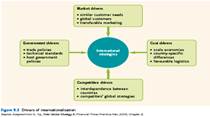
Internationalization, also known as globalization, refers to the process by which businesses and organizations expand their operations beyond their domestic markets and into other countries. There are a number of drivers that contribute to the internationalization of businesses, including access to new markets, cost advantages, increased competitiveness, and access to new technologies and resources.
One of the primary drivers of internationalization is the desire to access new markets. By expanding into other countries, businesses can tap into new customer bases and increase their revenue streams. This is especially attractive for businesses that have reached a saturation point in their domestic markets and are seeking new opportunities for growth.
Another driver of internationalization is the potential for cost advantages. For example, businesses may be able to take advantage of lower labor costs in other countries, or access raw materials at a lower cost. In addition, businesses may be able to benefit from economies of scale by producing goods in larger quantities and distributing them globally.
Increased competitiveness is another factor that can drive internationalization. By expanding into new markets, businesses can gain a competitive edge by offering products or services that are not available in those markets. In addition, by operating in multiple countries, businesses can benefit from a wider range of resources and expertise, which can give them a competitive advantage over their rivals.
Finally, access to new technologies and resources is another driver of internationalization. By operating in other countries, businesses can gain access to new technologies and resources that may not be available in their domestic markets. This can help them to improve the quality of their products and services, and increase their efficiency and competitiveness.
In conclusion, there are a number of drivers that contribute to the internationalization of businesses, including access to new markets, cost advantages, increased competitiveness, and access to new technologies and resources. By understanding these drivers, businesses can make informed decisions about whether and how to expand their operations beyond their domestic markets.