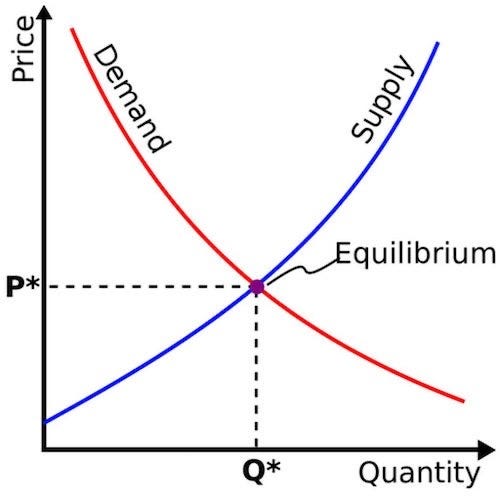
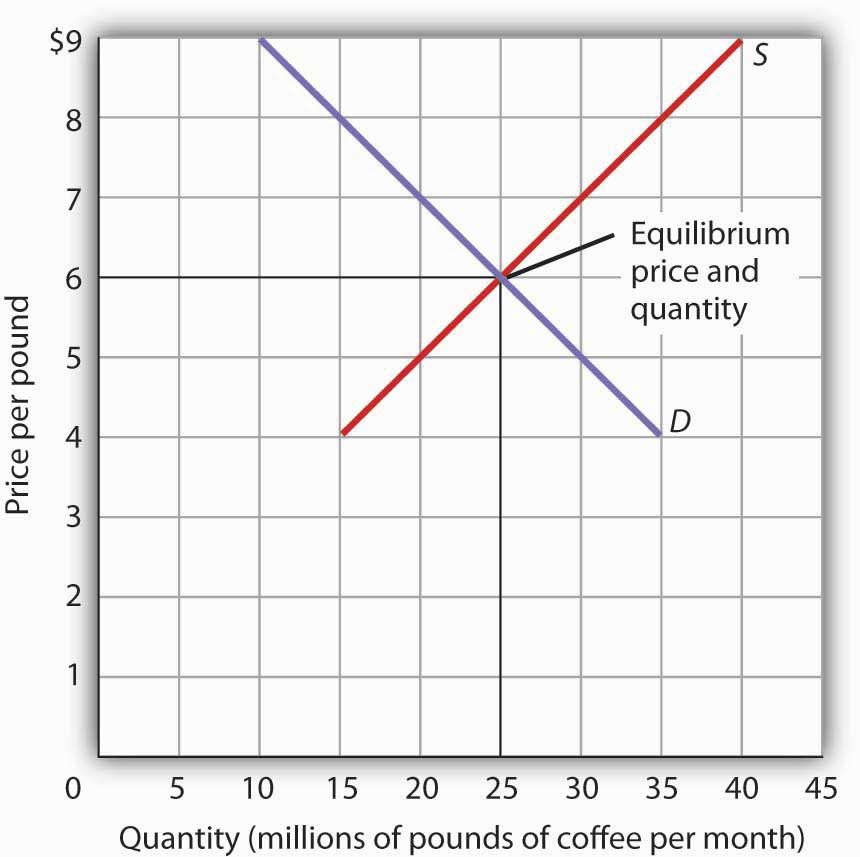
Equilibrium price, also known as market clearing price, is the price at which the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy is equal to the quantity that producers are willing and able to sell. In other words, it is the price at which the demand for a good or service is equal to the supply of that good or service.
