Enzymes are proteins that play a vital role in the chemical reactions that occur within living organisms. These proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
There are thousands of different enzymes in the human body, each with a specific function. Enzymes are responsible for a wide range of important processes, including digestion, metabolism, and cellular respiration.
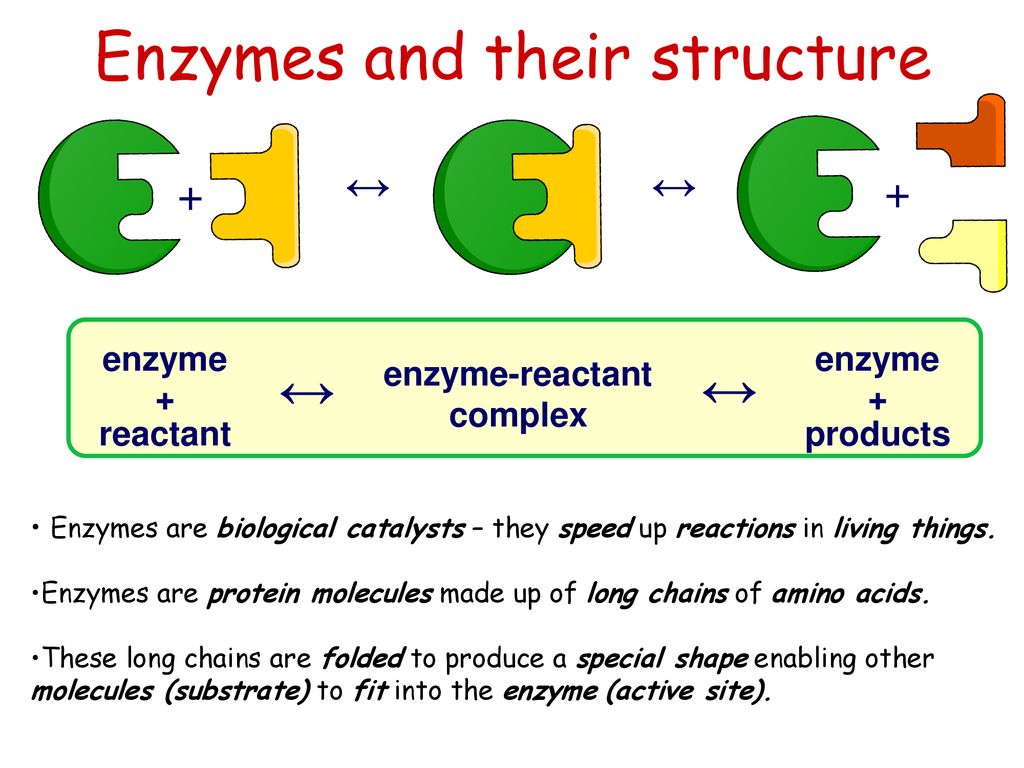
The structure of an enzyme is crucial to its function. Enzymes are made up of long chains of amino acids that are folded into a specific 3-dimensional shape. This shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in the enzyme's polypeptide chain.
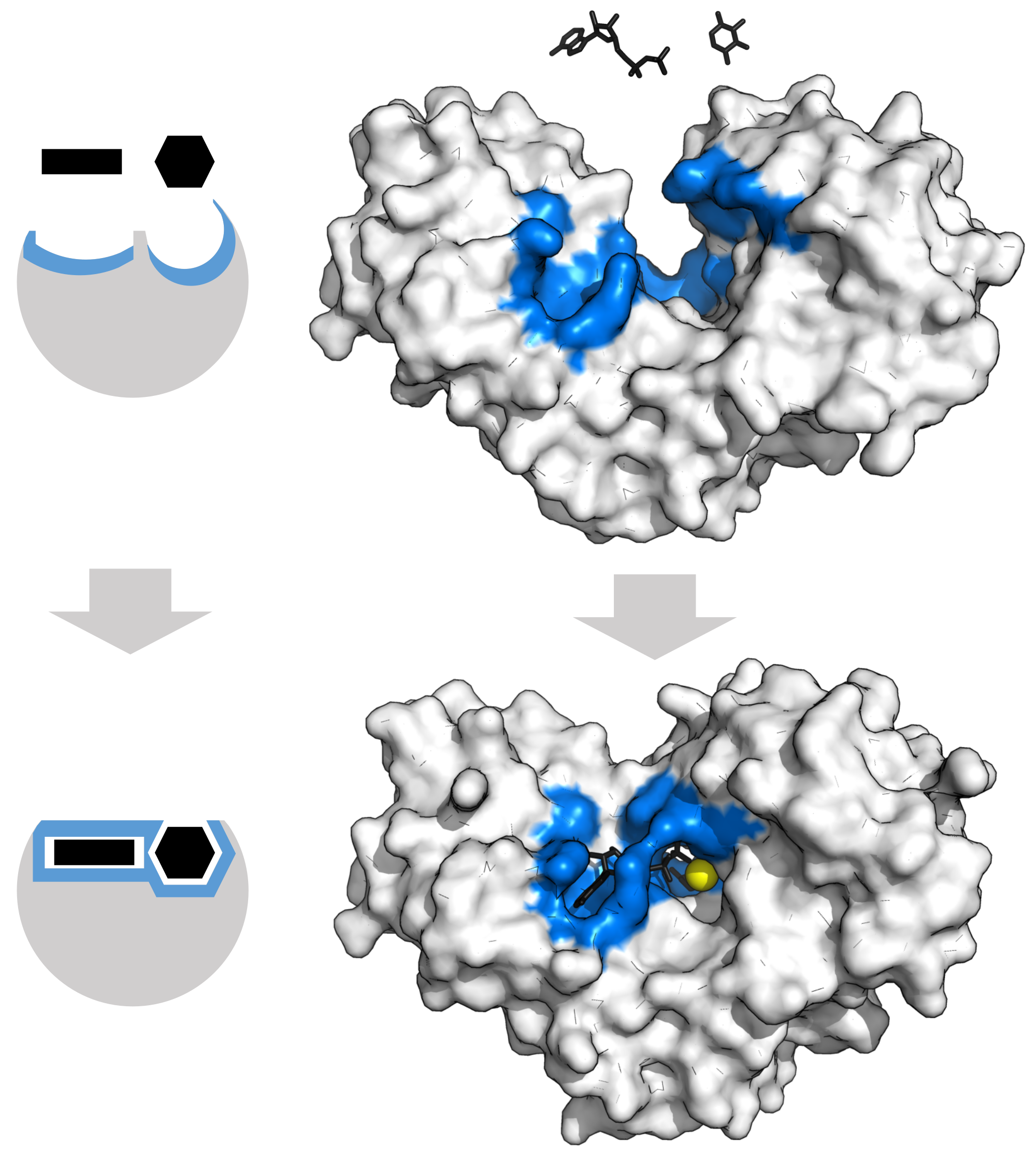
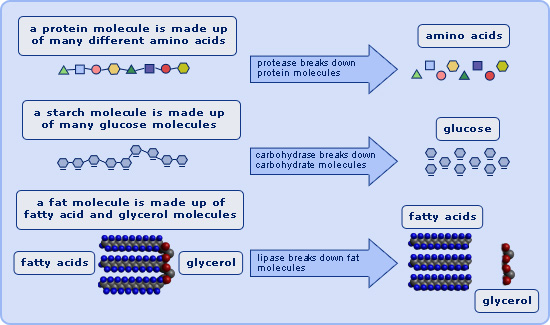
The active site of an enzyme is the region where the chemical reaction takes place. This site is specific to each enzyme and is made up of a small number of amino acids. These amino acids are arranged in such a way that they can interact with the substrate, the molecule that the enzyme acts upon.
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy is the energy needed to get a reaction started. Without enzymes, many of the chemical reactions that take place in the body would not happen, or would happen much more slowly.
Enzymes can be classified into different categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze. For example, there are enzyme classifications for oxidative reactions, hydrolytic reactions, and transferase reactions.
In conclusion, enzymes are essential proteins that play a vital role in the chemical reactions that occur within living organisms. They are made up of amino acids and are folded into a specific 3-dimensional shape. The active site of an enzyme is the region where the chemical reaction takes place and is made up of a small number of amino acids. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur and can be classified into different categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze.
What are Enzymes made up of ?

