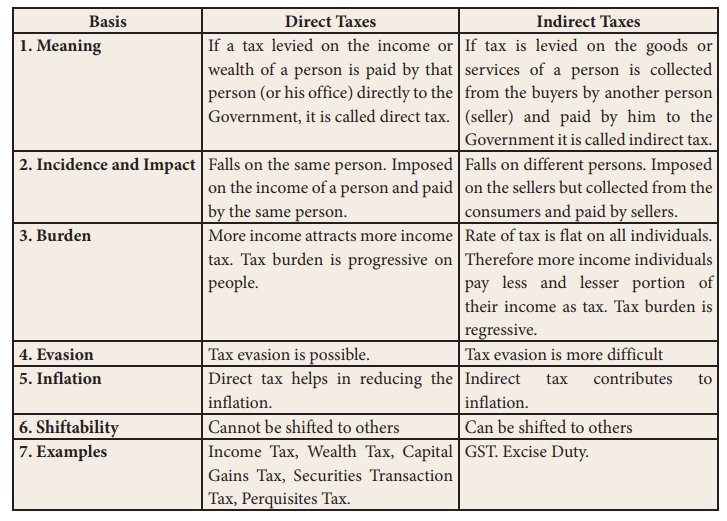
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed upon a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to fund various public expenditures. A tax may be either a direct tax or an indirect tax.
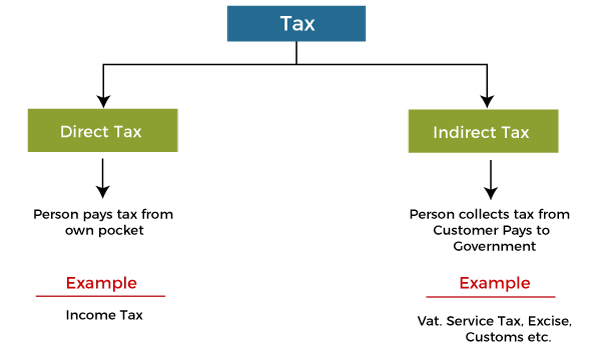
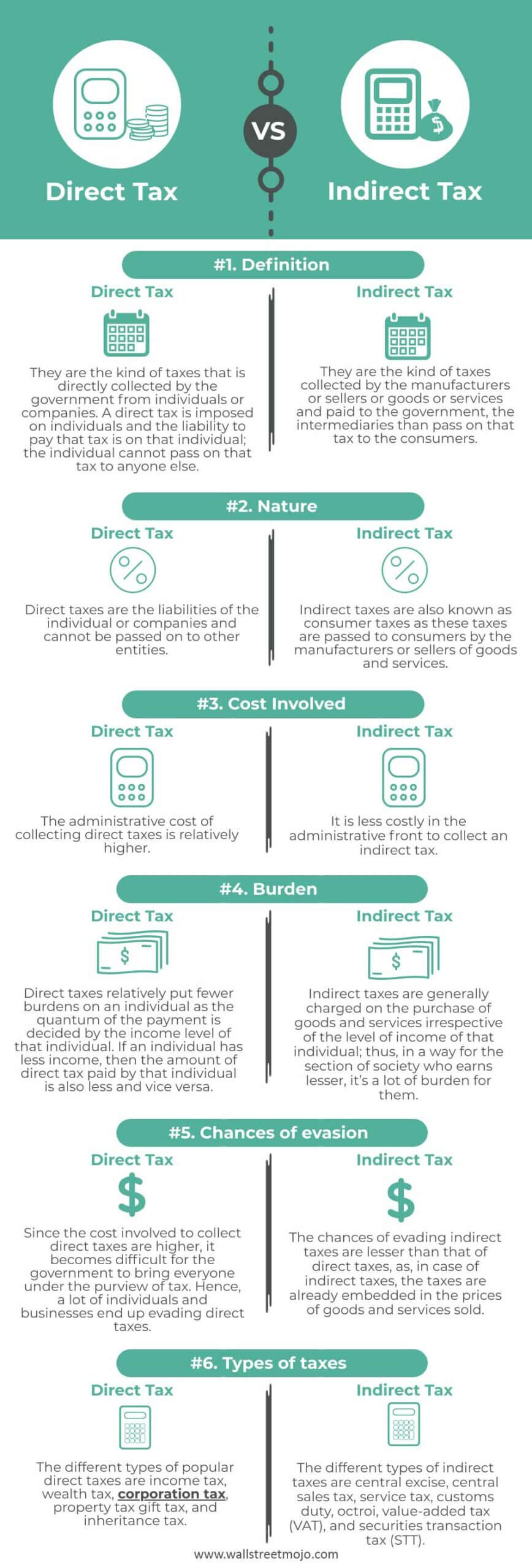
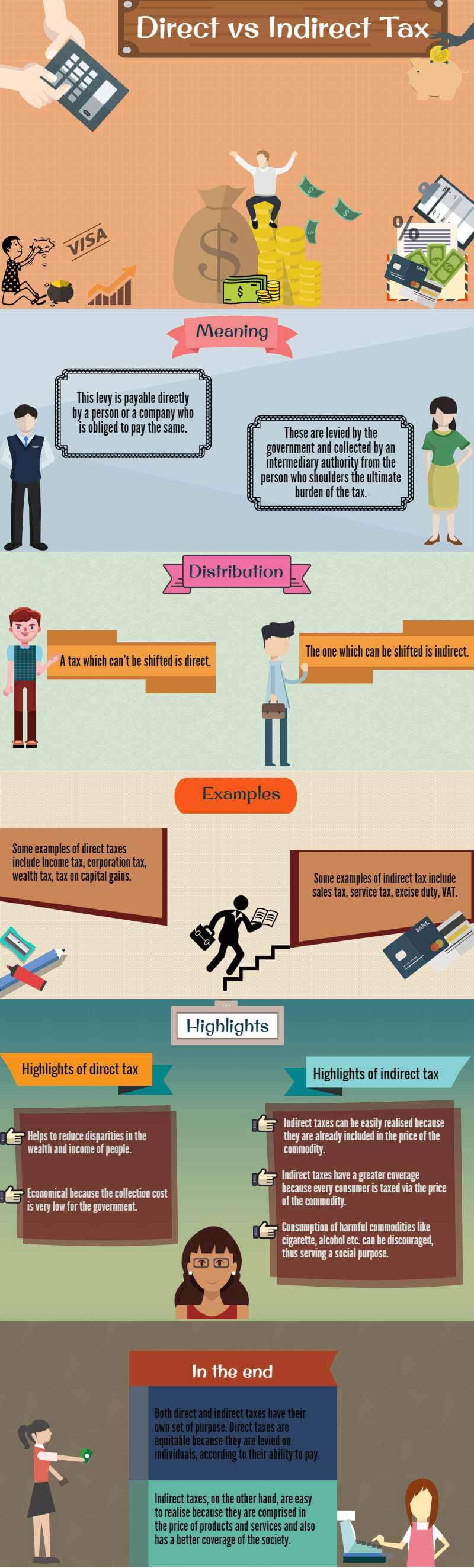
A direct tax is a tax that is levied directly on the income or wealth of an individual or organization. Examples of direct taxes include personal income tax, corporate income tax, and property tax. These taxes are generally based on an individual's or organization's ability to pay and are usually progressive, meaning that they take a larger percentage of income or wealth from those who are able to pay more.
An indirect tax, on the other hand, is a tax that is levied on the sale of goods or services. Examples of indirect taxes include value-added tax (VAT), sales tax, and excise tax. These taxes are usually regressive, meaning that they take a larger percentage of income from those who are able to pay less.
There are several advantages and disadvantages to both direct and indirect taxes. One advantage of direct taxes is that they are generally considered to be more equitable, as they are based on an individual's or organization's ability to pay. This means that those who are able to pay more will pay more in taxes, which can help to reduce income inequality. Direct taxes are also generally easier to administer and collect, as they are based on readily available information such as income or wealth.
However, direct taxes can also be seen as being less efficient, as they may discourage work and investment by increasing the cost of earning income or wealth. They may also be perceived as being more intrusive, as they require the disclosure of personal financial information to the government.
Indirect taxes, on the other hand, have the advantage of being more efficient, as they are typically collected at the point of sale and do not require the disclosure of personal financial information. They may also be less intrusive, as they are not directly tied to an individual's or organization's income or wealth.
However, indirect taxes can also be seen as being less equitable, as they disproportionately impact lower-income individuals and organizations, who tend to spend a larger percentage of their income on goods and services. They may also be more difficult to administer and collect, as they require the tracking of sales and the calculation of tax on each individual transaction.
In conclusion, both direct and indirect taxes have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two depends on the specific goals of a government and the needs of its citizens. Direct taxes are generally more equitable, but may be less efficient, while indirect taxes are generally more efficient, but may be less equitable. Ultimately, the decision on which type of tax to use should be based on a balance of these factors and the needs of the specific situation.