The Keynesian school of economic thought is named after the British economist John Maynard Keynes, who is widely considered to be one of the most influential economists of the 20th century. Keynesian economics is based on the idea that government intervention in the economy can help to stabilize output and employment.
According to Keynesian theory, the demand for goods and services drives the economy. When demand is low, businesses will produce less, leading to lower employment and income. To stimulate demand and boost the economy, Keynesians advocate for government spending on public works, social welfare programs, and other initiatives that can increase consumption and investment.
One key concept in Keynesian economics is the idea of the "multiplier effect," which states that an increase in government spending can have a larger impact on the economy than the initial spending itself. For example, if the government spends money on a public works project, the workers hired for the project will have more income to spend, which will in turn stimulate demand for other goods and services, leading to further economic growth.
Another key concept in Keynesian economics is the "liquidity trap," which occurs when the nominal interest rate is close to zero and the central bank is unable to stimulate economic activity through traditional monetary policy tools. In this situation, Keynesians argue that the government should step in and increase spending to boost demand and stimulate economic growth.
One criticism of Keynesian economics is that it can lead to high levels of government debt, as increased spending is financed through borrowing. Additionally, some argue that government intervention can lead to inefficiencies in resource allocation, as the government may not always be able to accurately predict and respond to changes in demand.
Overall, the Keynesian school of economic thought emphasizes the role of government intervention in stabilizing the economy and boosting demand. While it has been influential in shaping economic policy, it has also faced criticism for its potential impact on government debt and resource allocation.
32.1 The Great Depression and Keynesian Economics
From simple essay plans, through to full dissertations, you can guarantee we have a service perfectly matched to your needs. Understanding New Keynesian Economics Britisheconomist th century. Thus, Harrod developed the concept of the capital coefficient, which he defines as the ratio between the total capital stock and the national income, for a certain period of time. The contraction in output that began in 1929 was not, of course, the first time the economy had slumped. Economic historians estimate that in the 75 years before the Depression there had been 19 recessions. While both Keynes and Marx understood unemployment as occurring when aggregate demand and supply are not equal, Marx also viewed unemployment as a tool which can be manipulated within a capitalist economy for the benefit of bourgeoisie. And expansionary fiscal policy had put a swift end to the worst macroeconomic nightmare in U.
