Classical economics and Keynesian economics are two different schools of thought that have influenced the development of modern economic theory. Classical economists believe in the power of the market to regulate itself, while Keynesian economists believe in the role of government intervention in regulating the economy. Both viewpoints have their own set of assumptions, principles, and policies that shape their perspectives on economic issues.
Classical economics is based on the belief that free markets and individual self-interest will lead to economic prosperity. This school of thought is rooted in the belief that the economy is inherently stable and that supply and demand will naturally balance each other out. Classical economists believe in laissez-faire policies, which advocate for minimal government intervention in the economy and a reliance on market forces to drive economic growth.
According to classical economics, prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand in a competitive market. When there is a surplus of a particular good or service, the price will fall as sellers compete to unload their excess supply. Conversely, when there is a shortage of a good or service, the price will rise as buyers compete to purchase the limited supply. Classical economists believe that this price mechanism will lead to an efficient allocation of resources and promote economic growth.
Classical economists also believe in the concept of Say's Law, which states that supply creates its own demand. In other words, the production of goods and services generates income and consumption, which drives economic growth. Classical economists argue that government intervention in the economy can disrupt the natural balance of supply and demand and lead to inefficiencies and economic instability.
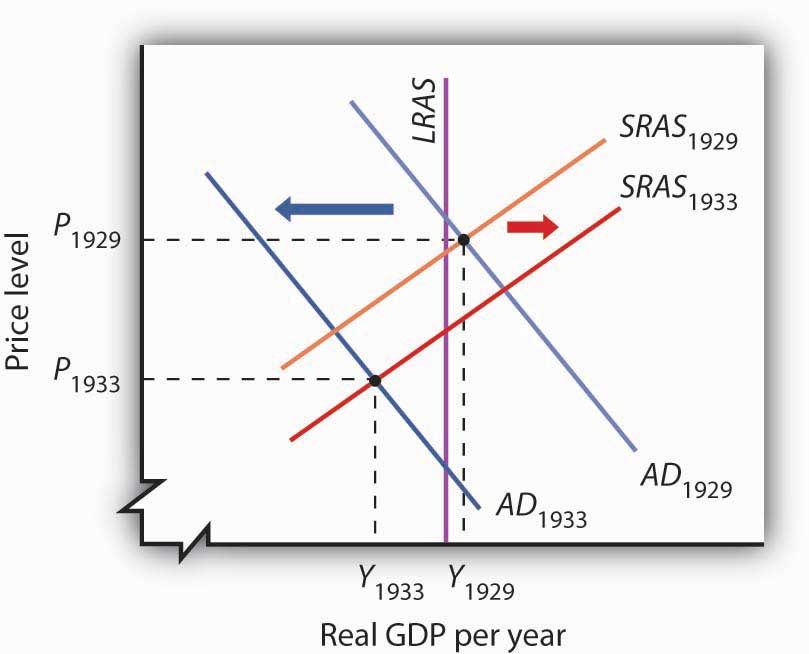
Keynesian economics, on the other hand, is based on the idea that the economy is prone to instability and that government intervention is necessary to promote economic growth and stability. This school of thought was developed by economist John Maynard Keynes in response to the Great Depression of the 1930s, which was characterized by high unemployment, low economic growth, and deflation.
According to Keynesian economics, the level of economic activity is determined by the level of aggregate demand, which is the total amount of goods and services that households, businesses, and the government are willing to buy. Keynesian economists argue that when aggregate demand is low, firms will produce less and unemployment will rise. In order to stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment, Keynesian economists advocate for government intervention in the form of fiscal policy, which refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence the level of aggregate demand.
Keynesian economists also argue that prices are not always flexible and that there may be times when the market is unable to adjust to changes in supply and demand. This can lead to economic stagnation, as firms are unable to sell their products and consumers are unable to buy them. In these situations, Keynesian economists believe that the government can step in and use fiscal policy to stimulate demand and increase economic activity.
In summary, classical economics and Keynesian economics are two different schools of thought that have shaped the development of modern economic theory. Classical economists believe in the power of the market to regulate itself and advocate for minimal government intervention, while Keynesian economists believe in the role of government intervention in promoting economic growth and stability. Both viewpoints have their own set of assumptions, principles, and policies that shape their perspectives on economic issues.


.jpg)