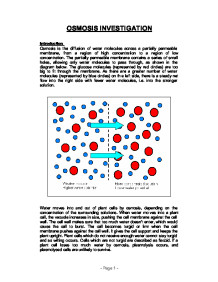
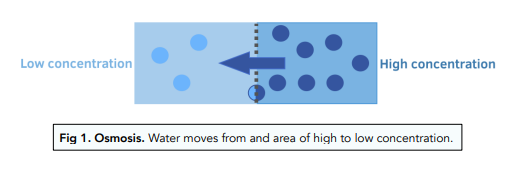
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. This movement occurs in order to equalize the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane. In plant cells, osmosis plays a vital role in maintaining the proper balance of water and solutes within the cell and ensuring the proper functioning of the plant.
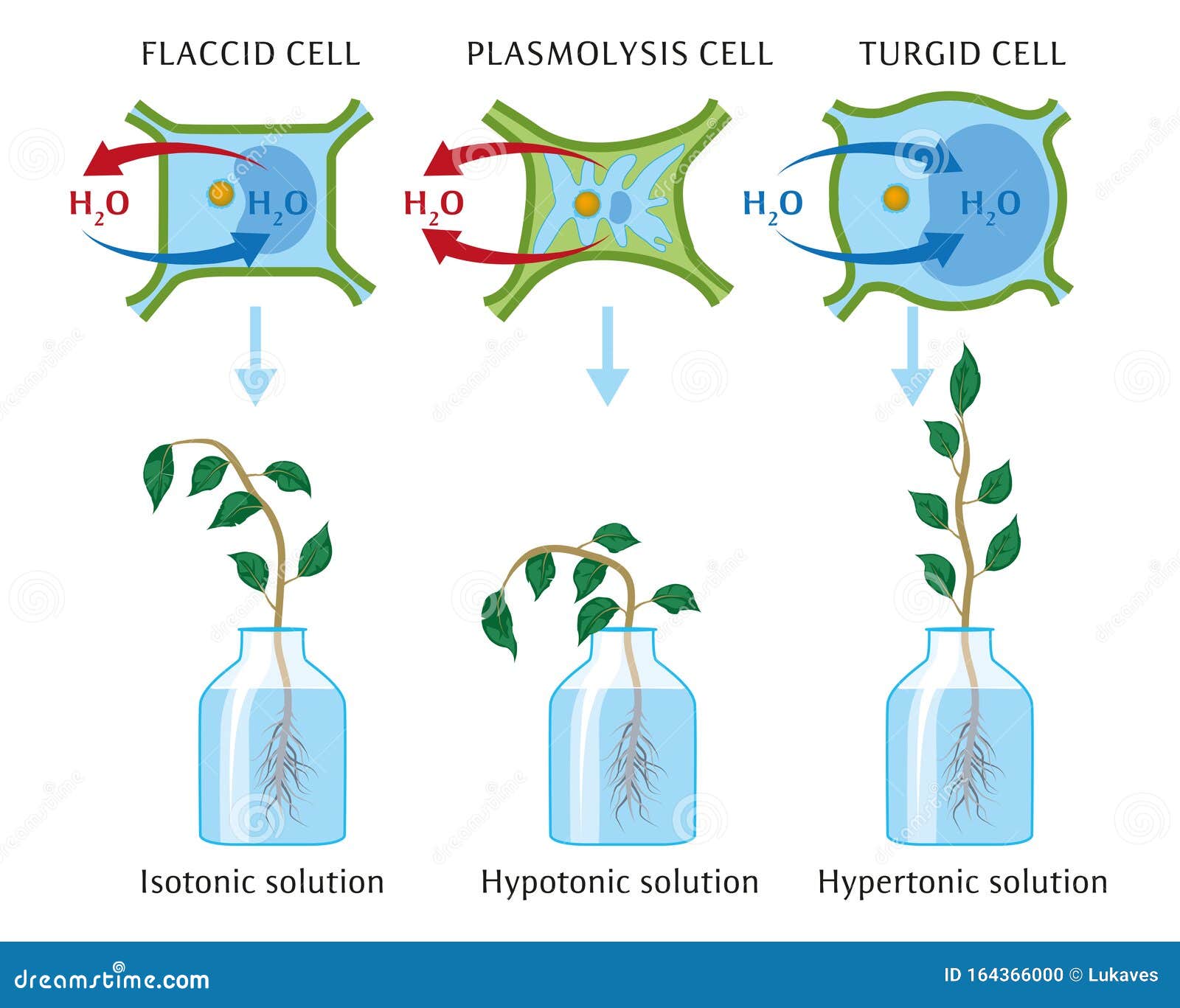
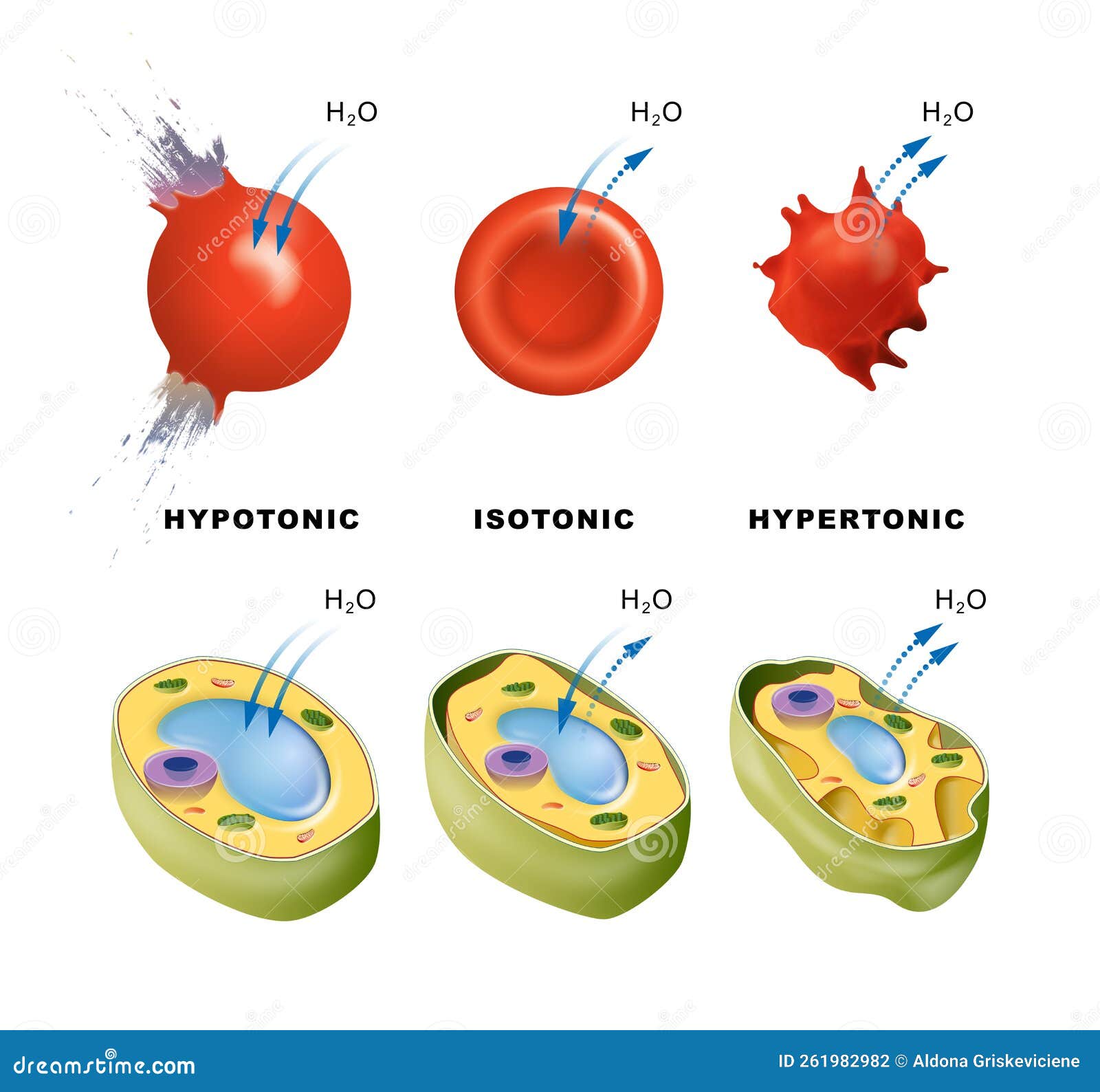
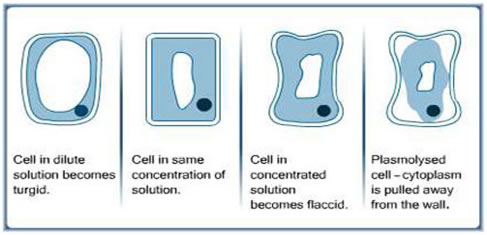
When a plant cell is placed in a solution with a higher concentration of solutes, such as salt, the water inside the cell will move out of the cell through the cell membrane by osmosis. This can lead to the cell becoming dehydrated and shrunken, a condition known as plasmolysis. On the other hand, if a plant cell is placed in a solution with a lower concentration of solutes, the water will move into the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to become swollen and turgid.
The effect of osmosis on plant cells is important for their survival and growth. Turgidity is necessary for the proper functioning of plant cells, as it allows them to maintain their shape and support the weight of the plant. If a plant cell becomes too turgid, it can burst, leading to cell death. On the other hand, if a plant cell becomes too dehydrated, it can become unable to carry out its functions properly, leading to reduced growth and development.
Osmosis is also important for the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant. Water is transported from the roots to the leaves through the xylem, a tissue that consists of hollow tubes made of cells with thick walls. When a plant is thirsty, the concentration of solutes in the cells of the xylem increases, causing water to move into the cells by osmosis. This increases the turgidity of the cells, which helps to push the water up through the plant to the leaves.
In conclusion, osmosis plays a vital role in the functioning and survival of plant cells. It helps to maintain the proper balance of water and solutes within the cells and plays a role in the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant. Understanding the effect of osmosis on plant cells can help us to better understand how plants grow and develop and can inform our efforts to support the health and well-being of plants.