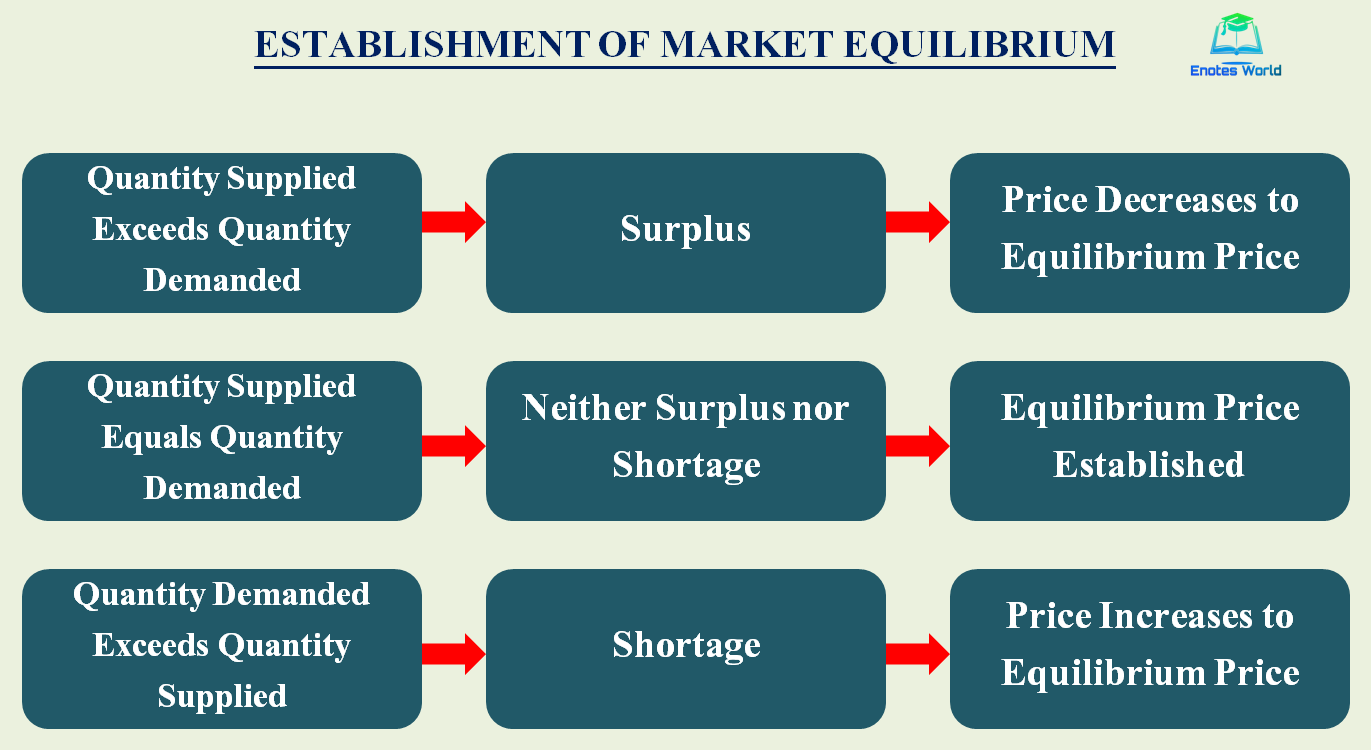
At the equilibrium price, there is no excess supply or demand for the good or service. This means that all the units of the good or service that are produced are sold, and there are no unsold units left over. Similarly, all the units of the good or service that consumers want to buy are available, and there is no shortage.
The equilibrium price is important because it determines the allocation of resources in an economy. If the price of a good or service is too high, then there will be a surplus of that good or service, which means that some producers will not be able to sell all their units. This will lead to a decline in production, and possibly even the exit of some producers from the market. On the other hand, if the price of a good or service is too low, then there will be a shortage of that good or service, which means that some consumers will not be able to buy all the units they want. This will lead to an increase in demand and possibly even an increase in the price of the good or service.
The equilibrium price is also known as the "invisible hand" in economics, because it is the price that emerges naturally in a market without any external interference or manipulation. It is determined by the forces of supply and demand, which are driven by the preferences and behavior of consumers and producers.
