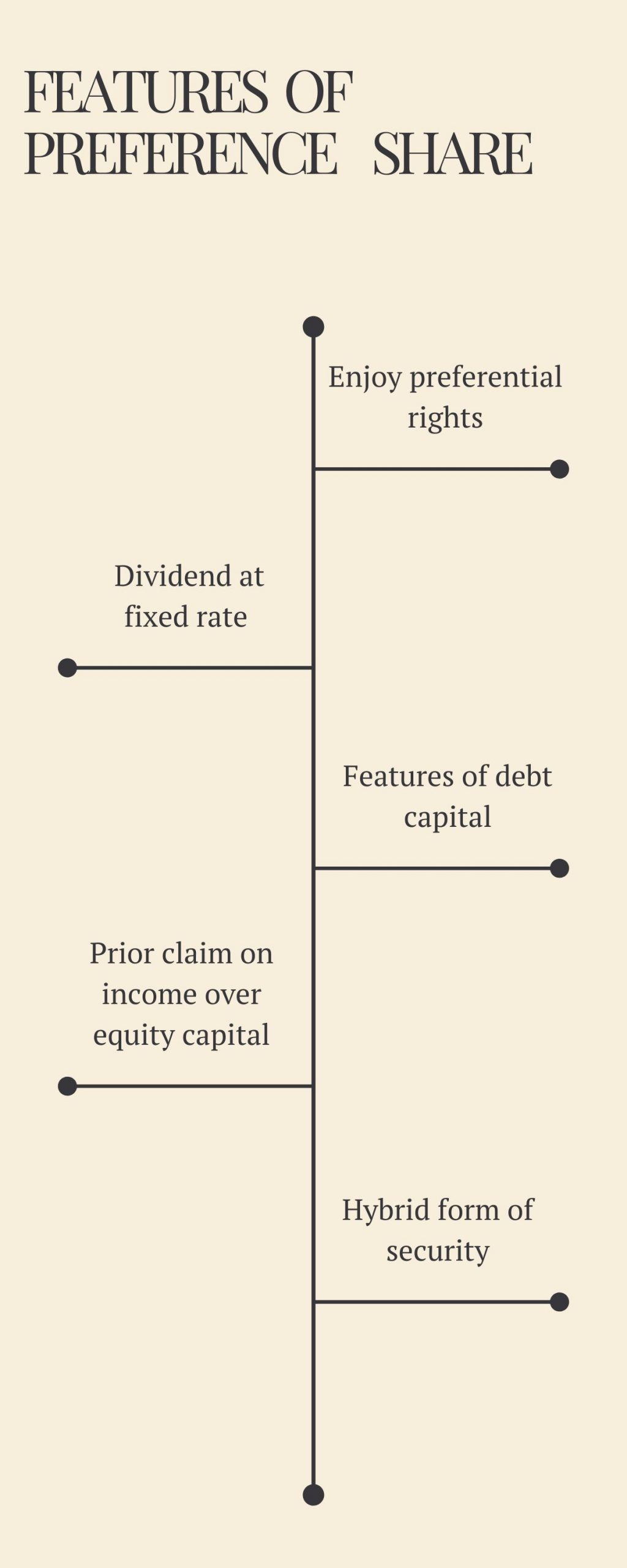
Preference shares, also known as preferred stock, are a type of equity security that represents ownership in a company. They are called "preference shares" because they have a higher claim on the company's assets and earnings than common stock. Preference shareholders are entitled to receive a fixed dividend before common shareholders receive any dividends, and they also have priority over common shareholders in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation.
There are several different types of preference shares, including:
Cumulative preference shares: These shares entitle the holder to receive any unpaid dividends from previous years before common shareholders receive any dividends.
Non-cumulative preference shares: These shares do not entitle the holder to receive unpaid dividends from previous years.
Participating preference shares: These shares entitle the holder to receive a fixed dividend as well as a share of any excess profits.
Convertible preference shares: These shares can be converted into common stock at the holder's discretion.
Redeemable preference shares: These shares can be bought back by the company at a predetermined price.
Preference shares differ from common shares in several key ways. First, preference shareholders are entitled to a fixed dividend, while the dividends paid to common shareholders can vary. Preference shareholders also have priority over common shareholders in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation, which means they will receive their share of the company's assets before common shareholders. Finally, preference shares do not usually have voting rights, whereas common shareholders are entitled to vote on important company decisions.
Overall, preference shares offer investors a way to participate in the ownership of a company while also providing a fixed income. They are often used by companies to raise capital and can be an attractive option for investors who are seeking a stable return on their investment.
Preference shares, also known as preferred stock or preference shares, are a type of equity security that represents ownership in a company. Unlike common shares, which represent ownership in a company and entitle the holder to vote at shareholder meetings and receive dividends, preference shares do not typically come with voting rights and have a fixed dividend rate.
Preference shares have a priority claim on a company's assets and earnings over common shares. This means that in the event of bankruptcy or liquidation, preference shareholders are entitled to receive their dividends and any remaining assets before common shareholders. This makes preference shares a safer investment compared to common shares, which have a lower claim on a company's assets and are more subject to market fluctuations.
Preference shares can be either cumulative or non-cumulative. Cumulative preference shares entitle the holder to receive any missed dividends before common shareholders receive any dividends. Non-cumulative preference shares do not have this feature and the holder is only entitled to receive the current dividend.
Preference shares can also be either participating or non-participating. Participating preference shares entitle the holder to a share of the company's profits above the fixed dividend rate. Non-participating preference shares do not have this feature and the holder is only entitled to the fixed dividend rate.
There are several advantages to investing in preference shares. One of the main advantages is the fixed dividend rate, which provides a steady stream of income for the investor. Preference shares are also a less risky investment compared to common shares, as they have a higher claim on a company's assets and earnings. Additionally, preference shares are often less sensitive to market fluctuations compared to common shares, which makes them a good option for investors looking for a more stable investment.
On the other hand, there are also some drawbacks to investing in preference shares. One of the main drawbacks is that preference shareholders do not have voting rights, which means they have less control over the company's operations and decision-making processes. Additionally, preference shareholders may not receive any dividends if the company is not performing well, which can be a risk for investors.
In summary, preference shares are a type of equity security that represent ownership in a company and provide the holder with a fixed dividend rate and a priority claim on the company's assets and earnings. While they offer some advantages over common shares, such as a fixed dividend rate and a lower risk of loss, they also come with some drawbacks, such as the lack of voting rights and the potential for missed dividends in the event of poor company performance.