argument is that the number of people reporting UFOs is so large, that they must exist. The fear and mystery of the subject gouged it wide open for exploitation by pseudoscientists.
The Difference between Science and Pseudoscience

Oftentimes, they are incorporated into the mainstream culture without being questioned or critiqued by the public. A common form of pseudoscience that is seen in pop science publications is astrology. This story began the transition from UFO sightings to extraterrestrial abduction reports, a craze which continued into the 1990s, and seems to have a correlation with both entertainment and news media. Pseudoscience often overlaps with superstition, mysticism, and other forms of non-scientific belief systems. Casual approach to evidence — Real science has evidence to back up its claims! Conclusion About The Differences Between Science And Pseudoscience Pseudoscience is a broad term that means false or misleading theories, claims, or practices. In practice, pseudoscience can manifest as a specific belief or practice which is regarded by some to be false or incompatible with established scientific facts. Appeals to myths — Humans tend to use pseudoscience in an attempt to formulate an explanation for things that they cannot easily understand.