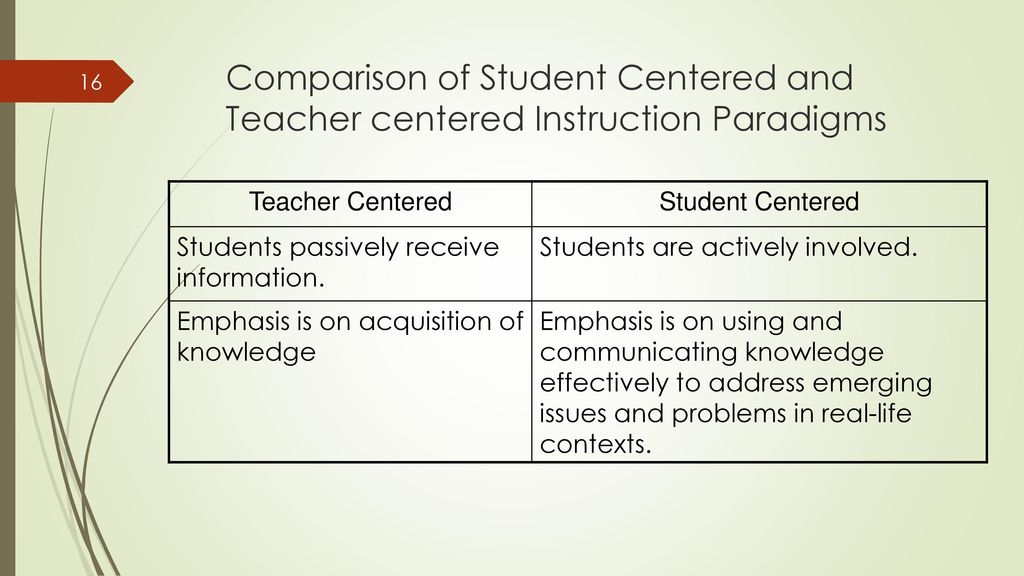
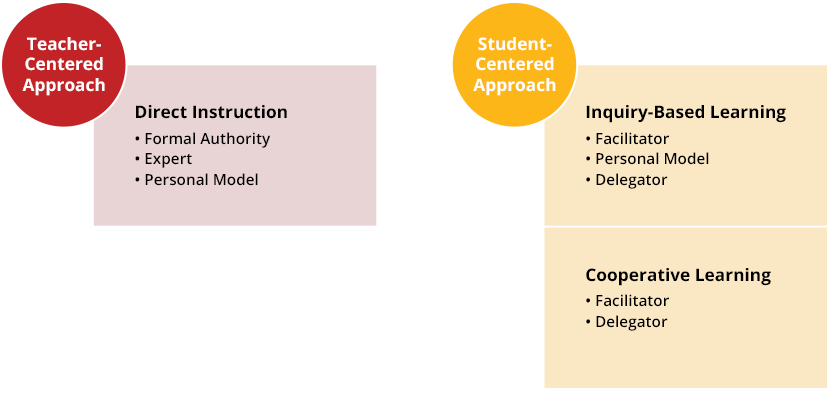
In the field of education, there are two main approaches to teaching and learning: student-centered and teacher-centered. While both approaches have their own benefits and drawbacks, they are fundamentally different in the way they approach the role of the student and the teacher in the classroom.
Student-centered learning is an approach that focuses on the needs and interests of the individual student. In a student-centered classroom, the teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding and supporting the students as they explore and learn on their own. This approach places a strong emphasis on critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-directed learning, and it encourages students to take an active role in their own education.
One of the main benefits of student-centered learning is that it allows students to take ownership of their own learning. This can be especially effective for students who are motivated and self-directed, as it gives them the opportunity to explore and learn about topics that interest them. Additionally, student-centered learning can be very effective at promoting deep learning, as it encourages students to think critically and to engage with the material on a deeper level.
However, student-centered learning can also be challenging for both students and teachers. It requires a high level of student engagement and self-motivation, and it can be difficult for some students to stay on task and make progress without the more structured support of a teacher-centered approach. Additionally, student-centered learning requires a high level of teacher expertise and organization, as the teacher must be able to facilitate learning and guide students in their exploration of the material.
Teacher-centered learning, on the other hand, is an approach that focuses on the teacher as the primary source of knowledge and instruction. In a teacher-centered classroom, the teacher is responsible for delivering lectures and providing instruction, and the students are expected to absorb and apply the information presented to them. This approach is often more structured and predictable, and it relies on traditional methods such as lectures and direct instruction.
One of the main benefits of teacher-centered learning is that it can be more efficient and effective at conveying information to students. By delivering lectures and providing direct instruction, teachers can cover a large amount of material in a relatively short period of time. This can be especially useful in subjects that require a lot of memorization or technical skills, where it is important to cover the material thoroughly and efficiently. Additionally, teacher-centered learning can be more effective for students who struggle with motivation or self-direction, as it provides a clear structure and guidance for learning.
However, teacher-centered learning can also have some drawbacks. It can be less engaging and interactive for students, and it can discourage critical thinking and problem-solving. Additionally, teacher-centered learning can be less effective at promoting deep learning, as it tends to focus more on memorization and surface-level understanding rather than encouraging students to explore and engage with the material on a deeper level.
In conclusion, student-centered and teacher-centered approaches to learning are fundamentally different in the way they approach the role of the student and the teacher in the classroom. Student-centered learning places a strong emphasis on critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-directed learning, while teacher-centered learning focuses on the teacher as the primary source of knowledge and instruction. Both approaches have their own benefits and drawbacks, and the most effective approach will depend on the needs and goals of the individual student and the subject being taught.