Economies of scale theory. Economies of Scale and Customs Union Theory 2022-12-18
Economies of scale theory
Rating:
9,9/10
1915
reviews
Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a business can achieve by producing a larger quantity of goods or services. These cost advantages arise from various sources, such as the ability to purchase raw materials or other inputs at a lower cost, the ability to spread fixed costs over a larger number of units, and the ability to take advantage of technological advances and specialized equipment.
There are two types of economies of scale: internal and external. Internal economies of scale occur within a firm and are the result of the firm's own operations, such as increasing the size of its production facilities or investing in more efficient technology. External economies of scale, on the other hand, are the result of the larger industry or market in which the firm operates, such as the availability of specialized suppliers or the development of transportation infrastructure.
Economies of scale can lead to lower average costs, which can give firms a competitive advantage in the market. For example, if a firm is able to produce a large quantity of goods at a lower cost than its competitors, it can sell those goods at a lower price and still make a profit. This can attract more customers and increase market share, leading to even greater economies of scale as the firm becomes even larger.
However, economies of scale are not always present and can sometimes be offset by other factors, such as diseconomies of scale. Diseconomies of scale occur when a firm becomes too large and inefficient, leading to higher costs and reduced competitiveness. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as poor communication and coordination within the firm, a lack of specialization among workers, or a lack of flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, economies of scale are an important concept in economics that refer to the cost advantages that a firm can achieve through increased production. These cost advantages can give firms a competitive advantage in the market, but they can also be offset by diseconomies of scale if a firm becomes too large and inefficient. Understanding the forces that drive economies of scale is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their operations and increase profitability.
Theory Of Economies Of Scale In The Motion Picture Industry

The Legacy of Piero Sraffa. The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics. Indeed, indivisibility only entails the existence of economies of scale produced by the balancing of productive capacities, considered above; or of increasing returns in the utilisation of a single plant, due to its more efficient use as the quantity produced increases. Economies of scale are cost advantages reaped by companies when production becomes efficient. Economies of scale are important because they can help provide businesses with a competitive advantage in their industry. That is why very few companies can build successful In addition to that, when a company reaches a certain level of scale, there is a sweet spot where these After a certain scale, though, also In a negative Network effects enable platform In Read Also: What are economies of scale? Generally speaking, economies of scale can be achieved in two ways. Internal Economies of Scale This refers to economies that are unique to a firm.
Next
6: Economies of Scale and International Trade

An industry may also be able to dictate the cost of a product if several different companies are producing similar goods within that industry. External economies of scale can also be reaped if the industry lessens the burdens of costly inputs, by sharing technology or managerial expertise, for example. For instance, suppose the government wants to increase steel production. She most recently worked at Duke University and is the owner of Peggy James, CPA, PLLC, serving small businesses, nonprofits, solopreneurs, freelancers, and individuals. In fact, the greater of the number of resources involved, the smaller, in proportion, is the quantity of reserves necessary to cope with unforeseen contingencies for instance, machine spare parts, inventories, circulating capital, etc. If a firm that manufactures product X makes about 50 thousand of it in a month and at this rate, they cost about 5 dollars each. Price ceilings are limits imposed on the price of a product, service, or commodity to protect consumers from prohibitively expensive items.
Next
Economies of Scale
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
They found that auction volume did not correlate with competition, nor with the number of bidders, suggesting that auction volume does not promote additional competition. Purchasing Firms might be able to lower average costs by buying the inputs required for the production process in bulk or from special wholesalers. A monopoly takes away that choice, which means consumers are stuck with that product or service no matter the condition, kind of like a dictatorship. This means that at the higher level of output, it requires less labor i. Most consumers don't understand why a smaller business charges more for a similar product sold by a larger company. See engineering texts on heat transfer.
Next
Economies of Scale and Customs Union Theory
The Dangers of Monopolies One of the first and obvious costs associated with a monopolistic market is the denial of choice. It explores a unique range of topics each year - from the frontier of theoretical developments in many new and important areas, to research on current and applied economic problems, to methodologically innovative, theoretical and applied studies in econometrics. Patrice Williams is a writer and the author of Looking Fly on a Dime. Economies of scale in production means that production at a larger scale more output can be achieved at a lower cost i. The companies themselves have to motivation to do better since they are kings of that industry. In addition, consumers tend to associate movies with its leading stars rather than the company that produces it, unlike for most products Moul, 2005. She teaches research skills, information literacy, and writing to university students majoring in business and finance.
Next
Advantages and Disadvantages of Economies of Scale

