Drug adulteration is the practice of intentionally adding impurities or contaminants to drugs, either to increase profit or to reduce costs. It is a serious problem that poses significant risks to public health, as adulterated drugs may be ineffective or even harmful to those who consume them.
Adulterated drugs can take many forms, including fake or counterfeit drugs that are sold as the real thing, or genuine drugs that have been tampered with in some way. Common forms of drug adulteration include the addition of inactive ingredients, the dilution of active ingredients, or the substitution of one drug for another.
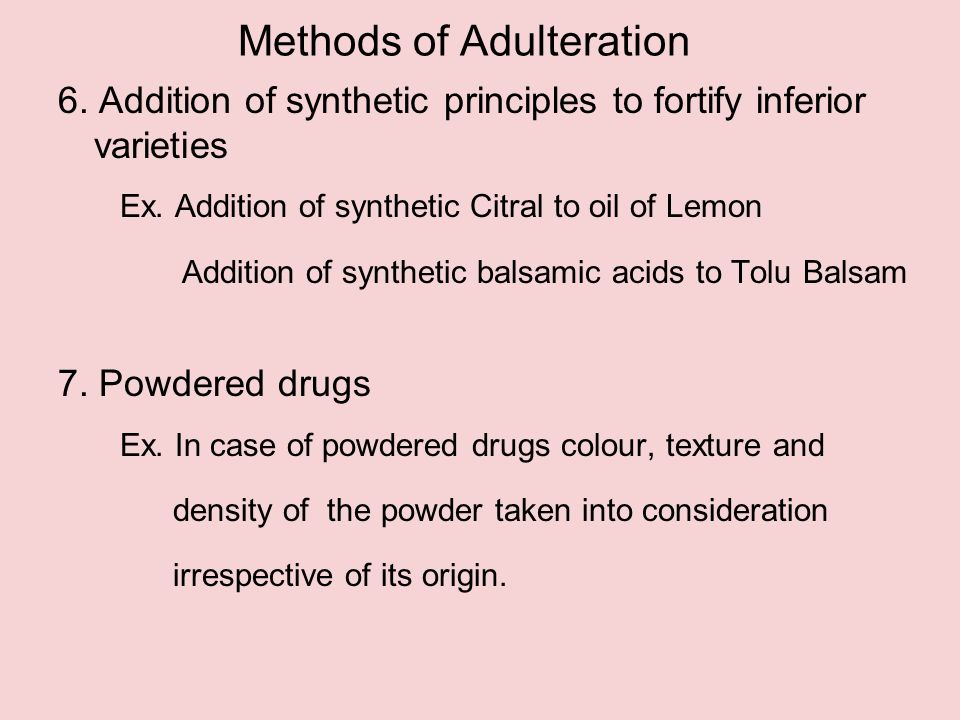
One of the most common forms of drug adulteration is the addition of inactive ingredients, also known as "fillers." These ingredients may be added to drugs to bulk up the volume, making it appear as though the drug contains more active ingredients than it actually does. This allows manufacturers to sell smaller amounts of the active ingredient at a higher price, while still maintaining the appearance of a full-strength product.
Another form of drug adulteration is the dilution of active ingredients. This can be done by adding water or other substances to the drug, which reduces the concentration of the active ingredient and makes the drug less effective. Dilution can also occur if a drug is stored improperly, or if it is not manufactured according to proper quality control standards.
Substitution of one drug for another is another form of drug adulteration. This can occur when a cheaper or less effective drug is sold as a more expensive or more effective drug. For example, a manufacturer may sell a generic drug as a brand-name drug, or may sell a cheaper version of a drug as the more expensive, extended-release version.
The dangers of drug adulteration are numerous. Adulterated drugs may be ineffective at treating the condition they are intended for, leading to worsening health outcomes for those who rely on them. In some cases, adulterated drugs may even be harmful, containing contaminants or impurities that can cause serious side effects or allergic reactions.
To combat the problem of drug adulteration, it is important for governments and regulatory agencies to enforce strict quality control standards and to vigorously prosecute those who engage in this practice. It is also important for consumers to be aware of the risks associated with adulterated drugs and to only purchase medications from reputable sources.
In conclusion, drug adulteration is a serious problem that poses significant risks to public health. It is important for governments and regulatory agencies to enforce strict quality control standards and for consumers to be aware of the risks associated with adulterated drugs. By taking these precautions, we can help to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the medications we rely on to maintain our health and well-being.