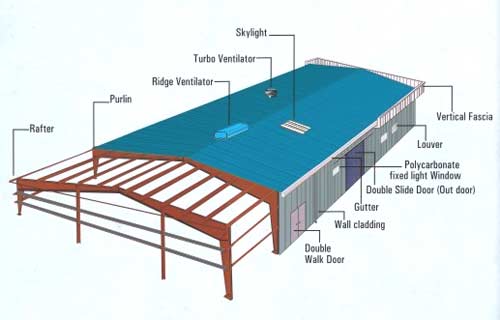
Pre-engineered buildings are structures that are prefabricated off-site and then assembled on-site. These buildings are often used for industrial, commercial, and agricultural purposes, and are known for their speed of construction and cost-effectiveness. However, there are also several disadvantages to using pre-engineered buildings.
One disadvantage of pre-engineered buildings is that they may not be as durable as traditionally built structures. The prefabricated components of these buildings are often made from lightweight materials, such as steel or aluminum, which may not be as strong as other building materials like concrete or brick. This can make them more susceptible to damage from natural disasters, such as earthquakes or hurricanes, and may require additional reinforcing or bracing to make them more structurally sound.
Another disadvantage is that pre-engineered buildings may not be as aesthetically pleasing as traditionally built structures. The prefabricated components of these buildings are often designed for efficiency and cost-effectiveness rather than aesthetics, which can result in a less attractive appearance. This may not be a concern for some types of buildings, such as warehouses or factories, but it can be a significant drawback for buildings that are intended to be seen by the public, such as office buildings or schools.
Pre-engineered buildings may also be less flexible in terms of design and layout. Because the components of these buildings are prefabricated, there may be limited options for customization or modification. This can be a disadvantage if a business or organization needs to make changes to the layout or design of the building in the future, as it may be more difficult or costly to do so with a pre-engineered building.
Finally, pre-engineered buildings may not be as energy-efficient as traditionally built structures. The prefabricated components of these buildings may not be designed with energy efficiency in mind, and may not have the same insulation or air sealing capabilities as a traditionally built structure. This can result in higher energy costs for heating and cooling the building, and may not be as environmentally friendly as other building options.
In conclusion, while pre-engineered buildings have some advantages in terms of speed of construction and cost-effectiveness, they also have several disadvantages, including potential durability issues, limited design flexibility, and lower energy efficiency. These drawbacks may make pre-engineered buildings less suitable for certain applications, and it is important for businesses and organizations to carefully consider the pros and cons of using these types of buildings before making a decision.