Elizabethan wars in ireland. Irish Rebellion of 1641 2022-12-16
Elizabethan wars in ireland
Rating:
4,8/10
1299
reviews
The Elizabethan wars in Ireland were a series of conflicts that took place in Ireland during the reign of Elizabeth I of England (1558-1603). These wars were fought between the English crown and various Irish factions, including Irish chieftains, the Irish Catholic Church, and the Spanish Empire.
The Elizabethan wars in Ireland were part of a larger conflict known as the Nine Years' War (1594-1603), which was fought between the English and Irish on one side, and the Spanish and Irish on the other. The conflict was sparked by the English crown's attempts to assert control over the island of Ireland and suppress the Irish Catholic Church, which was seen as a threat to English Protestantism.
The Elizabethan wars in Ireland were characterized by brutal violence and atrocities on both sides. English troops, led by soldiers such as Sir Henry Sidney and Sir William Russell, fought against Irish rebels led by Hugh O'Neill, Earl of Tyrone, and Red Hugh O'Donnell. The English used scorched earth tactics, destroying Irish crops and villages in order to starve out the rebels. The Irish, in turn, resorted to guerrilla tactics and ambushes, and often targeted English civilians.
The Elizabethan wars in Ireland ended in 1603 with the Treaty of Mellifont, which granted the English crown control over most of Ireland. However, the conflict left deep scars on the island, and tensions between the English and Irish continued for centuries. The Elizabethan wars in Ireland also had significant consequences for England and the rest of Europe, as they were part of a larger struggle for power and influence between the English and Spanish empires.
In conclusion, the Elizabethan wars in Ireland were a series of violent and devastating conflicts that took place during the reign of Elizabeth I of England. These wars were fought between the English crown and various Irish factions, and were part of a larger struggle for power and influence in Europe. The conflict left deep scars on Ireland and had significant consequences for the English and Spanish empires.
The Elizabethan Soldier in Ireland

Some Spanish mariners were so afraid of Drake that they believed he practiced witchcraft. In the Elizabethan Era, there were a lot of weapons and wars. There was little help for the sick, elderly, and orphans. In this vein, Hammer is particularly effective in following the line of Fissel, N. Portraits of Queen Elizabeth I Your browser does not currently recognize any of the video formats available. No viewing day of sale.
Next
History of Ireland (1536

John Locke, Toleration and Early Enlightenment Culture. The time period is named after Queen Elizabeth I who ruled England during this time. They realize, it may be, that these wars were brought about to some extent by national sentiment and to a greater extent by religious sentiment; they may also see that the struggle was a phase of the English war with Spain. A New History of Ireland: Volume III. The reasons for the Elizabethan War with Spain from 1585 — 1603 exploded due to various conflicts surrounding the wealth and power to be gained from trade from the New World.
Next
Why was the Elizabethan war fought?

Prince James She had a miscarriage and later engaged in a short affair with Louis Cond until he tried to take the crown from her husband. Under a settlement imposed after the rebellion, known as "composition", the Desmonds' military forces were limited by law to just 20 horsemen; their tenants were made to pay rent to them rather than supply military service or quarter their soldiers. They were led by the Earl of Desmond who was the head of the Fitzgerald Dynasty. The southern Geraldine axis of power was annihilated, and Munster was "planted" with English colonists given land confiscated from those who fought for their country. LIVE SALEROOM AUCTION: If you can't attend the auction in the saleroom you can email or post or telephone bids to us, or you can book a telephone line to bid during the sale. The first began when a group of slaves stood up against the Dutch.
Next
Irish Rebellion of 1641

The English war against Spain lasted from 1585 — 1603 18 years. However, the rebellion did not stop there but followed by successive events in constant upheaval to their belief. From the period of the original lordship in the 12th century onwards, Ireland had retained its own bicameral With the institutions of government in place, the next step was to extend the control of the English Kingdom of Ireland over all of its claimed territory. He imagined they would be welcomed. Religion was also seen as another factor because the English feared the support Catholicism could give to Irish from continental adversaries of England such as Spain as Protestantism was gaining more power in the land.
Next
The Elizabethan War with Ireland

