The trade cycle, also known as the business cycle, is the natural fluctuation of economic activity around a long-term growth trend. It is characterized by periods of expansion and contraction in economic activity, including changes in employment, production, and prices.
There are four main phases of the trade cycle: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
Expansion: During the expansion phase, economic activity is growing. Unemployment is low, and businesses are hiring and investing in new projects. Consumer spending is high, and prices are generally rising. This phase is also known as the recovery phase.
Peak: The peak phase is the highest point of economic activity in the trade cycle. Unemployment is at its lowest, and businesses are operating at full capacity. However, this phase is often short-lived as it is followed by the contraction phase.
Contraction: During the contraction phase, also known as the recession phase, economic activity slows down. Unemployment starts to rise, and businesses may start to lay off workers or reduce their investments. Consumer spending and prices also start to decline.
Trough: The trough phase is the lowest point of economic activity in the trade cycle. Unemployment is at its highest, and businesses are struggling. This phase is also known as the depression phase.
It is important to note that the trade cycle is not a precise science, and the length and severity of each phase can vary. Some economists believe that government policies, such as monetary and fiscal policies, can help to mitigate the negative effects of the contraction phase and smooth out the trade cycle.
Overall, the trade cycle is a natural fluctuation in economic activity that affects businesses and individuals alike. Understanding the different phases of the trade cycle can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions and prepare for the ups and downs of the economy.
Business or Trade Cycle: Meaning, Characteristics and Theories

In view of high profits and business optimism, entrepreneurs invest more and expand further. Finally, the cash flow during the launch phase is also negative but dips even lower than the profit. The majority of settlements are now T+2. Rise and fall in economic variables The economic variables i. Profits of business firms dwindle. Such induced investment will cause a rise in employment and income. The business risk cycle is inverse to the sales and debt funding cycle.
What are the different phases of trade cycle?

In other words, instead of a balanced budget, a surplus or a deficit budget should be pursued to achieve stability in the economy. Employment and income of the factors of production in capital goods industries will increase. That is to say, it is repetitive in character. Lower incomes — lower income tax. The industry experiences steep growth, leading to fierce competition in the marketplace.
Trade Cycle: 4 Phases of Trade Cycle