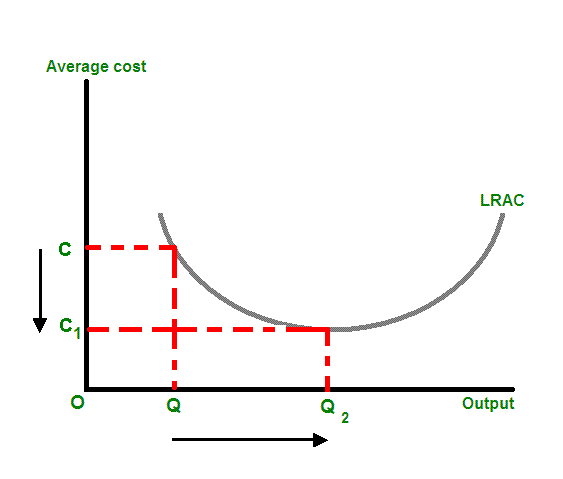
That's because the cost per unit depends on how much the company produces. Managerial Firms might be able to lower average costs by improving the management structure within the firm. It can be described as elastic, where consumers are responsive to price changes, or inelastic, where consumers are less responsive to price changes. For example, it is much easier for a restaurant chain to offer new dishes than to start a new restaurant chain offering the same new foods. A company that benefits from economies of scope has lower average costs because costs are spread over a variety of products. Economies of scale apply to a variety of organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a business or manufacturing unit, plant or an entire enterprise.
Next
What Are Economies Of Scale And Why They Matter
The country takes into account the influence of film upon tourism not only because of its worldwide promotion, but particularly because of its economic impact. Because there are numerous ways to conceive of strategic interactions between firms, there are also numerous models and results that could be obtained. Advertising can promote multiple dishes at the same time, and the new foods can be prepared and served using the same equipment and personnel. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. A higher production scale can make the different production capacities compatible.
Next
6.2: Economies of Scale and Returns to Scale
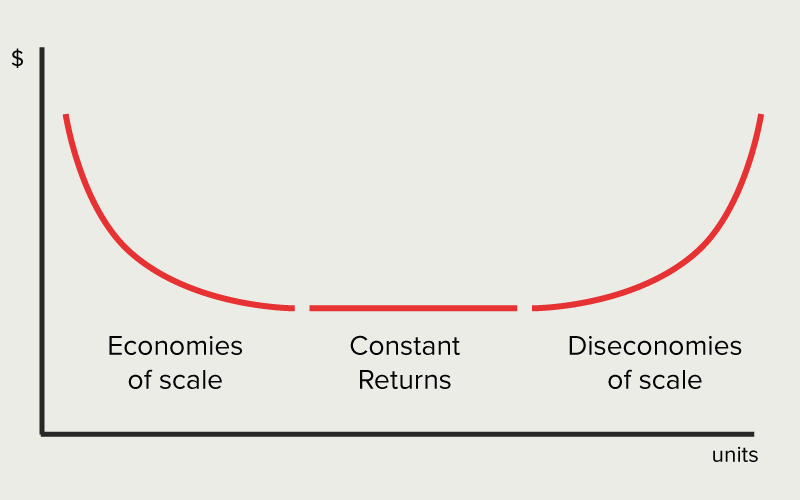
The lack of choice in a monopoly is what results in the rest of the collective dangers of monopolies. Price Inflation Without the availability of choice, monopolies can set the price however they want it. Thus, when an industry's scope of operations expands due to outside developments, external economies of scale might result. Internal economies are caused by factors within a single company while external factors affect the entire industry. A production function has constant returns to scale if increasing all inputs by some proportion results in output increasing by that same proportion. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. This happens because costs are spread over a larger number of goods.
Next
Household Economies of Scale in Consumption: Theory and Evidence on JSTOR

Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output. Thus, the supplier is able to use this circumstantial advantage to bargain and demand wages higher than the market …show more content… Furthermore, stars can directly contribute to movie revenues as well because consumers might be attracted to a particular movie due to their interest in or loyalty to the star of the film Donahue 1987; Vogel 2010. For instance, a firm may hold a patent over a mass production machine, which allows it to lower its average cost of production more than other firms in the industry. Cambridge, New York: Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge. Beware of diseconomies of scale In Economics, a Diseconomy of Scale happens when a company has grown so large that its costs per unit will start to increase.
Next
Economies of Scale and The Dangers of Monopolies

In a natural monopoly, these barriers are other factors that do not involve any legal procedures like jacked up prices of rent spaces while in Legal monopoly there are legal rights that make any competitor at the risk of a lawsuit. The Unbound Prometheus: Technological Change and Industrial Development in Western Europe from 1750 to the Present. As in the popular television game show, you are given an answer to a question and you must respond with the question. In consumer behavior, price sensitivity describes and measures fluctuations in product demand as the price of that product changes. Often operational efficiency is also greater with increasing scale, leading to lower variable cost as well.
Next
Economies of Scale: What Are They and How Are They Used?

The modern film industry has placed a greater emphasis on profit and brand by exploiting franchises in order to create sequels and remakes, which, in turn, makes the film industry a commercialized conveyor… The Film Industry It is at the forefront of creativity, marketing and technology, allowing films to be displayed in ways never seen before. The cost of a unit of capacity of many types of equipment, such as electric motors, centrifugal pumps, diesel and gasoline engines, decreases as size increases. These limits are usually imposed by the government but can also be set in the resale price maintenance RPM agreement between a product manufacturer and its distributors. This tends to make them appear above the law. In an attempt to lower costs and make health care a free market, we must let informed patients make these crucial decisions about their care. Often smaller usually older manufacturing facilities remain viable by changing from commodity-grade production to specialty products. In the same way association re-establishes, now on a rational basis, no longer mediated by serfdom, overlordship and the silly mysticism of property, the intimate ties of man with the earth, for the earth ceases to be an object of huckstering, and through free labor and free enjoyment becomes once more a true personal property of man.
Next

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)





