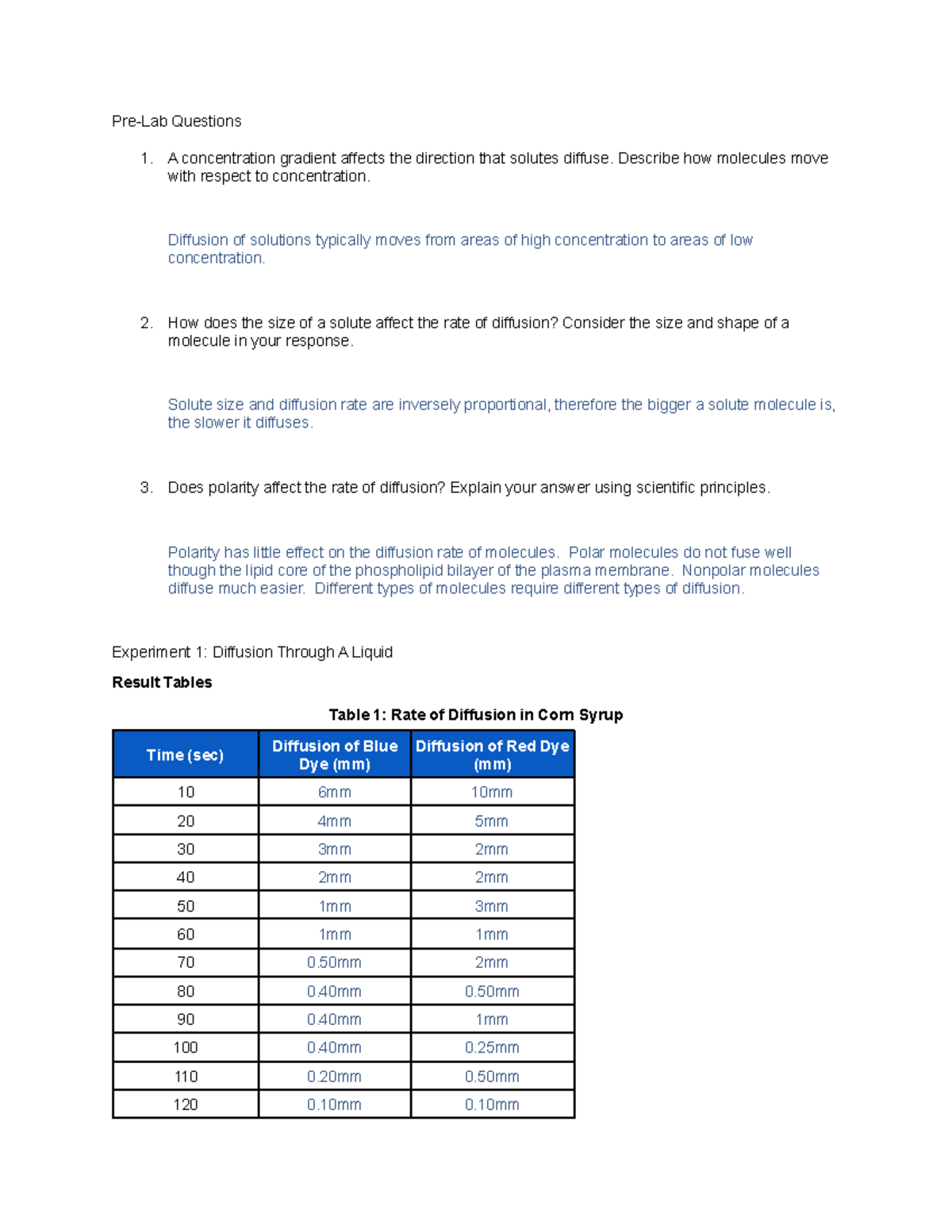
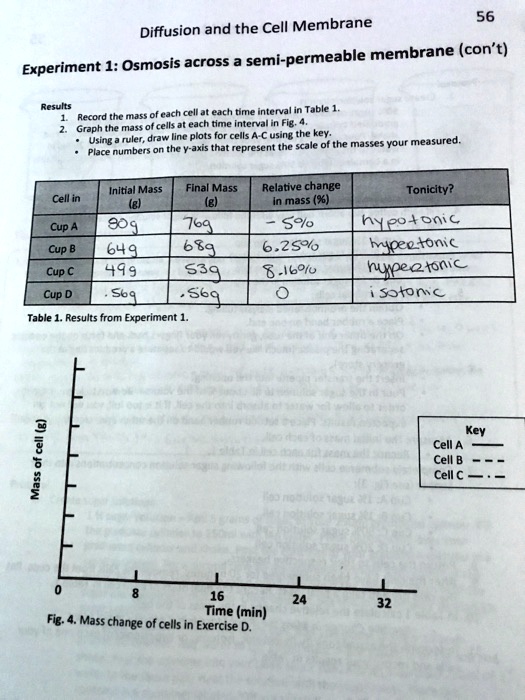
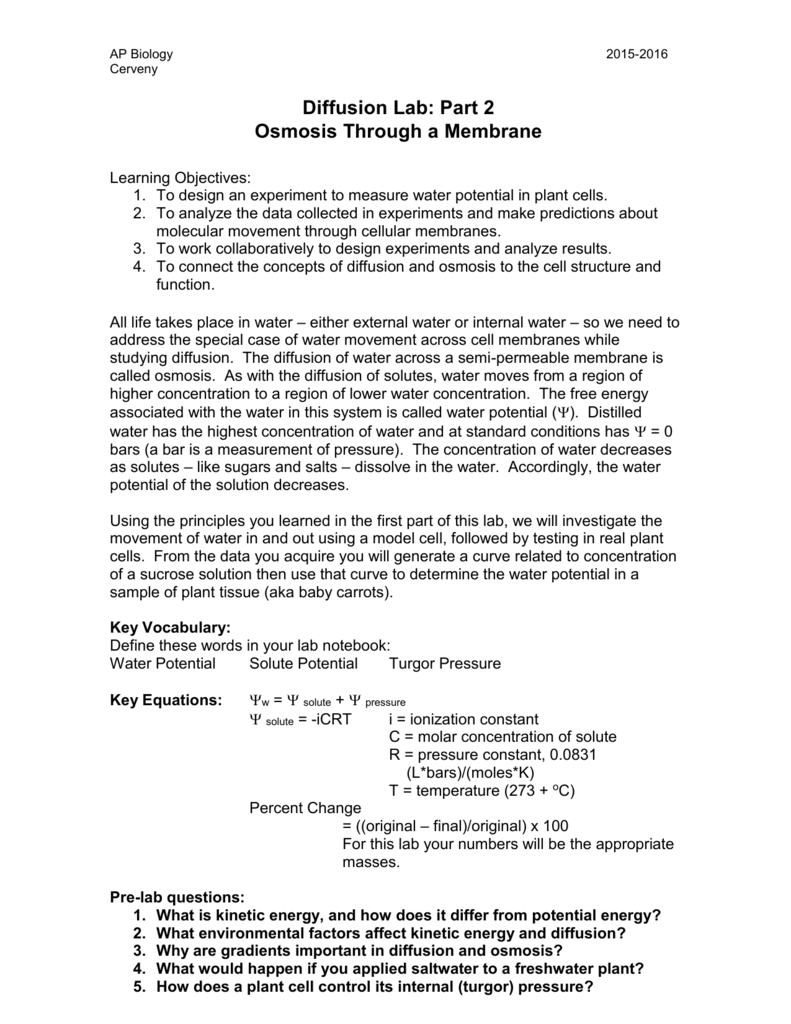
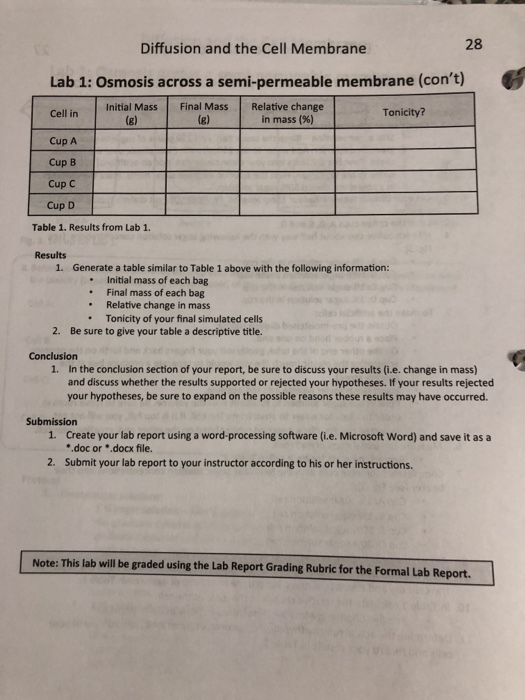
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It is a fundamental process that occurs in all living cells and is essential for maintaining homeostasis, the balance of chemical and physical conditions within the cell. In this lab, we will explore the process of diffusion through a membrane, using a model membrane made of dialysis tubing.
To begin the lab, we will need to prepare the dialysis tubing. This can be done by soaking the tubing in distilled water for a few hours, until it becomes swollen and soft. Next, we will tie off one end of the tubing to create a sealed pouch. We will then fill the pouch with a solution of glucose and iodine, which will serve as the solute. The pouch will be placed in a beaker containing distilled water, which will serve as the solvent.
Over the next few hours, we will observe the movement of the glucose and iodine molecules through the dialysis tubing. As the molecules diffuse across the membrane, the concentration of the solute in the beaker will increase, while the concentration of the solute in the pouch will decrease. We can measure the change in concentration by taking regular readings of the solution in the beaker using a spectrophotometer.
As the experiment progresses, we will also observe the movement of water molecules through the dialysis tubing. Water molecules are small and able to pass through the semi-permeable membrane of the dialysis tubing, but the larger glucose and iodine molecules are too large to pass through. As a result, we will see a net movement of water from the beaker into the pouch, which will cause the pouch to become more swollen.
In addition to observing the movement of molecules through the dialysis tubing, we can also manipulate the conditions of the experiment to see how they affect the rate of diffusion. For example, we can vary the temperature of the solution in the beaker or the size of the pouch to see how these variables affect the rate of diffusion.
Overall, this lab serves as a useful model for understanding the process of diffusion through a membrane. By observing the movement of molecules across the dialysis tubing, we can gain insights into the fundamental processes that occur within living cells. Understanding the role of diffusion in maintaining homeostasis is crucial for understanding the functioning of cells and organisms as a whole.