It is not easy to transfer resources from capital goods industries to consumer goods industries and vice versa. Over-Saving or Under Consumption Theory: This theory is the oldest explanation of the cyclical fluctuations. Thus it is quite likely that a state of fairly stable business depression may lead to recovery or it may decline to further recession. Even by lowering down the interest rates financial institutions do not find enough borrowers. According to this theory, depression is due to over-saving. Similarly, the manufacturing and retail sectors may also be affected by the trade cycle, as changes in consumer demand can impact their sales and profits.
The Trade Life Cycle Explained
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-the-business-cycle-3305912-v3-5b3151ecff1b7800373c1d8a.png)
The depression is thus, a period of great suffering, low income and unemployment. The trades cycle or business cycle are cyclical fluctuations of an economy. The extreme points are the peak and the trough. What are the six stages of a business? On the settlement date the sell side must have transferred their security and the buy side must have transferred the money for their purchase. Recovery: Recovery denotes the turning point of business cycle form depression to prosperity. Investment demand becomes less responsive to a change in income when accelerator takes a value less than one. Output, income and employment to grow.
Business Cycle
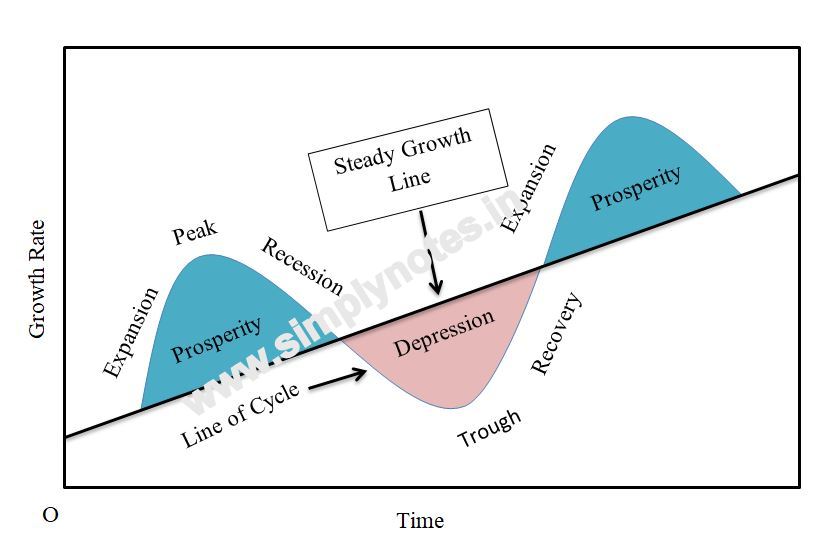
A global economic downturn will tend to affect individual economies. Purchasing power of people is improving 6. Everyone feels pessimistic about the future profitability of investment. Employment increases purchasing power and this leads to an increase in demand for consumer goods. To relieve the economy from depression it is essential to increase the stock of money to step up aggregate demand. What is a complete business cycle? Business cycles are identified as having four distinct phases: peak,trough,contraction,and expansion.
Business Life Cycle
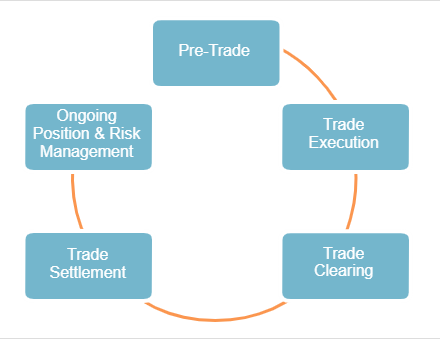
What are the 5 phases of the business cycle? This lag is important as it relates to the funding life cycle, which is explained in the latter part of this article. Similarly, to contain depressionary phase, tax cuts are recommended by the government so that disposable incomes rise. Every cycle exhibits similarities in its nature and direction though no two cycles are exactly the same. Phase Five: Decline In the final stage of the funding life cycle, sales begin to decline at an accelerating rate. Thus, fluctuations are due to optimism leading to prosperity and pessimism resulting depression. The process of revival and recovery becomes cumulative and leads to prosperity. Phase Three: Shake-out During the shake-out phase, sales continue to increase, but at a slower rate, usually due to either approaching market saturation or the entry of Phase Four: Maturity When the business matures, sales begin to decrease slowly.
Define the term Trade Cycle & its Different Phases
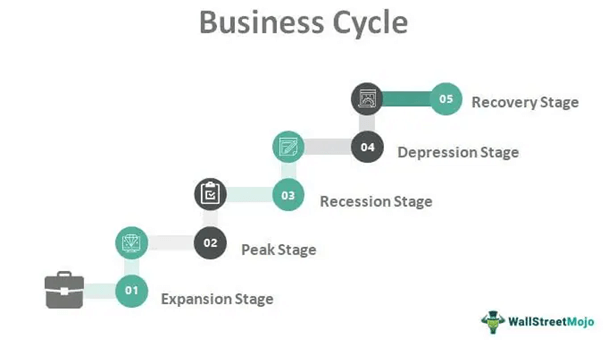
Such good or bad Trade is called the business Cycle or Trade cycle. When cyclical fluctuations start in one sector it spreads to other sectors. Employment rate is increasing Boom, Peak A period of good trade is called boom. The process of expansion goes on till the boom is reached. However, unlike the earlier stages where the business risk cycle was inverse to the sales cycle, business risk moves in correlation with sales to the point where it carries no business risk.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-the-business-cycle-3305912-v3-5b3151ecff1b7800373c1d8a.png)


