Amazon is a company that has revolutionized the way we shop and do business. With its vast inventory and efficient delivery system, it has become the go-to online retailer for many consumers. However, managing such a large inventory is no easy task. In this case study, we will explore how Amazon manages its inventory and the strategies it uses to ensure that its products are available to customers when they want them.
One key strategy that Amazon uses to manage its inventory is the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies allow Amazon to analyze data on customer demand and purchasing patterns in real-time, allowing the company to make informed decisions about how much of a particular product to stock and when to reorder.
Another important aspect of Amazon's inventory management is its fulfillment centers. These are large warehouses where Amazon stores its products and processes orders for delivery. Amazon has a network of fulfillment centers located around the world, allowing it to get products to customers quickly and efficiently. The company also uses advanced automation technology in these centers, including robots that can move and sort packages, further increasing the speed and efficiency of the fulfillment process.
In addition to its use of technology, Amazon also employs various strategies to manage its inventory and ensure that it has the products customers want when they want them. One of these strategies is the use of just-in-time inventory management, which involves only ordering the amount of a product that is needed at a particular time. This helps to reduce the risk of excess inventory and reduces the costs associated with storing and managing excess inventory.
Another strategy that Amazon uses is cross-docking, which involves shipping products directly from the manufacturer to the customer without the need for intermediate storage. This helps to reduce the amount of time and cost associated with storing and handling products in fulfillment centers.
Finally, Amazon also relies on its vast network of third-party sellers to help manage its inventory. These sellers are able to list their products on Amazon's marketplace, allowing customers to purchase a wide range of products from a single location. This helps to ensure that Amazon has a diverse range of products available to customers and helps to manage inventory levels more effectively.
In conclusion, Amazon's inventory management is a complex and multifaceted process that involves the use of advanced technologies, strategic planning, and a network of fulfillment centers and third-party sellers. By using these strategies and technologies, Amazon is able to manage its vast inventory and provide customers with the products they want when they want them, further solidifying its position as the world's leading online retailer.
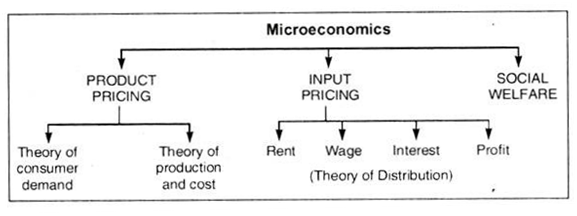
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two branches of economics that study different aspects of the economy. Microeconomics is the study of individual economic units, such as households and firms, and how they make decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources. On the other hand, macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
One key difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics is the level of analysis. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual economic units and how they interact with each other in markets. It is concerned with how households and firms make decisions about what to produce, how much to produce, and at what price to sell their goods and services. Microeconomics also studies the determinants of supply and demand in markets, and how prices are determined.
In contrast, macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole and how it functions. It examines the overall performance of the economy and how it is affected by various factors, such as government policies, international trade, and changes in the money supply. Macroeconomists study topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth, and how these affect the overall health of the economy.
Another difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics is the type of decisions that are studied. Microeconomics focuses on the decisions made by individual households and firms, while macroeconomics looks at the decisions made by governments and central banks. For example, microeconomics would study how a firm decides how much to produce and at what price to sell its products, while macroeconomics would study how the government sets monetary and fiscal policies to influence economic growth and stability.
In summary, microeconomics and macroeconomics are two branches of economics that study different aspects of the economy. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual economic units and how they make decisions in markets, while macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole and how it is affected by various factors. While both fields are important for understanding how the economy functions, they approach the study of economics from different angles and focus on different types of decisions.