A DLC (difference in leukocyte count) blood test is a medical examination that measures the number of white blood cells in a person's blood. White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are an essential part of the body's immune system and play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases. The DLC test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that involves drawing a small sample of blood from the patient's arm and analyzing it in a laboratory.
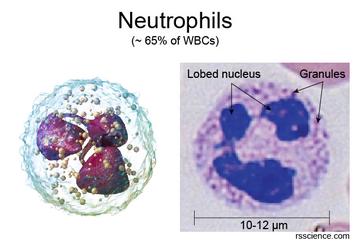
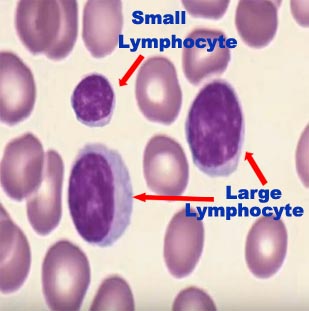
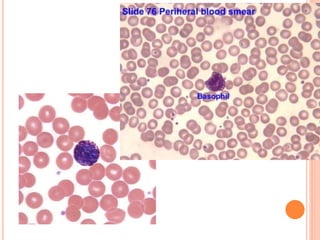
There are several different types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type of white blood cell has a specific function in the body's immune system. For example, neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell and are responsible for fighting off bacterial infections. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, help to identify and destroy infected cells and play a crucial role in the body's immune response to viruses. Monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils also play important roles in the immune system and are involved in various immune responses.
The DLC test is typically ordered by a healthcare provider as part of a routine physical examination or as part of a diagnostic evaluation for a specific medical condition. It can be used to help diagnose a variety of medical conditions, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and certain types of cancer. For example, a high white blood cell count (leukocytosis) may indicate an infection or inflammation, while a low white blood cell count (leukopenia) may be a sign of a bone marrow disorder or immune system deficiency.
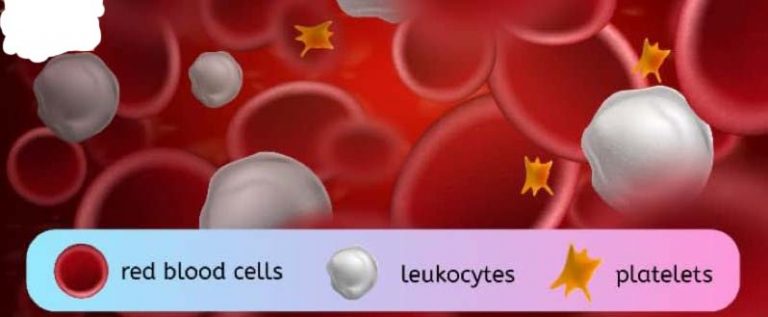
The DLC test is usually performed as part of a complete blood count (CBC) test, which is a standard blood test that measures the levels of various components in the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The results of the DLC test are typically available within a few days and are usually interpreted by a healthcare provider or a medical laboratory technician.
In conclusion, the DLC blood test is a simple and non-invasive procedure that is used to measure the number of white blood cells in a person's blood. It is an important tool in the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of medical conditions and can help healthcare providers to identify and treat infections, inflammatory diseases, and certain types of cancer.