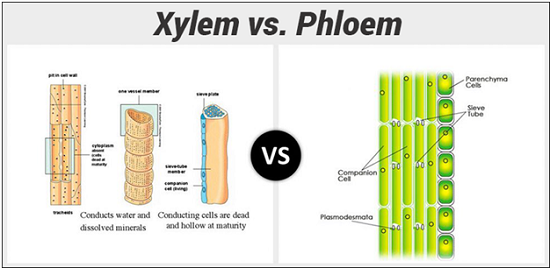
Xylem and phloem are two essential tissue systems found in plants that are responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. These tissue systems are made up of several different types of cells, each with its own unique function.
Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. It is composed of several different cell types, including tracheids, vessel elements, and xylem parenchyma cells. Tracheids are long, narrow cells with thick walls that provide support to the plant and help to transport water from the roots to the leaves. Vessel elements are larger, tube-like cells that also help to transport water, but they have thinner walls and a larger diameter than tracheids. Xylem parenchyma cells are smaller cells with thin walls that are found throughout the xylem tissue. These cells help to store sugars and provide support to the plant.
Phloem tissue is responsible for transporting sugars and other nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant. It is made up of several different cell types, including sieve tube elements, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma cells. Sieve tube elements are long, thin cells with perforated walls that allow sugars and other nutrients to pass through them. Companion cells are smaller cells that are found alongside sieve tube elements and help to regulate the flow of nutrients through the phloem tissue. Phloem parenchyma cells are also small cells with thin walls that help to store sugars and provide support to the plant.
In summary, the xylem and phloem tissue systems in plants are made up of several different types of cells, each with its own unique function. Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, while phloem tissue is responsible for transporting sugars and other nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Together, these tissue systems play a vital role in the overall health and function of the plant.
Difference Between Xylem and Phloem

In autumn wood, tracheids and fibres are more abundant than those found in the spring wood. Tracheid enlargement is irreversible and drought sensitive processes, and is largely determined by the ability of the cell to generate and maintain positive turgor Compared to earlywood width, latewood width, as well as the thickness of cell walls in latewood, seemed to be more variable, whereas the average lumen dimension of latewood tracheids was stable. We thank Martin Cregeen for language editing. When describing the structure of phloem tissue with an electron microscope, it is seen that this tissue is composed of three types of cells and one type of fiber. Cell Wall Thickness Xylem: Cell walls of the xylem is thick. But we can classify the xylem based on the type of growth- Primary and Secondary. Also, they have followed the latest syllabus to make sure that everything is covered.
Phloem vs Xylem

Many times it stores water. Hence, it gives the rigidity to plants. Left figure: Mean values of radial dimension of A initial early phloem sieve EP cells and B terminal late phloem LP sieve cells in Picea abies at Panška reka PA , Menina planina ME , and Rájec-Němčice RN in 2009 black columns , 2010 gray columns , and 2011 white columns. This takes place from roots to the upper parts of the plant. It is developed into the metaxylem containing wider vessels than protoxylem. Xylem fibers Xylem fibers are sclerenchyma cells. Phloem transports food materials that are prepared by the green parts of the plants to other parts of the plant.
Xylem Vs Phloem

In plants, there are different plant tissues which include the reproductive tissue, meristematic tissues, and permanent tissues. The team of Vedantu believes in providing the best educational services to guide students and help them to excel in their classes. Working of Phloem The translocation process is an active type of transport that demands energy in the form of ATP. These tissue cells help transport water and liquid food. It is responsible for transporting proteins and mRNAs throughout the plant. Phloem: Phloem consists of phloem parenchyma, phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells and companion cells. The system which enables this transport in the upward direction, i.
Write the function of xylem and phloem cells.

High The phloem structure consists of different components like sieve tubes, sieve cells, parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and companion cells. Phloem: Phloem occupies a small part of the plant body. It is found in all types of organs. Thus, the main difference between xylem and phloem is in the material transported by each of the two vascular tissues. Based on the origin and development, phloem tissue is divided into two parts. Right figure: Correlation coefficients calculated between mean values and climatic conditions in this period.