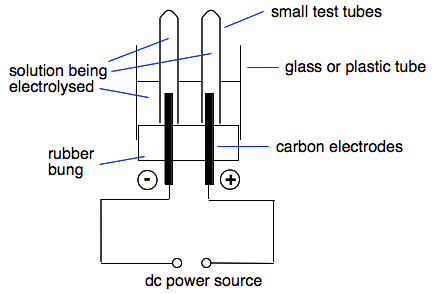
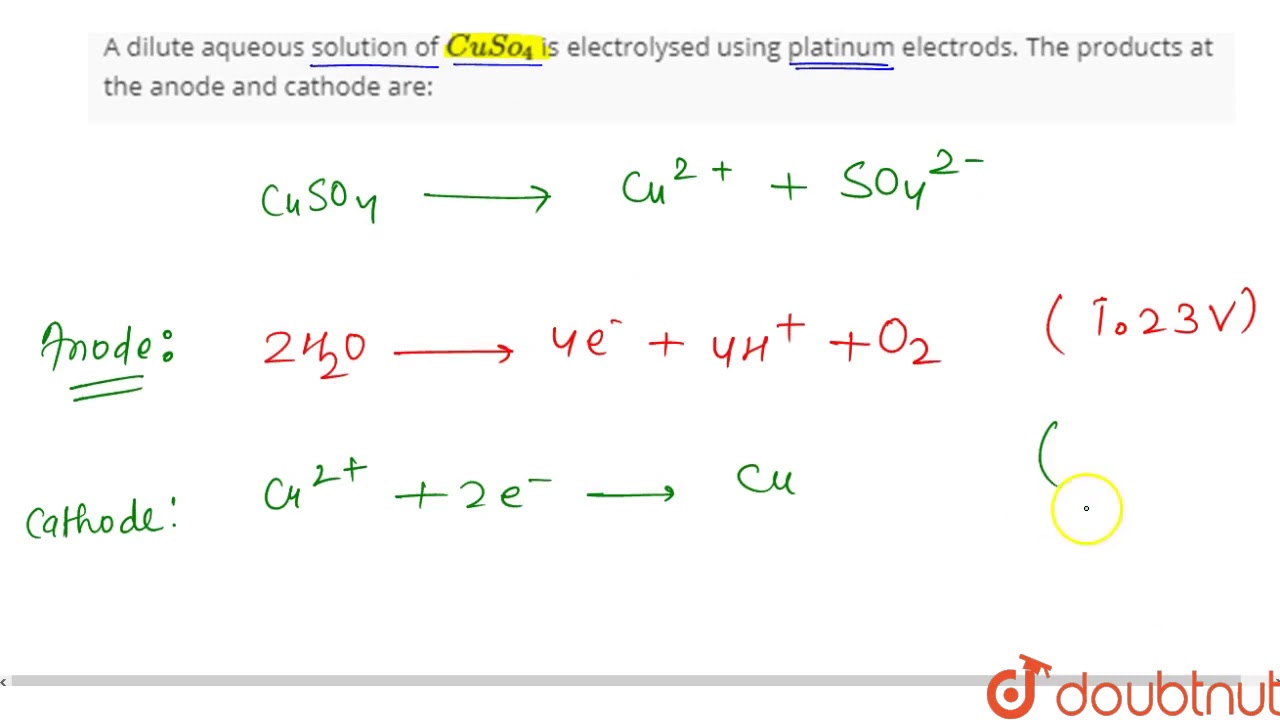
Electrolysis is a process in which an electric current is used to drive a chemical reaction that would not occur spontaneously. One example of electrolysis is the decomposition of copper sulfate using platinum electrodes.
To perform the electrolysis of copper sulfate, a copper sulfate solution is prepared by dissolving copper sulfate crystals in water. The solution is then poured into an electrolysis cell, which is a container with two electrodes, one positive and one negative, immersed in the solution. The positive electrode, or anode, is made of platinum, and the negative electrode, or cathode, is also made of platinum.
A direct current power source, such as a battery or a power supply, is then connected to the electrodes to supply the electrical energy needed for the electrolysis reaction to occur. When the current is applied, the electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the external circuit, and the ions in the solution flow towards the opposite electrodes.
At the anode, the copper ions in the solution are oxidized, which means they lose electrons and become copper atoms. These atoms are then deposited on the anode as a layer of metallic copper. At the same time, the platinum electrode remains unchanged and does not participate in the reaction.
At the cathode, the sulfate ions in the solution are reduced, which means they gain electrons and become sulfur dioxide gas, which is released into the air. The electrons that are gained by the sulfate ions come from the external circuit, which completes the circuit and allows the current to flow.
The electrolysis of copper sulfate using platinum electrodes is an important process in the extraction of copper from its ores. Copper is one of the most widely used and valuable metals in the world, and it is essential for the production of a wide range of products, including electrical wires, plumbing pipes, and coins. The electrolysis of copper sulfate using platinum electrodes is a key step in the production of high-purity copper, which is used in a variety of applications where its electrical and thermal conductivity is important.
In conclusion, the electrolysis of copper sulfate using platinum electrodes is a chemical process that uses an electric current to drive a reaction that would not occur spontaneously. The reaction results in the extraction of metallic copper from the copper sulfate solution, and the production of sulfur dioxide gas. This process is an important step in the extraction of copper from its ores and in the production of high-purity copper.