In terms of a normal proportional reaction rate to the concentration level, the rate equation is considered as first order. Essentially, an enzyme is a specific type of protein that performs a very specific function. Generally, all enzymes are proteins, made up of chains of amino acids, and they perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell. After completing his doctoral studies, he decided to start "ScienceOxygen" as a way to share his passion for science with others and to provide an accessible and engaging resource for those interested in learning about the latest scientific discoveries. An enzyme is a type of protein found within a cell.
2.3.6: Enzymes

However, slight changes above this set homeostasis can drive all of the reactions forward in your body, causing you to burn more energy, which partially escapes in the form of heat. There are many different kinds of molecules that inhibit or promote enzyme function, and various mechanisms exist for doing so. Metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes Intermediates A — D, Enzymes 1 — 5. Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Are enzymes made up of living cells? These reaction specific catalysts are required to keep our body alive. How are enzymes made in the cell? Coenzymes are small nonprotein molecules that are associated to some enzymes.
What is an enzyme made of?
Where are most digestive enzymes produced quizlet? The name of the reactants that enter a substrate to form products at a faster time are called substrates. Ultimately, industrial enzymes are produced by fermentation, similar to the production of beer or wine. How Are Cell Membranes Synthesized? They participate in the oxidation of glucose to produce ATP III. What is the protein part of an enzyme called? Enzymes are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies. One of the first challenges in drug development is identifying the specific molecule that the drug is intended to target. Among the organic macromolecules, enzymes belong in the category of proteins. All living things make enzymes, but we collect ours from microbes.