Globalization is the process of increasing interconnectedness and interdependence among countries through the exchange of goods, services, and ideas. It is driven by advances in technology, transportation, and communication, which have made it easier for countries to trade with one another and for people to travel, work, and live in different parts of the world.
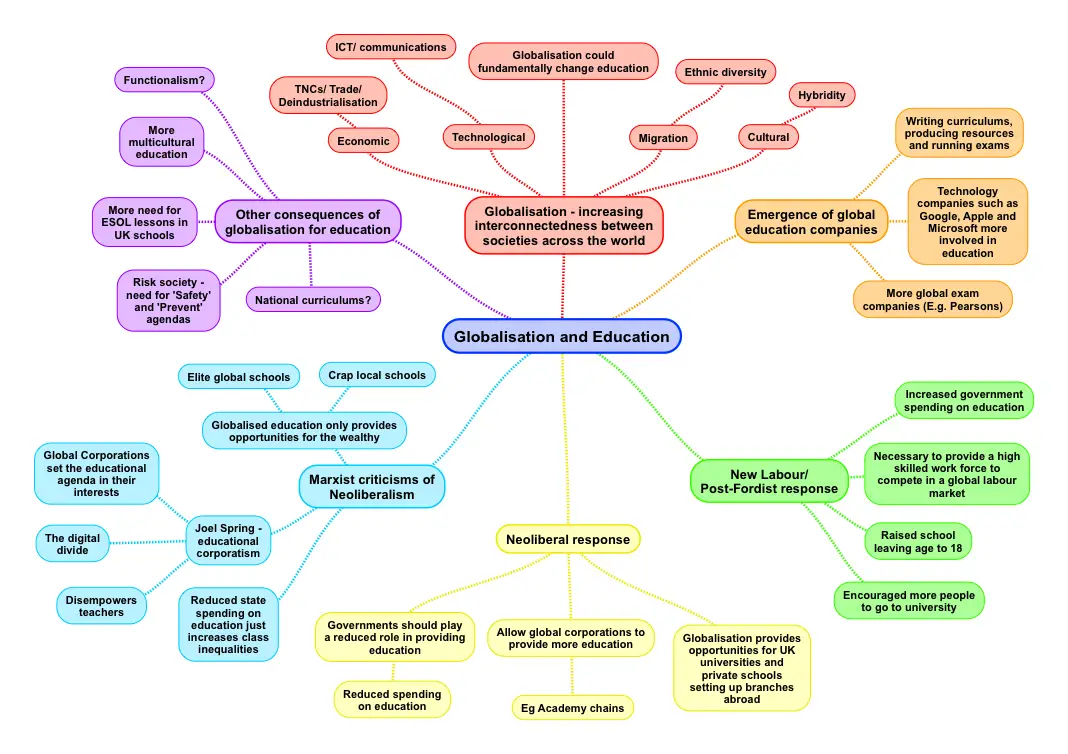
One of the main effects of globalization on social policy is that it has led to the spread of neoliberalism, a political ideology that emphasizes free markets, limited government intervention, and individual responsibility. Neoliberalism has influenced social policy in many countries, leading to the privatization of public services, the deregulation of industries, and the reduction of welfare state programs.
For example, in the United States, the welfare state has been scaled back in recent decades, with programs such as Medicaid, food stamps, and cash assistance becoming means-tested and subject to stricter eligibility requirements. This has led to a decrease in the number of people receiving assistance, and an increase in poverty and inequality.
Similarly, in Europe, social policy has been influenced by the European Union's emphasis on fiscal austerity and economic competitiveness. This has led to cuts in welfare state programs and an increase in the use of private and market-based solutions for social problems.
Another effect of globalization on social policy is the rise of international organizations and supranational bodies that have a role in shaping social policy. The World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organization are examples of organizations that have influenced social policy in developing countries through their lending practices and trade agreements. These organizations often promote neoliberal policies and impose conditions on their loans and assistance that require countries to reduce social spending and increase private sector involvement in social services.
On the other hand, globalization has also led to the spread of international human rights norms and the development of transnational social movements that advocate for social justice and equality. These movements have pressured governments and international organizations to adopt more progressive social policies and to address issues such as poverty, inequality, and discrimination.
In conclusion, the effects of globalization on social policy are complex and varied. While globalization has led to the spread of neoliberalism and the influence of international organizations, it has also sparked transnational movements for social justice and the spread of international human rights norms. Overall, the impact of globalization on social policy depends on the specific context and the balance of power among different actors.