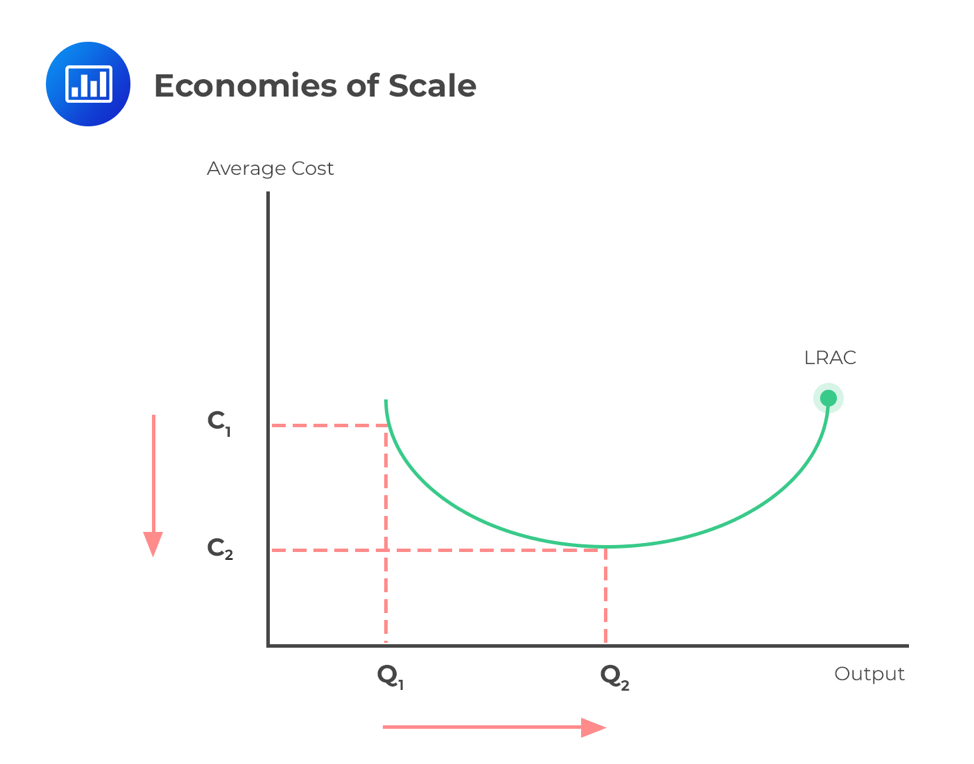
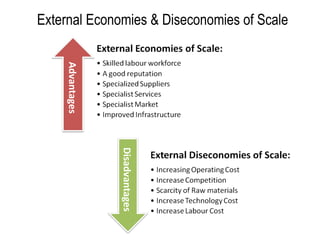
External diseconomies of scale refer to the negative externalities or costs that are imposed on society as a result of a firm or industry becoming too large. These costs can occur in various forms and can have significant negative impacts on both the economy and society as a whole. In this essay, we will explore the causes and consequences of external diseconomies of scale and discuss ways in which they can be addressed.
There are several potential causes of external diseconomies of scale. One common cause is the negative impact on the environment. As a firm or industry grows, it may generate more pollution or waste, which can have negative effects on the environment and public health. For example, a large manufacturing plant may release toxic chemicals into the air or water, which can harm wildlife and people living nearby.
Another cause of external diseconomies of scale is the negative impact on small businesses and local communities. As a large firm or industry grows, it may have an advantage over smaller competitors due to its size and economies of scale. This can lead to small businesses being pushed out of the market, which can have negative consequences for the local economy and community.
Another potential cause of external diseconomies of scale is the negative impact on wages and working conditions. As a firm or industry becomes larger, it may have more bargaining power and be able to negotiate lower wages and worse working conditions for its employees. This can lead to income inequality and a decline in living standards for workers.
There are several consequences of external diseconomies of scale that can have significant negative impacts on the economy and society as a whole. One consequence is the decline in competition and innovation. If a large firm or industry is able to push out smaller competitors, there may be less competition in the market, which can lead to higher prices and less innovation.
Another consequence is the decline in local economies and communities. If small businesses are pushed out of the market due to the growth of a large firm or industry, it can have negative effects on the local economy and community, as small businesses often play a vital role in these areas.
Finally, external diseconomies of scale can lead to income inequality and a decline in living standards for workers. If a large firm or industry is able to negotiate lower wages and worse working conditions for its employees, it can lead to a decline in living standards for workers and contribute to income inequality.
There are several ways in which external diseconomies of scale can be addressed. One way is through the use of regulatory policies and laws that limit the negative externalities of large firms and industries. For example, governments can implement environmental regulations that limit pollution and waste, or they can implement competition policies that promote a level playing field for small businesses.
Another way to address external diseconomies of scale is through the use of taxes and subsidies. Governments can use taxes to discourage negative behaviors, such as pollution, and they can use subsidies to encourage positive behaviors, such as the development of renewable energy sources.
Finally, external diseconomies of scale can be addressed through the use of social and environmental standards. Governments and businesses can adopt social and environmental standards that set minimum standards for the treatment of workers, the environment, and other stakeholders.
In conclusion, external diseconomies of scale are negative externalities or costs that are imposed on society as a result of a firm or industry becoming too large. These costs can occur in various forms and can have significant negative impacts on both the economy and society as a whole. There are several ways in which external diseconomies of scale can be addressed, including through regulatory policies, taxes and subsidies, and social and environmental standards.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Economies-of-scale-c65a2c76b28247f48ec7bb763f3245b0.jpg)