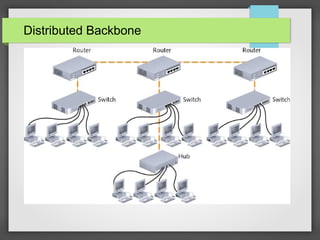
A distributed backbone network is a type of network architecture that is designed to provide a high level of connectivity and reliability for a wide area network (WAN). It is composed of a series of interconnected nodes or hubs that are distributed across a geographic region, such as a country or continent. These nodes are connected to each other using high-capacity links, such as fiber optic cables or microwave radio links, to form a redundant and fault-tolerant network that can support a large number of users.
One of the main benefits of a distributed backbone network is its ability to support a high level of scalability. As the demand for network connectivity increases, the network can be easily expanded by adding more nodes or upgrading the capacity of existing links. This allows the network to support a growing number of users and devices without experiencing any significant performance degradation.
Another advantage of a distributed backbone network is its inherent fault tolerance. With multiple nodes and links, the network can continue to operate even if one or more nodes or links fail. This ensures that users can always access the network and its resources, even in the event of a network outage.
In addition to these benefits, a distributed backbone network also provides a high level of security and privacy. With multiple nodes and links, it is more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access the network or intercept data transmitted over the network. This makes it an attractive solution for organizations that need to secure sensitive data or communications.
Overall, a distributed backbone network is a powerful and reliable solution for providing high-capacity connectivity and communication over a wide area. It is well-suited for organizations that need to support a large number of users and devices, and require a high level of scalability, fault tolerance, and security.
In a distributed backbone network all of the devices that access the backbone
Internet as a backbone The Internet is an extremely vast network and is commonly referred to as a backbone. Another way to save yourself from Security from Day 1: Building in good security measures from Day 1 is increasingly critical to protect your network availability. This layer also connects user-devices such as PCs, IP phones, wireless access points, printers, and scanners to the network. The technologies used for the core network facilities primarily include data link and network layer technologies, such as IP, asynchronous transfer mode ATM , internet protocol IP , synchronous optical networking SONET , and dense wavelength division multiplexing DWDM. Distributed backbone: Backbone cabling is then run between floors or buildings, connecting the main hub or router for each department into a bus-style network see illustration. Within the core nodes, next in the hierarchy, come the distribution networks, followed by the edge networks. The Switched backbone is a logical structure that clearly segments the network into subnets.
Types and Uses of Backbone Networks

This can increase the initial installation cost of a collapsed backbone network, compared to a distributed backbone network. PSUs, controllers, blades, inter-chassis links, distribution-to-core links—even whole buildings—can be lost and users remain connected to a functional network backbone. Here are the cybersecurity trends. Each of these two designs has its This white paper discusses how to create a network design that combines both distributed and collapsed backbones. The Allied Telesis switch clustering technology is called VCStack The stacking of Allied Telesis pizza-box and SwitchBlade® x908 Generation 2 switches provides excellent options that are optimized for different size networks. This model suggests that instead of designing a flat campus LAN network, an administrator should design a hierarchical campus LAN network. For redundancy, if the LAN adds additional connections, the number of required connections will also increase in parallel.
Backbone network

Retrieved 2 October 2013. Usually, the term denotes the high-functioning communication facilities that interlink the primary nodes. In a collapsed backbone, every new node must connect right back to the core node. If the network contains layers, it is known as the hierarchical network. The pieces of the network connections for example: ethernet, wireless that bring these departments together is often mentioned as network backbone.
Benefits of Distributed Collapsed Backbones
When organizations are looking for a very strong and trustworthy backbone they should choose a parallel backbone. A 1-Gigabit backbone might be sufficient for now. Nodes have limited individual knowledge and capabilities: they do not know their positions in a coordinate system in the plane, further they do not know their neighborhoods, nor do they know the size of the network n, and finally they cannot sense collisions resulting from simultaneous transmissions by at least two neighbors. They also form a star topology backbone, in which numerous LANs are connected by a bus backbone to exchange data and share resources. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Fundamentals of Computation Theory FCT , Lecture Notes in Computer Science vol. Working of core networks In general, core networks offer the following functionalities: Aggregation Core nodes deliver the highest level of aggregation in a service provider network SPN.
What is a core network? How does the core network work?

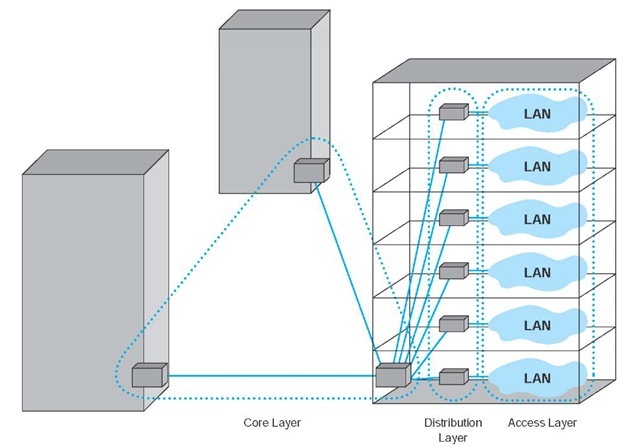
A backbone's capacity is expected to exceed that of the networks it supports. Instead, it can be dedicated to just the one core node. It can also mean a significant step up in technology—the money that would have been invested in multiple moderately capable backbone units, can instead be utilized to create one very high capability node. The following image show how distribution switches connect the access switches in the network. Additionally, if the connections from the core chassis to distribution nodes consist of aggregated links, terminated on different blades of the chassis, then the network is also resilient to the failure of any one blade. These points are then connected to users located in far-flung areas via telecommunications lines.