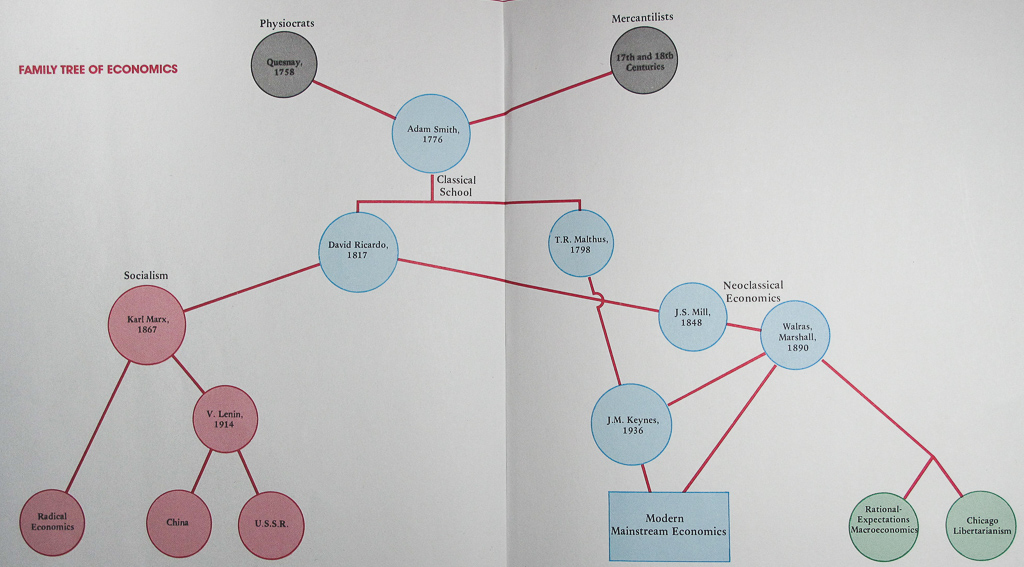
Marxism and Keynesian economics

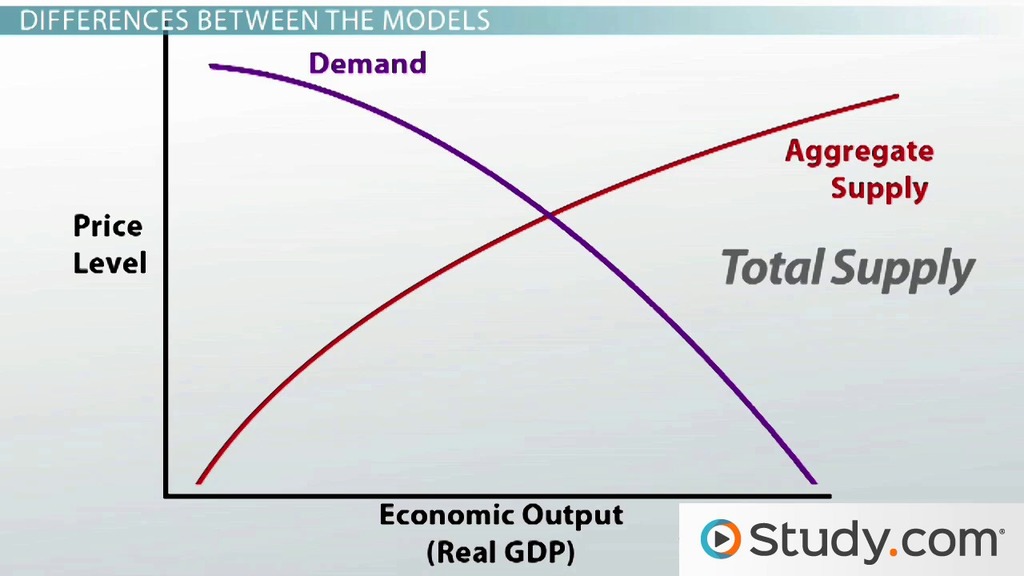
An alternative approach would be to do nothing. Burzhuaznye ekonomicheskie teorii i ekonomicheskaia politika imperialisticheskikh stran. If the interest rate charged by the financial sector to the productive sector is below the marginal efficiency of capital at that level of technology and capital intensity then investment is positive and grows the lower the interest rate is, given the diminishing return of capital. Classical Economics Supply and Demand Model. Article Link to be Hyperlinked For eg: Source: Keynesian economics is different from classical economics, which claims that aggregate supply and not aggregate demand keeps an Economy An economy comprises individuals, commercial entities, and the government involved in the production, distribution, exchange, and consumption of products and services in a society. He saw the economy as unable to maintain itself at full employment automatically, and believed that it was necessary for the government to step in and put purchasing power into the hands of the working population through government spending. On The Principles of Political Economy and Taxation.
Keynesian Economics Vs. Classical Economics

You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc. However, others argue that though menu costs are typically low for companies, it is not negligible. The federal government, for example, doubled income tax rates in 1932. The Fed could have prevented many of the failures by engaging in open-market operations to inject new reserves into the system and by lending reserves to troubled banks through the discount window. The short-run aggregate supply curve increased as nominal wages fell. .
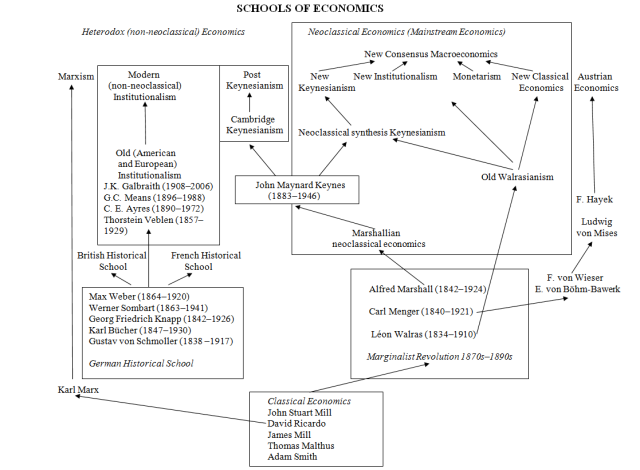
New Keynesian Economics: Definition and Vs. Keynesian
The Invisible Hand: Economic Thought Yesterday and Today. It began in the United States on October 29, 1929, with the Wall Street Crash and lasted till 1939. Updated December 27, 2022 What is New Keynesian Economics? Krugman, Introduction to the General Theory. The European Heritage in Economics and the Social Sciences. This ideology was somewhat similar with some other school of thoughts such as, classical economics, neo-classical Economics, new classical economics and supply side economics. There are few, if any, examples of a pureblood Keynesian economy since its conception.