At the end of this period, the bidder who has submitted the highest bid wins the lot, provided the bidexceeds the reserve price. Irish landowners continued to be threatened by the arrival of English colonists to settle on land confiscated from the Irish. First, there is the inevitable effort of the Renaissance states to absorb the surviving Celtic communities, as France did in Brittany, England in Wales and Cornwall, Scotland in some degree in her own Highlands. They were: The Desmond Rebellion, the English War against Spain and the Tyrone Rebellion. What was life like in Elizabethan era? A contemporary Catholic source wrote that O'Neill "strove to contain the raskall multitude from those frequent savage actions of stripping and killing" but "the floodgate of rapine, once being laid open, the meaner sort of people was not to be contained". He had to get that money somewhere, so he How Did The Great War Changed The Relationship Between England And Its American Colonies 1131 Words 5 Pages 4.
Next
Elizabethan era war history

When did Mary return to England? Successive rebellions broke out, the first in There were two main reasons for the chronic violence that dogged the central government in Ireland. Elizabeth II Elizabeth Alexandra Mary Windsor; born 21 April 1926 is Queen of the United Kingdom and 15 other Commonwealth realms. . Still, if the system for maintaining the war effort was as fundamentally sound as Hammer asserts, one must wonder why the government of James I was in quite such a hurry to demobilize. Devil Land: England under siege, 1588-1688.
Next
Desmond Rebellions

The Seven Years War took place in the American continent and the War between Britain and France was fought in Europe. After these wars, control in Java was almost non-existent but, the Dutch East India company continued to rule over the islands. Commodore George Dewey It would be the first overseas war fought by the United States, involving campaigns in both Cuba and the Philippine Islands. England Prepares for Invasion That April, the Queen authorized Francis Drake to make a preemptive strike against the Spanish. Inspired by two articles L. A synthesis such as this is valuable contribution to the literature of Elizabethan and early modern military history as a summation of what has been achieved in this field, a chance to consider where we stand today.
Next
Elizabeth’s Wars: War, Government and Society in Tudor England, 1544

