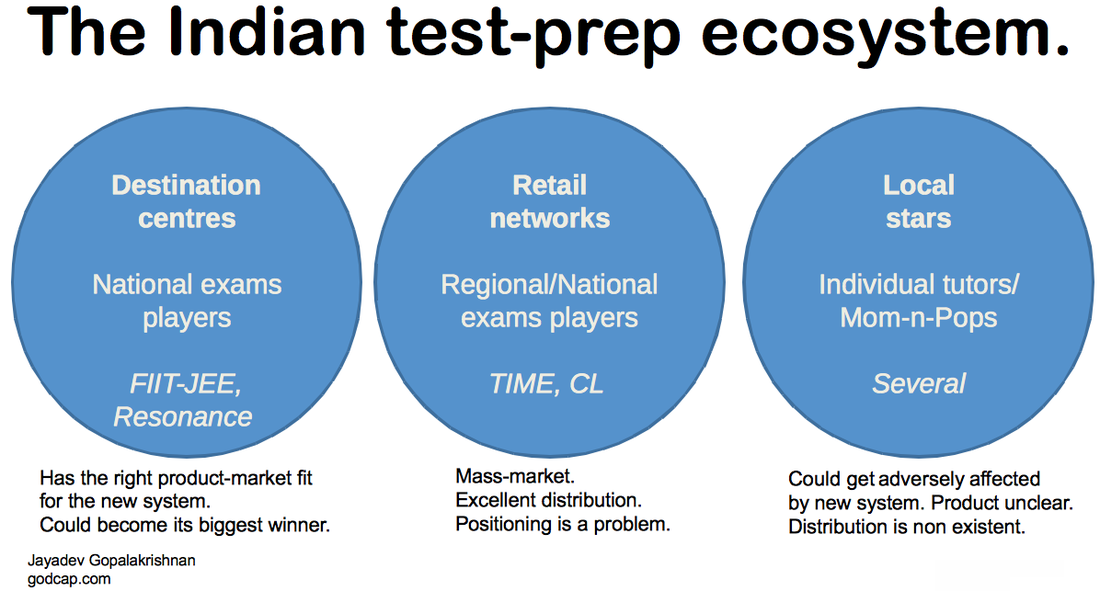
The examination system in India plays a crucial role in determining the future of students. It is a process through which students' knowledge, skills, and abilities are evaluated. The examination system in India is a blend of traditional and modern methods, and it has evolved significantly over the years.
In India, the examination system starts at the school level, where students appear for annual or semester exams. These exams are conducted by the school itself or by external agencies such as the state board or the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). The exams at the school level are generally subjective and aim to assess the overall development of the students.
After completing school, students can choose to pursue higher education, which is either vocational or academic. Vocational courses are job-oriented and offer practical training in a particular field, while academic courses are theoretical and focus on in-depth knowledge of a subject. The examination system for higher education is conducted by universities, and the exams are usually objective in nature.
In India, the most prestigious exam for higher education is the Joint Entrance Exam (JEE), which is conducted for admission to engineering colleges. The JEE is a national-level exam that is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA) and is considered to be one of the toughest exams in the country. Other exams for higher education include the Common Admission Test (CAT) for management courses and the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) for medical courses.
The examination system in India has its fair share of criticism, with students and educators pointing out various issues. One of the main criticisms is the focus on rote learning, where students are expected to memorize large amounts of information without fully understanding the concepts. This approach is believed to stifle creativity and critical thinking skills.
Another issue with the examination system in India is the pressure it puts on students. The fear of failure and the desire to succeed can lead to anxiety and stress among students, which can have negative impacts on their mental health.
To address these issues, there have been various reforms proposed for the examination system in India. One of the proposed reforms is the adoption of continuous and comprehensive evaluation (CCE), which aims to assess students on a continuous basis rather than just through a single exam. This approach is believed to reduce the reliance on rote learning and encourage the development of critical thinking skills.
In conclusion, the examination system in India plays a crucial role in the education of students and has evolved significantly over the years. While it has its fair share of criticism, reforms such as the adoption of CCE may help address some of the issues faced by the system.