Cryopreservation, or the process of freezing living tissue or cells at extremely low temperatures, has been used for decades in the medical and scientific fields for a variety of purposes. However, it is not a perfect solution and there are several disadvantages to consider when it comes to cryopreservation.
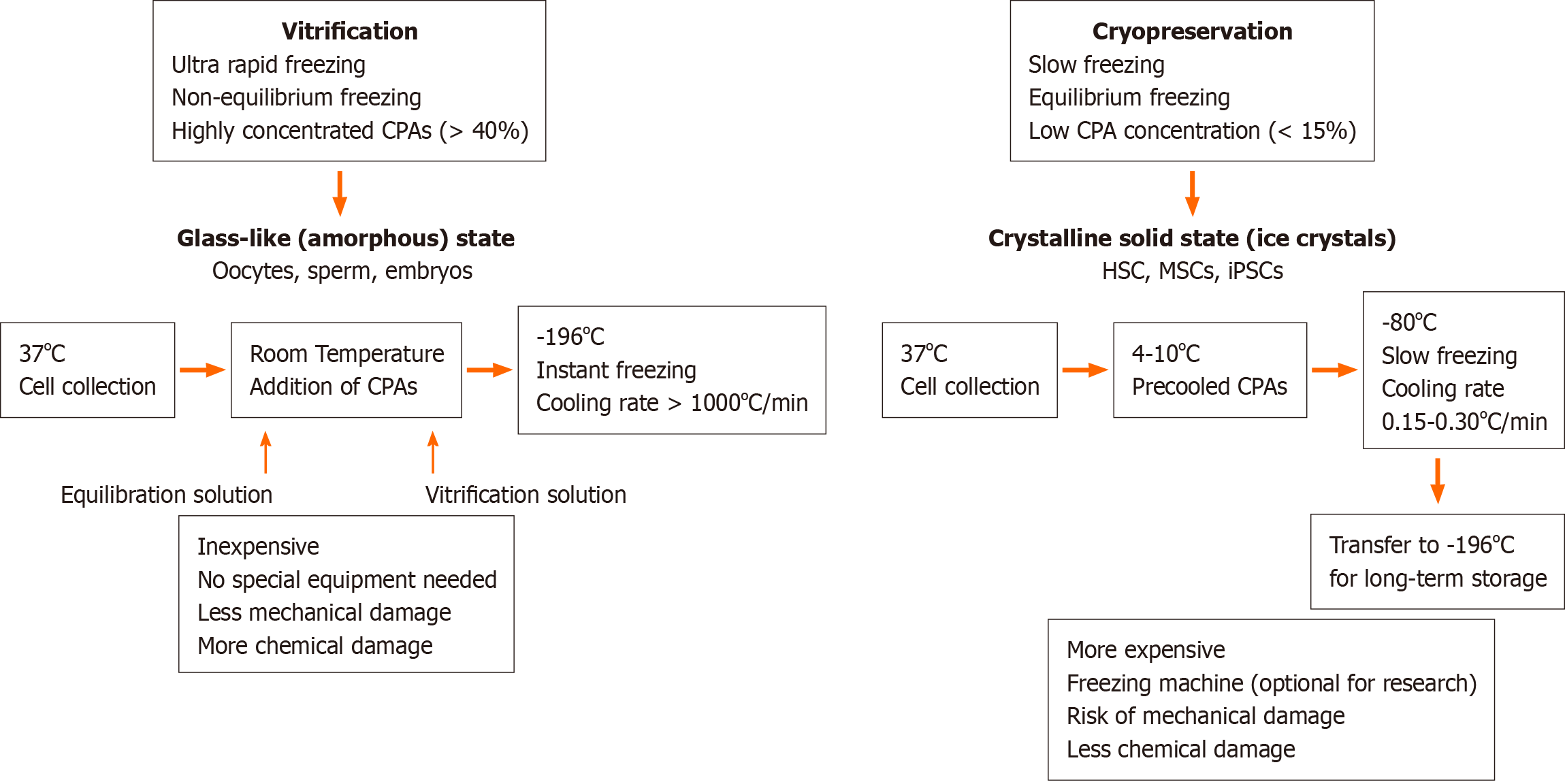
One of the main disadvantages of cryopreservation is the potential for damage to cells or tissues during the freezing process. When water inside cells freezes, it expands and can cause cells to rupture or become damaged. This can result in the loss of viability or function of the cells or tissues, making them unusable for future research or medical purposes.
