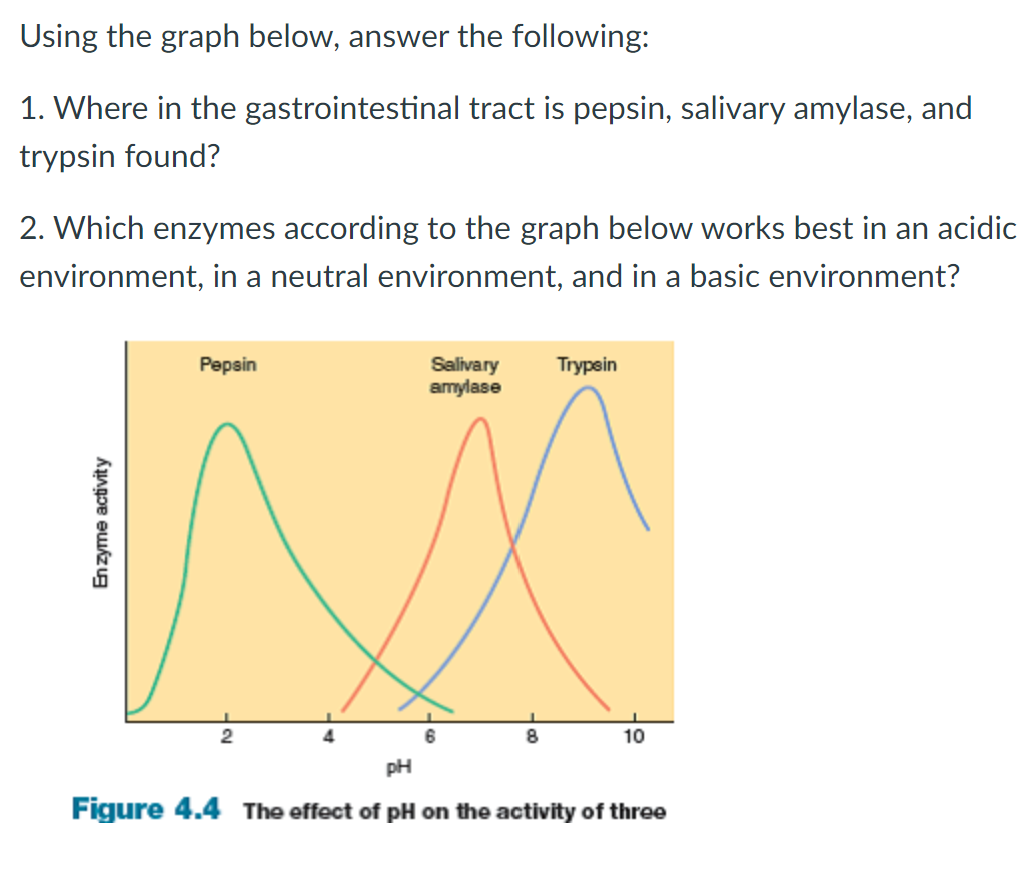
Salivary amylase is an enzyme produced in the salivary glands that plays a crucial role in the digestion of carbohydrates. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch and other complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, such as maltose and glucose, which can be easily absorbed by the body. The activity of salivary amylase is affected by various factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of other enzymes and substances. In this essay, we will focus on the effect of pH on salivary amylase.
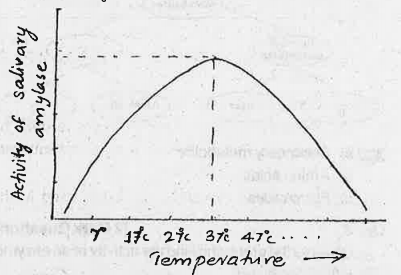
The pH of the environment in which salivary amylase functions plays a significant role in its activity. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions, and their three-dimensional structure is crucial for their function. The structure of an enzyme can be altered by changes in pH, leading to a change in its activity. In general, enzymes have an optimal pH at which they function best. For salivary amylase, the optimal pH is around 6.7 to 7.0, which is close to neutral.
At pH values below the optimal range, the activity of salivary amylase decreases significantly. This is because the protein structure of the enzyme is disrupted at low pH values, leading to denaturation. Denaturation refers to the loss of the enzyme's three-dimensional structure and function. At very low pH values, the enzyme becomes inactive and is unable to catalyze the hydrolysis of carbohydrates.
On the other hand, at pH values above the optimal range, the activity of salivary amylase also decreases. This is because the protein structure of the enzyme is again disrupted at high pH values, leading to denaturation. However, the decrease in activity is not as pronounced as at low pH values.
In conclusion, the pH of the environment plays a significant role in the activity of salivary amylase. The enzyme functions optimally at a pH of around 6.7 to 7.0, and its activity decreases significantly at both low and high pH values due to denaturation. It is essential to maintain the optimal pH range for the proper functioning of salivary amylase and the efficient digestion of carbohydrates.
Practical

The change in pH would affect the ionisation of the side groups in the enzymes amino acid residues this would then affect the overall shape of the enzyme molecule and would then affect the efficiency of formation of enzyme-substrate complexes. How do you investigate the effect of pH on amylase? This means that the sunstrate is no longer able to bind to the active site and the reaction will not take place, therefore decreasing the activity of amylase. These conclusions help us confirm or deny our original hypothesis. Often, mathematical equations can be made from graphs. What is the optimum pH for amylase and why? Tube 4 is slightly basic, tube 5 is very basic. As the environment grows warmer, the amylase is going to become more energetic and more effective. Enzyme activity can be affected by a variety of factors, such as temperature, pH, and concentration.
Effect Of Different PH On The Activity Of Salivary Amylase On Starch
Amylase is an enzyme that exists in human saliva, in the pancreas of humans most animals, and in the cells of a number of plants and bacteria. The digestive system is a complex network of organs as well as other structures which all work together to supply the body with the necessary nutrients and energy required. This can be in the form of a table of processed numerical data, or graphs. How does low pH affect amylase? Hundreds have been crystallized, and the amino acid sequences and three-dimensional structure of a significant number have been fully determined through the technique of X-ray crystallography. In fact, it is swallowed with chewed food and subsequently inactivated by extremely low gastric pH; amylase in fact has an optimal pH around 7, and the pH of saliva is generally between 6. When raw data gets processed mathematically, for example, it becomes results.
effect of pH on amylase activity

Enzymes are biological catalysts that can cause a specific chemical change in any part of the body Walsh, 2002. Starch keeps on giving blue color with iodine till it is completely digested into maltose. If problem occurs along the digestive tract the consequences can be fatal. So instead of 2, 4, 6 and 8 drops you will use 1, 2,…and 9 drops. If you determine that experimental errors are influencing your results, carefully rethink the design of your experiments.