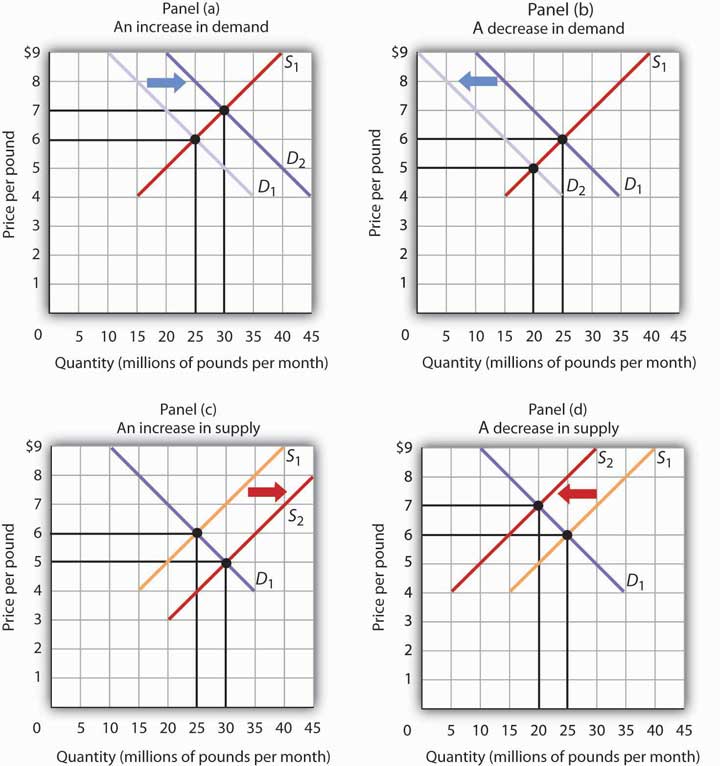
The equilibrium price can be affected by various factors, such as changes in the cost of production, changes in consumer preferences, and changes in the availability of substitutes. These factors can lead to shifts in the supply and demand curves, which in turn can cause changes in the equilibrium price.
In summary, the equilibrium price, also known as the market clearing price, is the price at which the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy is equal to the quantity that producers are willing and able to sell. It is determined by the forces of supply and demand and is important because it determines the allocation of resources in an economy.
What is Equilibrium Price and How Does it Relate to the Market?
Cause and Results Generally, when this happens, prices of these goods go down and this happens because of an oversupply of goods and services, this as result, increases the demand for these goods and services. So clearly, at the equilibrium price, both buyer and seller are in the position of no change. Looking at the graph of the So far, we have seen that consumers and producers want opposite things in terms of the price. You buy a soda because you get a utility from it, and that utility is what you are paying for. Now, we can check that at this price the demand and the supply will coincide in the quantity.
The equilibrium price is also known as the market clearing price It clears the

In theory, the amount of merchandise demanded by buyers is equal to the amount delivered by vendors at this price. When equilibrium is reached, prices will stop rising because there will be enough of the good to meet consumer needs without any shortages. This tells us that equilibrium price is a price where both the seller and the buyer are in the position of no change. To learn more about such intriguing economic and mathematics-related topics, you can check out the abundant study material available at Vedantu along with living-learning and downloadable PDFs containing all the concepts, answers for the textbook questions, important questions and much more, right here on our app and website. Equilibrium Price affects market in a number of ways: 1 It determines what goods will be produced in a given economy 2 It determines how much of each good will be produced 3 It determines what goods will be imported or exported from a given economy The Importance of Equilibrium to Consumers and Producers Equilibrium is a state of balance in the economy. Check out these related courses: Economics A Guide to Price Elasticity of Demand Ever wondered why some things never seem to go on sale? The price is set by the demand and supply of a product. A change in a nonprice determinant of demand changes the relationship between price and quantity demanded, either increasing or decreasing quantity demanded at every price.
Equilibrium Price

Yes, a supply shock does affect the equilibrium price and quantity, sometimes positively and sometimes negatively. Particularly, for any value lower than Rs 60, the quantity of supply is more than demanded, hence there is a surplus. MARKET- CLEARING PRICE: The price that exists when a market is clear of shortage and surplus, or is in equilibrium. Higher profits from selling to the British made it so the Irish and British market was at an equilibrium price that was higher than what consumers could pay, and consequently many people starved. Similarly, for any value more than Rs. The equilibrium price is the market price where the quantity of goods supplied is equal to the quantity of goods demanded. For example, the food markets in Ireland were at equilibrium during the great potato famine in the mid-1800s.