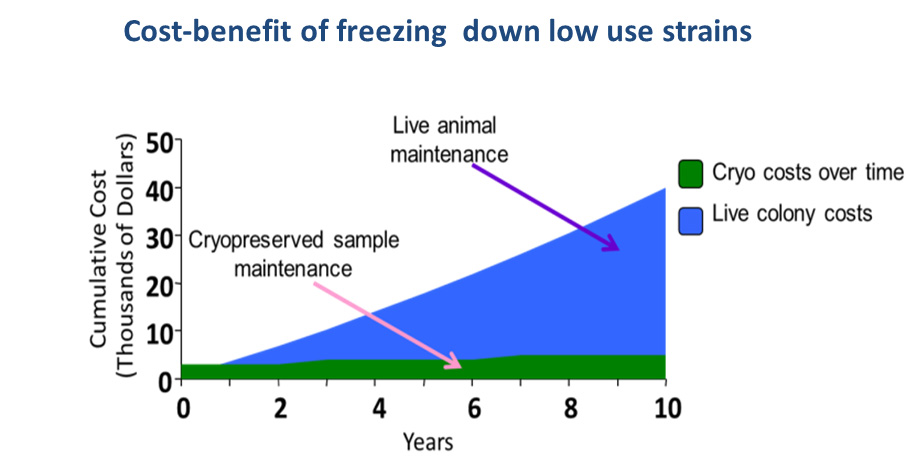
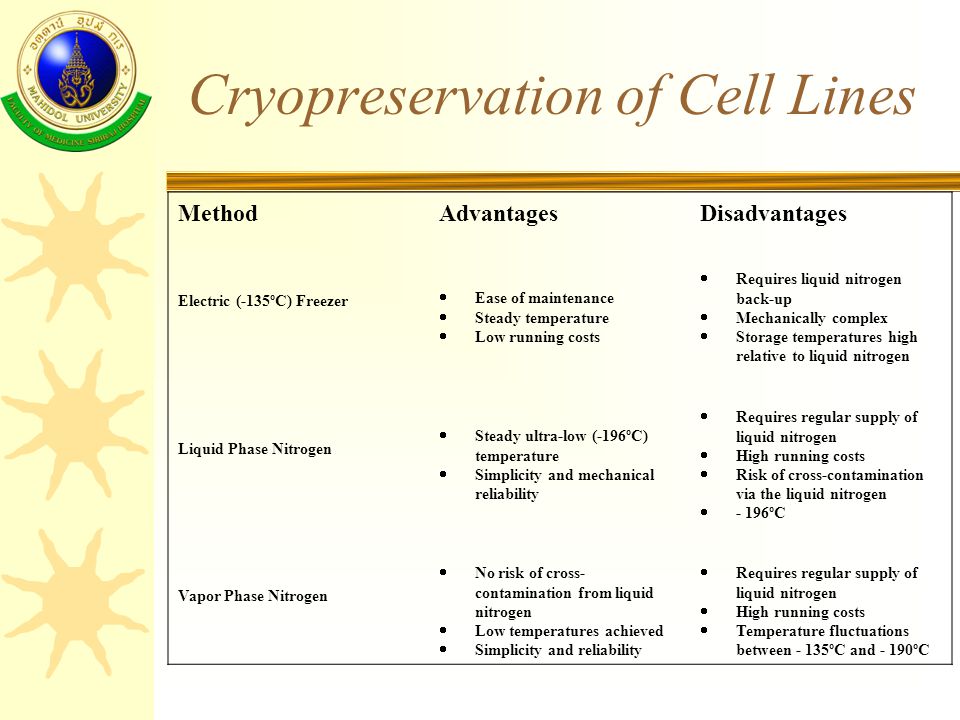
Another disadvantage of cryopreservation is the cost and time involved in the process. Cryopreservation requires specialized equipment and materials, and the process itself can be lengthy and complex. This can make it cost-prohibitive for some organizations or individuals, particularly when large quantities of cells or tissues need to be frozen.
There is also the issue of long-term storage and stability of cryopreserved materials. While cryopreservation can extend the shelf life of cells or tissues for many years, there is still the risk of degradation over time. This can lead to the loss of viability or function of the materials, making them unusable for research or medical purposes.
In addition, there are ethical considerations surrounding cryopreservation, particularly when it comes to the cryopreservation of human embryos or whole organisms. There is ongoing debate about the potential risks and benefits of cryopreservation in these cases, and it is an area of research that is still being explored.
Overall, while cryopreservation has many potential applications, it is not without its disadvantages. It is important to carefully consider the potential risks and limitations of cryopreservation before deciding to use it for research or medical purposes.