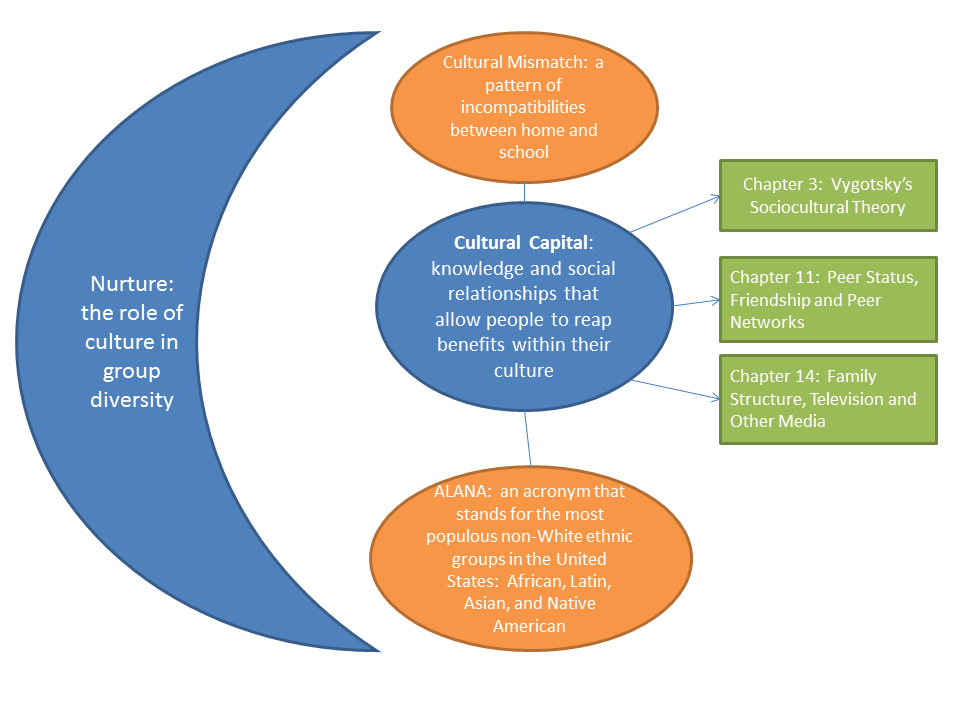
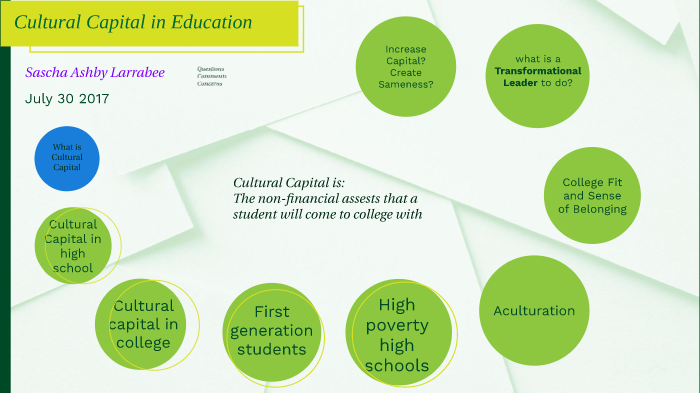
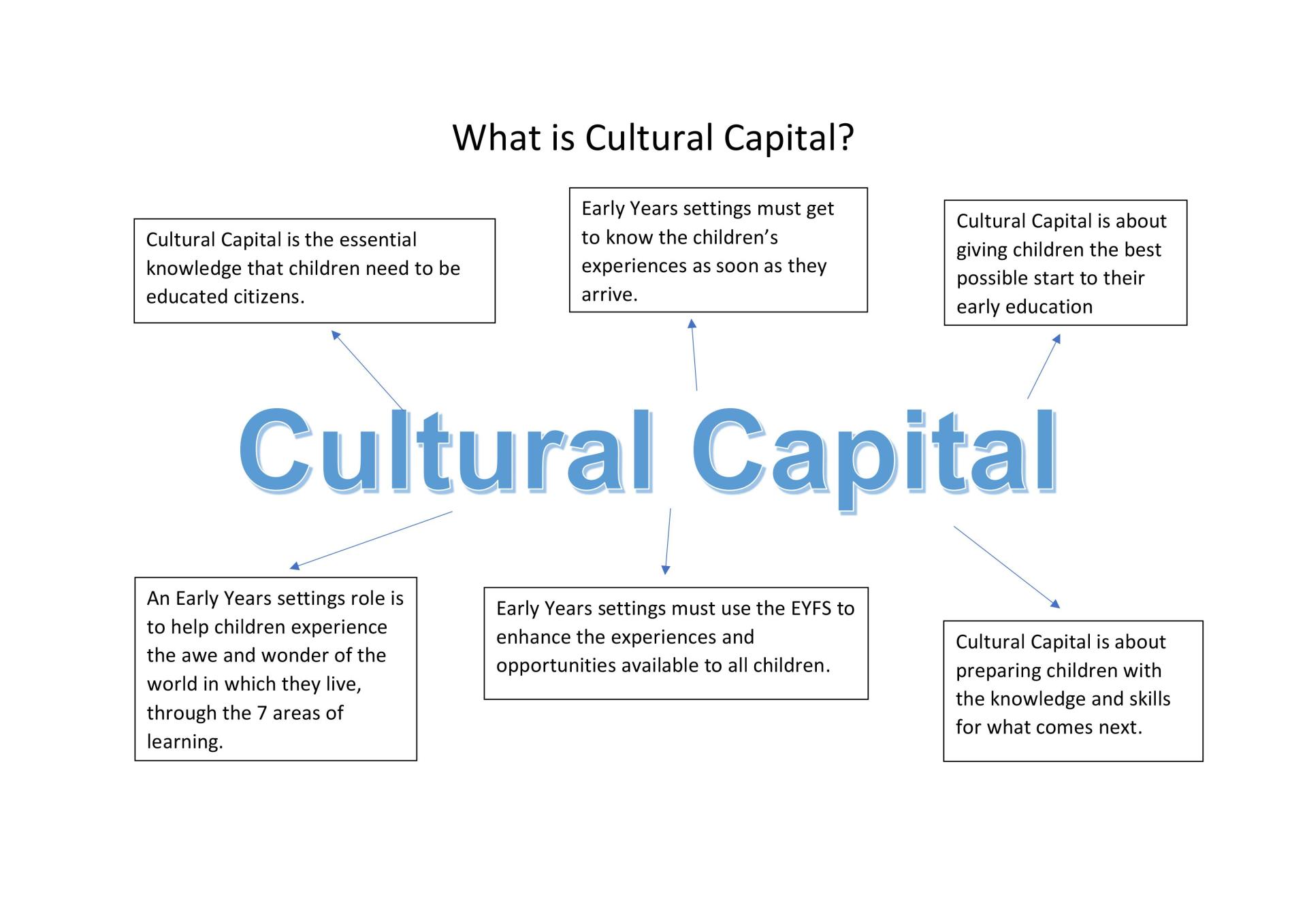
Cultural capital refers to the knowledge, skills, education, and other cultural assets that individuals possess and that give them a certain social status or advantage. In the context of education, cultural capital can manifest in a variety of ways and can have a significant impact on academic success and opportunities.
One example of cultural capital in education is the importance of language proficiency. Students who speak a language other than English at home may have an advantage in certain subjects, such as foreign language classes, where they already have a foundation in the language being taught. Similarly, students who are proficient in English may have an advantage in language arts and literature classes, as they are able to understand and analyze texts more easily.
Another example of cultural capital in education is the value placed on extracurricular activities, such as music or sports. Students who have the resources to participate in these activities may have an advantage in college admissions or job applications, as they can demonstrate skills and experiences that may not be reflected in their academic record. In addition, students who have access to extracurricular activities may have the opportunity to develop valuable skills and relationships that can benefit them in their future endeavors.
A third example of cultural capital in education is the importance of having a supportive and resource-rich home environment. Students who have parents who are highly educated, involved in their education, and able to provide resources such as books, computers, and tutoring may have an advantage over their peers who do not have the same level of support at home.
Finally, cultural capital can also manifest in the form of access to higher education. Students who come from families with a history of attending college may be more likely to attend college themselves, as they may have role models and support systems in place to help them navigate the process. In contrast, students who come from families with no college-going tradition may face more barriers to higher education and may be less likely to pursue it.
In conclusion, cultural capital plays a significant role in education, as it can impact a student's language proficiency, extracurricular opportunities, home environment, and access to higher education. Understanding and addressing the ways in which cultural capital influences education can help to create a more equitable and inclusive educational system.