The second generation of computers, also known as the transistor era, was a significant milestone in the development of modern computing. These computers were much faster, smaller, and more reliable than their first-generation counterparts, which relied on vacuum tubes for processing.
One example of a second-generation computer is the IBM 1401, which was introduced in 1959. The 1401 was designed for business applications and was widely used in banks, insurance companies, and other organizations for tasks such as payroll processing, accounts payable, and inventory control.
One of the key features of the 1401 was its use of transistors instead of vacuum tubes. Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify and switch electronic signals, making them more reliable and efficient than vacuum tubes. The 1401 also used punched cards for input and output, which was a common method of data storage at the time.
Another example of a second-generation computer is the Univac 1108, which was introduced in 1964. The 1108 was a mainframe computer that was used by large organizations for tasks such as scientific and engineering research, data processing, and business applications.
Like the IBM 1401, the Univac 1108 used transistors and punched cards for input and output. It also had a larger memory capacity than the 1401, with a maximum of 64K words of main memory. The 1108 was also notable for its use of magnetic tape for data storage, which was faster and more reliable than punched cards.
In summary, the second generation of computers, represented by the IBM 1401 and Univac 1108, marked a significant step forward in the development of modern computing. These computers were faster, smaller, and more reliable than their first-generation counterparts, and laid the foundation for the subsequent development of the personal computer and the Internet.
What is the second generation of computer example?

It had hardware that could perform double-precision floating-point arithmetic. This development of computers can be classified into generations of computers according to their features, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and the hardware they are equipped with. Second Generation Computer The transistor is a semiconductor device used to regulate current or more output signals to input signals. A low cost B reduced heat dissipation problem C low weight D All of the above Solution: The correct option is D, i. They are designed and developed for specific tasks and operations. The transistors were highly reliable and easier to handle and maintain than the vacuum tubes. As compared to the vacuum tube, the transistor was far better through which made possible computers to become more reliable, smaller in size, faster in speed, more energy-efficient, and cheaper comparing to the first generation of computers.
Second Generation of Computers

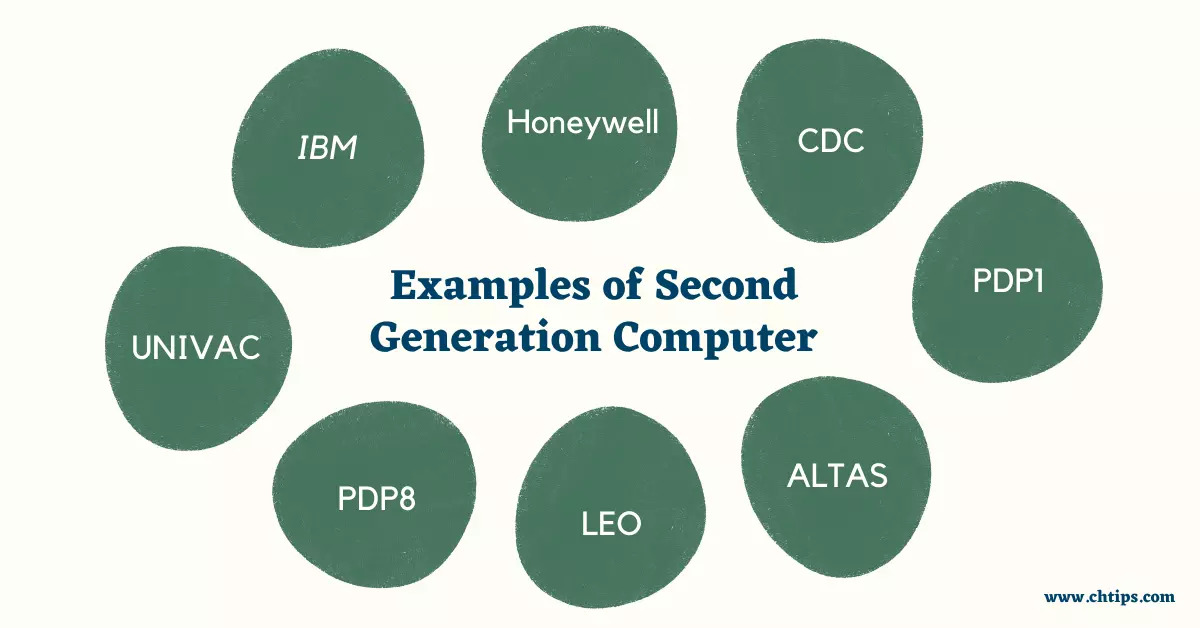
Some second generation of computers are IBM 1920, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, IBM 1401, etc. The speed of second-generation computers was far better than first-generation computers due to the use of transistors, which was far better, advanced, and enhanced than their counterparts. These second 2nd generations of computer systems use high-level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN. All of these different types of 2nd generation computers are important and can be very helpful in a variety of ways. I was hoping you could share this article with your friends and colleagues; this motivates me to write more on the related topics.
Top 10 Characteristics and Features of Second Generation Computer System In Points
I was curious to find out how you center yourself and clear your head prior to writing. The ENIAC was invented by J. What were used in second generation of computer? Introduction In this article, I will discuss and explain the basic Characteristics and Features of Second Generation Computer System in Points with advantages, speed, types, explanation with examples and images. Features of the Second Generation of Computers As the computers made in the second generation used transistors that made them more reliable, smaller in size, faster in speed, more energy-efficient, and cheaper compared to the first generation of computers. In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic tape and magnetic disks as secondary storage devices. Transistors Used in Computers; IBM 7000 Series IBM 7090, 1959 The IBM 7000 series was developed throughout the 1950s and early 1960s.