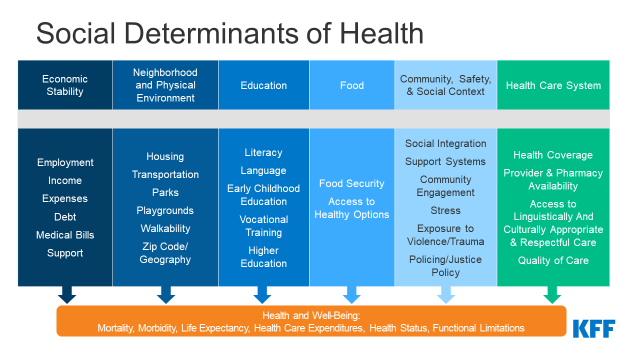
Social determinants of health are the various social, economic, and environmental factors that contribute to health outcomes and disparities in health among different populations. These factors can include access to education, employment, housing, transportation, and healthcare, as well as the social and economic policies and practices that shape these systems.
One key social determinant of health is income and wealth. People with higher income and wealth tend to have better health outcomes, due in part to their greater access to resources and opportunities that can promote good health. Conversely, people with lower income and wealth are more likely to experience poorer health outcomes due to their limited access to these resources and opportunities.
Education is another important social determinant of health. People with higher levels of education tend to have better health outcomes, as they may have greater knowledge and understanding of how to maintain good health, as well as more opportunities to access healthcare and other resources that promote health. People with lower levels of education may face barriers to accessing these resources and opportunities, leading to poorer health outcomes.
Access to healthcare is also a critical social determinant of health. People who have access to quality healthcare are more likely to receive timely and appropriate medical treatment, which can improve their health outcomes. In contrast, people who lack access to healthcare may not receive the care they need, leading to worsening health outcomes.
Housing is another important social determinant of health. People who live in safe, affordable, and stable housing are more likely to have better health outcomes than those who live in overcrowded, unhealthy, or unstable housing. Housing conditions can affect health through various pathways, such as by influencing exposure to environmental toxins, promoting or hindering physical activity, and impacting mental health.
Transportation is also a social determinant of health, as it can affect a person's ability to access healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. People who have access to reliable and affordable transportation are more likely to have better health outcomes, as they can more easily access the resources and opportunities that promote health.
In addition to these individual-level social determinants of health, there are also structural and systemic factors that can influence health outcomes and disparities. These can include social and economic policies and practices, such as employment and labor laws, welfare policies, and tax policies, as well as cultural and societal norms and values.
Understanding and addressing the social determinants of health is crucial for promoting health equity and improving the health of all populations. This can involve efforts to address income and wealth inequality, improve access to education and healthcare, address housing and transportation issues, and reform policies and practices that contribute to health disparities. By addressing the social determinants of health, we can create a more equitable and healthy society for all.