The Beer-Lambert law, also known as the Beer-Lambert-Bouguer law or the Beer's law, is a fundamental principle in the field of spectrophotometry. It describes the relationship between the absorbance of a solution and the concentration of the absorbing species within it. The law is named after the German physicist August Beer and the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Lambert, who independently developed it in the early 19th century.
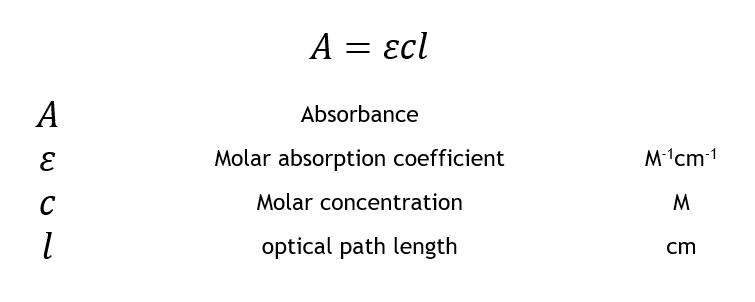
The Beer-Lambert law states that the absorbance of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species and the path length of the light through the solution. This can be expressed mathematically as:
A = εcl
Where A is the absorbance of the solution, ε is the molar absorptivity of the absorbing species, c is the concentration of the absorbing species, and l is the path length of the light through the solution.
The molar absorptivity (ε) is a constant that is specific to each chemical species and is dependent on the nature of the chemical bonds within the molecule. It is typically determined experimentally by measuring the absorbance of a series of known concentrations of the species.
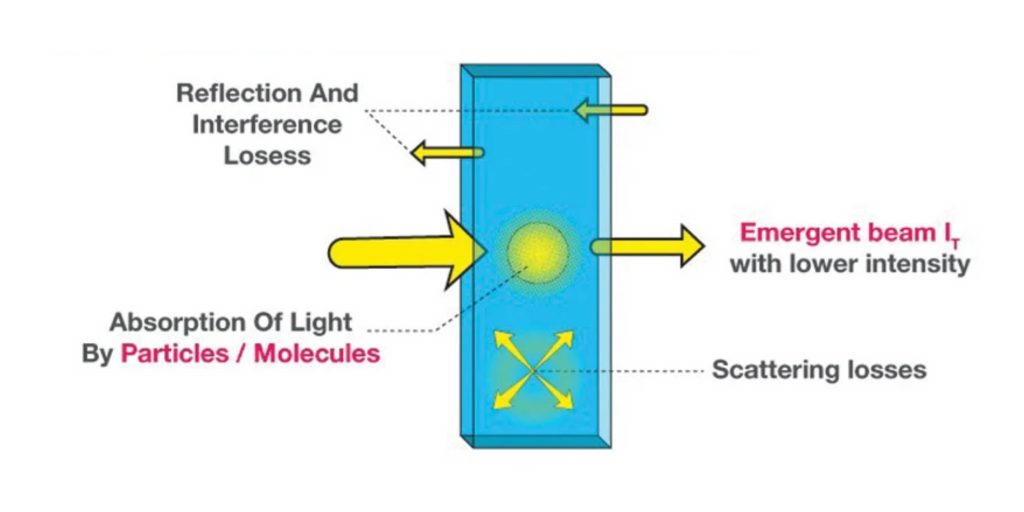
The Beer-Lambert law is an important tool in analytical chemistry, as it allows for the determination of the concentration of an absorbing species in a solution. This is commonly done using a spectrophotometer, which is a device that measures the intensity of light as it passes through a solution. By measuring the absorbance of the solution at a specific wavelength, the concentration of the absorbing species can be calculated using the Beer-Lambert law.
There are several assumptions that are made in the application of the Beer-Lambert law. One assumption is that the absorbing species is present in the solution in a dissolved state, rather than in a suspended or precipitated form. Another assumption is that the absorption is due to the presence of a single absorbing species, rather than multiple species. Additionally, the law assumes that the absorption is homogeneous throughout the solution, meaning that the absorption is the same at all points within the solution.
Despite these assumptions, the Beer-Lambert law is widely used in a variety of applications, including the analysis of food and drink, environmental samples, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in the fields of biology and medicine, where it is used to measure the concentration of substances such as proteins and enzymes in biological fluids.
Overall, the Beer-Lambert law is a fundamental principle in spectrophotometry that allows for the determination of the concentration of an absorbing species in a solution. Its wide range of applications makes it an important tool in a variety of fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.