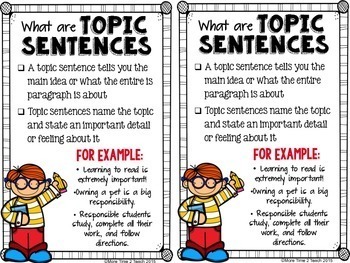
A paragraph is a group of related sentences that focus on a single main idea or topic. Paragraphs are an essential part of any written work, as they help to organize and structure the content in a logical and coherent manner. They also help the reader to understand the main points of the text by breaking it up into manageable chunks of information.
There are several different types of paragraphs that students may encounter when writing, and it is important to understand how to construct each type effectively. Here are some examples of paragraphs that students may come across:
- Narrative paragraphs: These paragraphs are used to tell a story or describe an event or experience. They often begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, and then use specific details and examples to support and develop that idea. For example:
"It was a hot summer day when I decided to go for a swim in the lake. I had always been a strong swimmer, but as I dove into the cool water, I suddenly felt a tug on my leg. Panic set in as I realized I was caught in a strong current and being pulled out to sea. I tried to swim against the current, but it was too strong. Just as I was about to give up, I felt a hand grab onto my arm and pull me to safety. It was my best friend, who had followed me into the water and risked his own life to save mine."
- Descriptive paragraphs: These paragraphs are used to describe something in detail, using sensory language and vivid imagery to help the reader visualize and understand the subject. For example:
"The old oak tree stood tall and proud in the center of the park, its gnarled branches reaching out like gnarled fingers. Its leaves rustled in the gentle breeze, and its trunk was deeply grooved and scarred from years of weathering. As I sat beneath its shade, I felt a sense of peace and tranquility wash over me, as if the tree was a living, breathing entity that had stood witness to countless stories and memories."
- Expository paragraphs: These paragraphs are used to explain or inform the reader about a particular topic. They often begin with a topic sentence that states the main idea, and then use supporting sentences to provide more information and examples. For example:
"The Civil War was a significant event in American history that lasted from 1861 to 1865. It was fought between the Northern states, which were against slavery, and the Southern states, which were in favor of it. The war resulted in the deaths of over 600,000 soldiers and civilians, and had a lasting impact on the country's political, social, and economic landscape. It was a turning point in the nation's history, as it marked the end of slavery and the beginning of the Reconstruction Era."
- Persuasive paragraphs: These paragraphs are used to argue a particular point or persuade the reader to adopt a certain perspective. They often include strong language and persuasive techniques, such as rhetorical questions, emotional appeals, and logical arguments. For example:
"We should all be required to recycle in order to reduce waste and protect the environment. Recycling helps to conserve natural resources, such as water and timber, and reduces the amount of pollution and greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. It is a simple yet effective way to make a positive impact on the world, and it is our responsibility to do our part. So next time you throw something away, think about whether it can be recycled instead. Together, we can make a difference."
In conclusion, paragraphs are an important element of any written work, and it is essential for students to understand how to construct them effectively. By using the different types of paragraphs