Imperial Power In Indonesia 956 Words 4 Pages Specifically, there were three. Living Members of the Royal Family. Ireland from Independence to Occupation, 1641—1660. Mary then fled to England. One was composition, where private armed forces were abolished, and provinces were occupied by English troops under the command of governors, titled lords president. During this era England experienced peace and prosperity while the arts flourished.
Next
What wars did Queen Elizabeth I fight in?
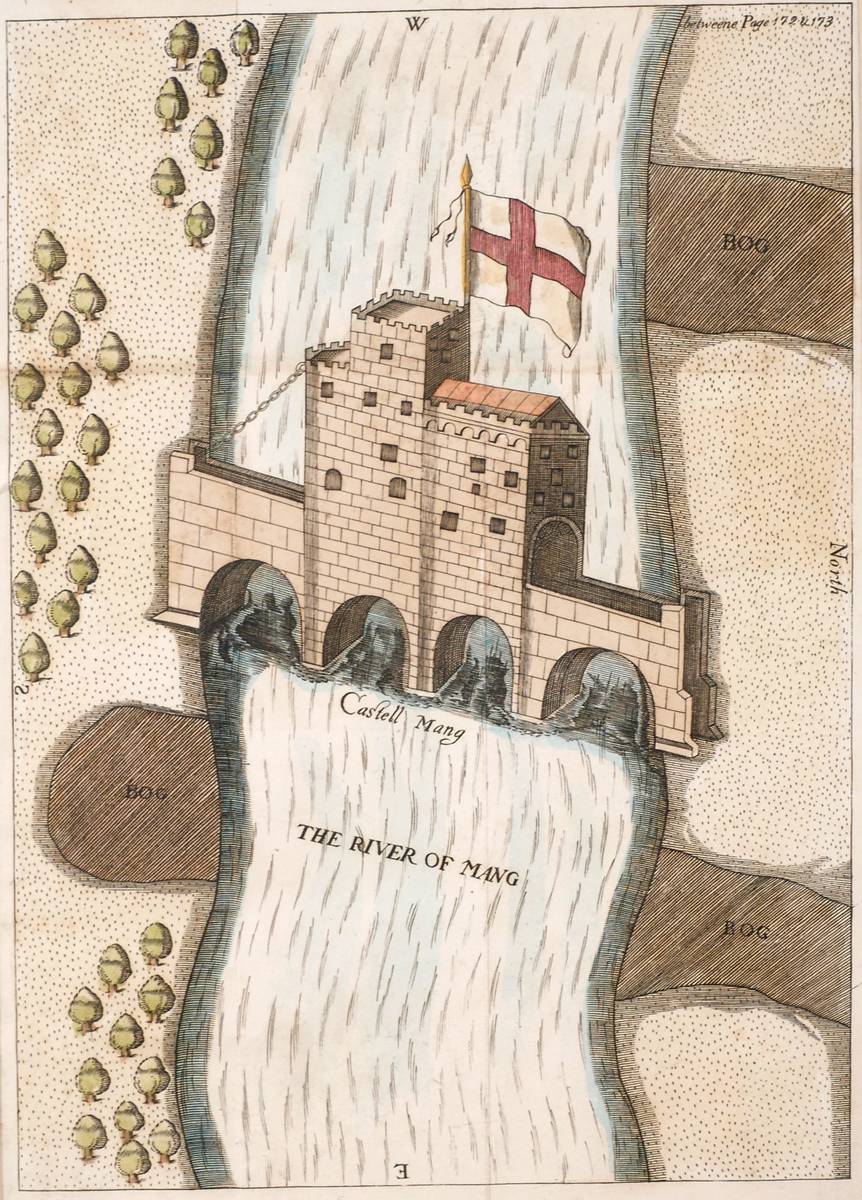
England wasn't the type of country to start a war and the trained military men felt uncomfortable using small weapons so Queen Elizabeth I immediately advanced the strength and the agility of the weapons. And the control later gained by Oliver Cromwell would turn England into a military dictatorship with few religious freedoms and leave another black mark on Ireland's history. It's the fears of the Irish which are created in 1641, the fear of massacre, the fear of attack, that somehow or other accommodations which had been made before were no longer possible after that because the Irish were quite simply, as John Temple put it in his history of the rebellion 'untrustworthy'. Who was the King of England during the Elizabethan era? Fitzmaurice himself had lost the land he had held at Kerricurrihy in To discourage Sidney from going ahead with the Lord Presidency for Munster and to re-establish Desmond primacy over the Butlers, FitzMaurice planned rebellion against the English presence in the south, and against the Earl of Ormonde. In 1588, the Spanish Armada was defeated.
Next
Warfare in Elizabethan Ireland

There has been a veritable cornucopia of articles examining aspects of Elizabethan military history by Simon Adams, R. A new history of Ireland: Early modern Ireland, 1534—1691. These were inexperienced soldiers, many recruited for the first time and with little idea of where they were or what they were doing. However, the descriptions are not intended to be, are not and are not to be taken to be, statements of fact or representations of fact in relation to the lot. At Babi Yar the executioners were Einsatzgruppen who sat behind machine guns, smoking cigarettes, and mowing down the victims into a mass grave. Name of royal Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom Rank whilst active Subaltern equivalent to Army Lieutenant , Junior Commander equivalent to Army Captain Unit None Military training and qualifications None Who is the king and Queen of England? Clearly, it was time to reassess the military practices of Elizabethan England, consider how they measured against contemporary military practices elsewhere and reevaluate their importance in Elizabethan society.
Next








