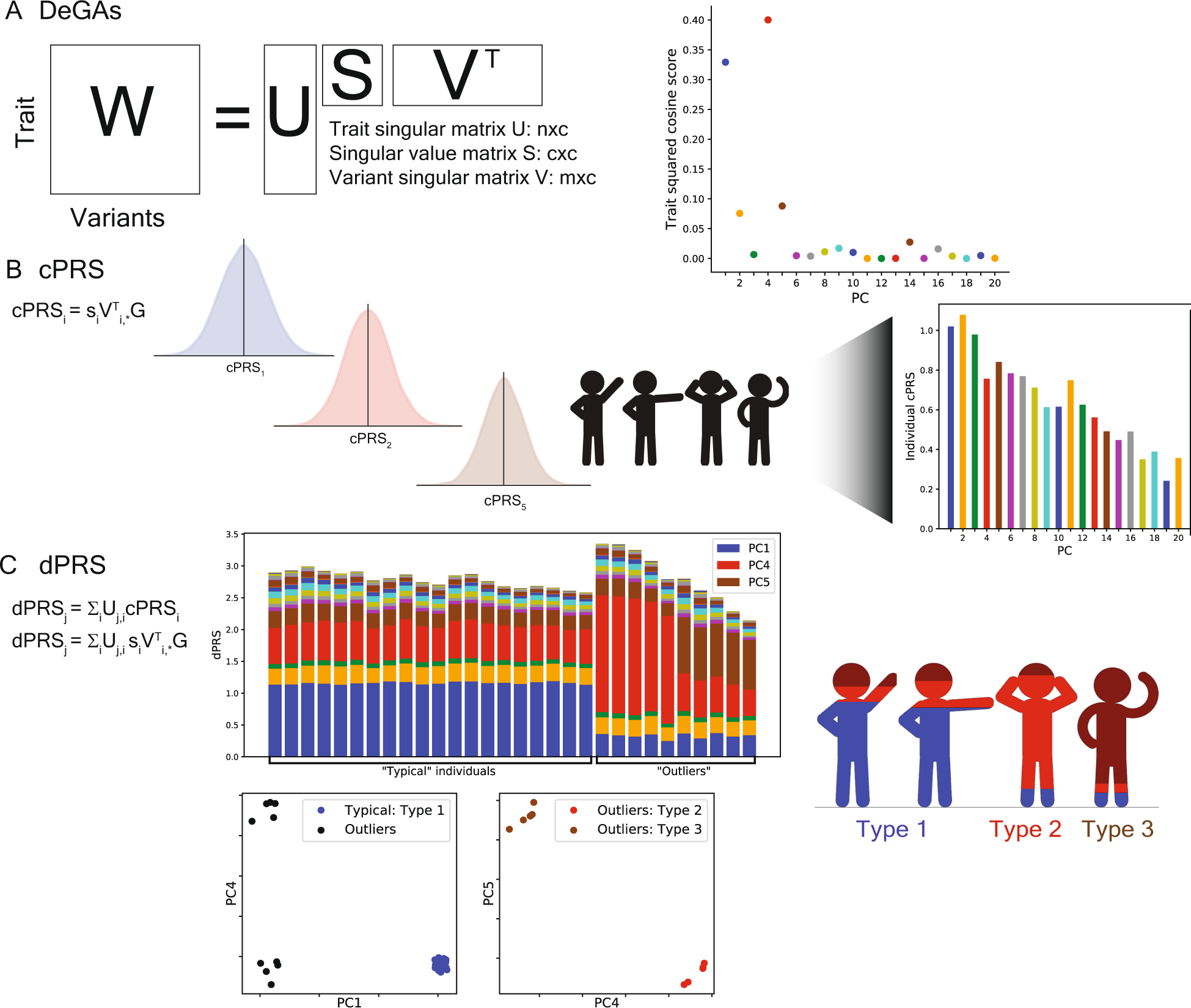
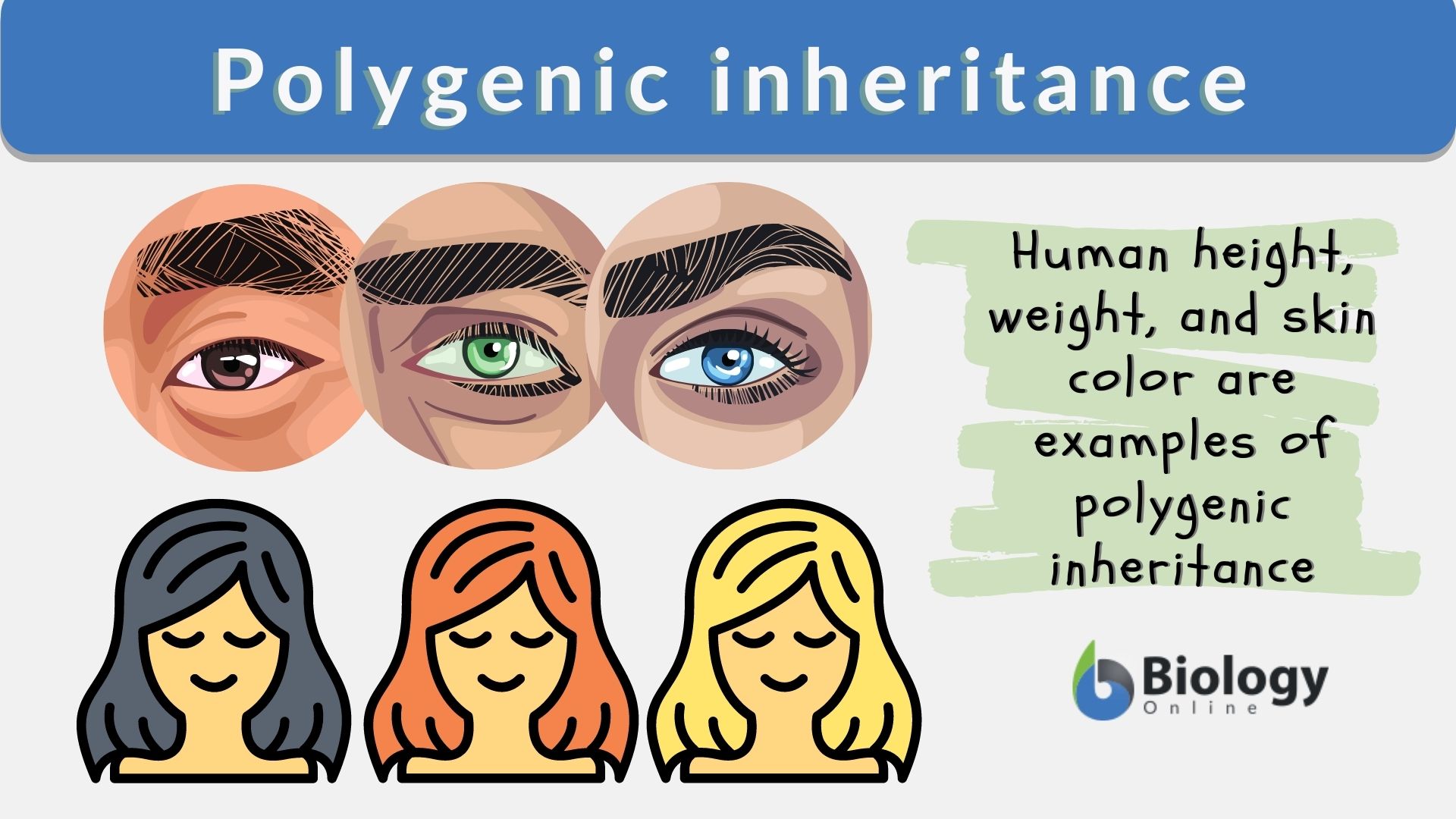
Polygenic traits are traits that are determined by the combined effect of multiple genes. These traits are often continuous, meaning that they can vary in degree rather than being present or absent, and are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Examples of polygenic traits in humans include height, weight, eye color, skin color, and intelligence.
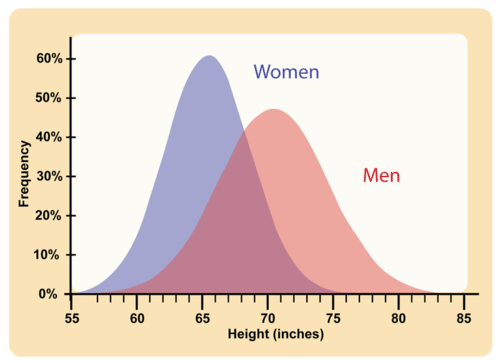
Height is a classic example of a polygenic trait in humans. While genetics play a significant role in determining an individual's height, other factors such as nutrition, hormonal balance, and environmental conditions also contribute to this trait. A person's height is determined by the combined effect of many different genes, each of which may have a small or large impact on the trait.
Weight is another polygenic trait that is influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. While genetics can influence an individual's propensity to gain or lose weight, other factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress also play a role in determining a person's weight.
Eye color is another example of a polygenic trait in humans. While genetics play a significant role in determining eye color, environmental factors such as exposure to sunlight can also affect this trait. Eye color can range from blue to green to brown and is determined by the presence and amount of pigment in the iris of the eye.
Skin color is another polygenic trait in humans. While genetics play a significant role in determining skin color, environmental factors such as sunlight exposure and diet can also affect this trait. Skin color can range from very pale to very dark and is determined by the presence and amount of pigment in the skin.
Intelligence is a highly complex trait that is influenced by multiple genetic and environmental factors. While genetics play a role in determining an individual's intellectual abilities, other factors such as education, nutrition, and social environment can also influence intelligence.
In conclusion, polygenic traits are traits that are determined by the combined effect of multiple genes and are often influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Examples of polygenic traits in humans include height, weight, eye color, skin color, and intelligence.