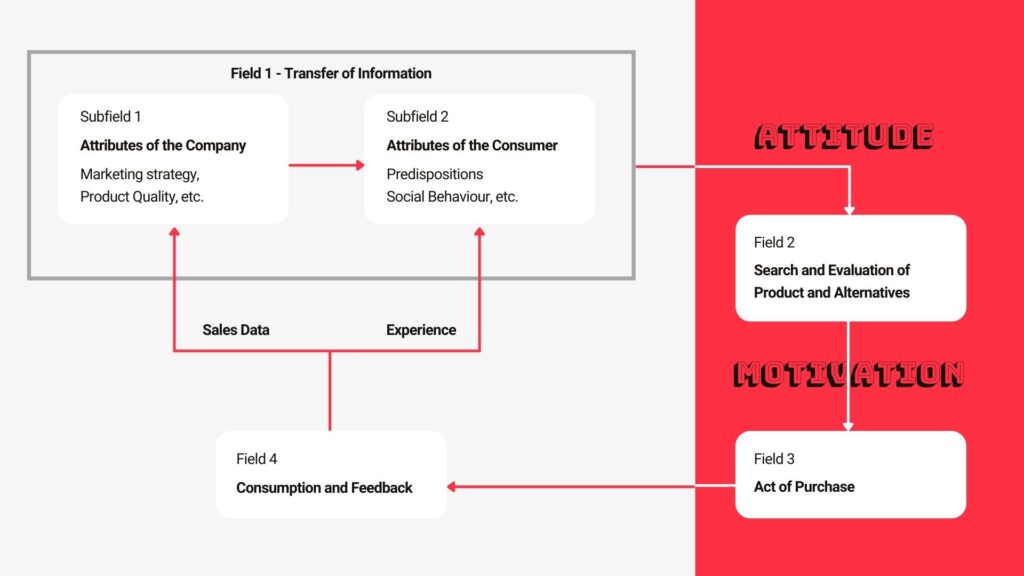
Consumer behavior refers to the actions and decisions made by individuals and households when purchasing and consuming goods and services. Understanding consumer behavior is important for businesses, as it helps them to effectively market and sell their products to their target audience.
There are several different models of consumer behavior that have been developed over the years to help explain and predict consumer decision-making processes. These models often rely on different assumptions and perspectives, and can be used to analyze consumer behavior in a variety of contexts.
One of the most well-known models of consumer behavior is the consumer decision-making process model. This model suggests that consumers go through a series of steps when making a purchase decision. These steps include: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation.
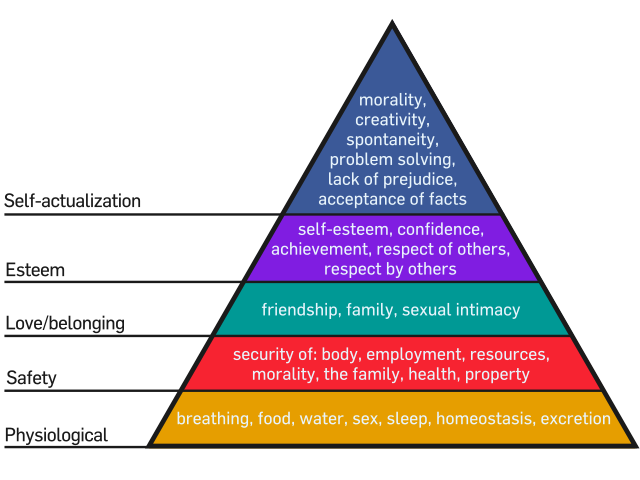
Another model of consumer behavior is the Maslow's hierarchy of needs. This model suggests that people's behavior is motivated by their basic needs and desires, and that these needs are organized in a hierarchy. According to Maslow, people's behavior is driven by physiological needs (such as food, water, and shelter), safety needs (such as security and stability), social needs (such as love, belonging, and companionship), esteem needs (such as self-esteem and respect from others), and self-actualization needs (such as personal growth and self-fulfillment).
Another model of consumer behavior is the decision rules model, which suggests that consumers use specific strategies or rules when making purchase decisions. These rules may include minimizing costs, maximizing benefits, or minimizing risks. Consumers may also use heuristics, or mental shortcuts, to make decisions more quickly and efficiently.
A fourth model of consumer behavior is the cognitive dissonance model, which suggests that consumers experience discomfort or conflict when their beliefs or actions do not align. For example, a consumer may feel dissonance if they value environmental sustainability but also enjoy consuming products that have a negative impact on the environment. To resolve this dissonance, the consumer may either change their beliefs or behaviors, or find a way to justify their current behavior (such as by believing that the environmental impact of their consumption is minimal).
In conclusion, there are several different models of consumer behavior that can help to explain and predict the actions and decisions made by consumers. Understanding these models can be useful for businesses looking to effectively market and sell their products, as well as for researchers studying consumer behavior.