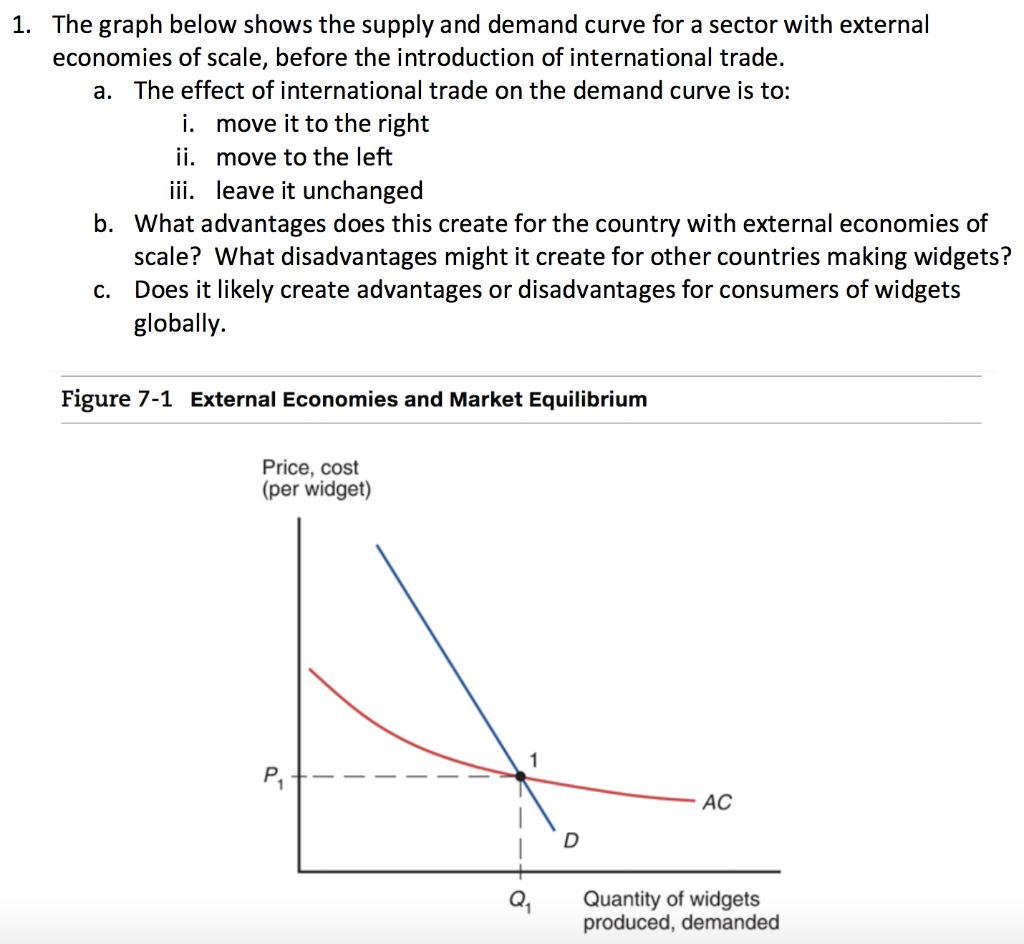
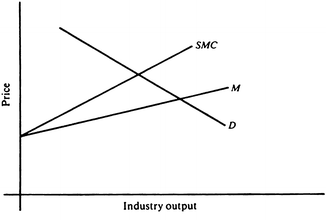
External economies refer to the economic benefits that accrue to a firm or industry as a result of external factors, rather than the firm's own actions. These benefits can take the form of lower production costs, increased efficiency, or access to new markets and resources. External economies can be classified into two main categories: internal and external.
Internal external economies refer to the benefits that a firm or industry derives from being located in close proximity to other firms or industries that are part of the same production process. For example, a firm that produces car parts may benefit from being located near an automobile assembly plant, as it allows the firm to reduce its transportation costs and increase its efficiency by taking advantage of the assembly plant's specialized equipment and skilled labor.
External external economies, on the other hand, refer to the benefits that a firm or industry derives from being located in an area with a well-developed infrastructure, such as transportation networks, utilities, and skilled labor. For example, a firm that produces software may benefit from being located in a city with a strong tech industry, as it allows the firm to access a pool of skilled labor and to take advantage of the city's well-developed transportation and communication networks.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of external economies. One important factor is the presence of specialized inputs, such as raw materials or specialized labor, that are necessary for the production of a particular good or service. The availability of these inputs can make it more attractive for firms to locate in an area, as it reduces their production costs and increases their efficiency.
Another important factor is the presence of complementary industries, which are industries that produce goods or services that are used as inputs in the production of other goods or services. For example, the automobile industry and the rubber industry are complementary, as the automobile industry uses rubber to produce tires. The presence of complementary industries can make it more attractive for firms to locate in an area, as it allows them to take advantage of economies of scale and to specialize in a particular production process.
External economies can have significant economic effects, as they can lead to the development of clusters of firms or industries that are concentrated in a particular geographic area. These clusters can drive economic growth and innovation, as they allow firms to take advantage of the specialized inputs and complementary industries that are available in the area.
However, external economies can also have negative effects, as they can lead to the concentration of economic activity in a particular area, which can result in regional imbalances in economic development. In addition, external economies can also lead to the development of market power, as firms that are located in an area with strong external economies may be able to charge higher prices for their products due to their increased efficiency and lower production costs.
In conclusion, external economies refer to the economic benefits that accrue to a firm or industry as a result of external factors, such as the availability of specialized inputs or the presence of complementary industries. These benefits can drive economic growth and innovation, but they can also lead to regional imbalances and the concentration of economic activity.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/economies-of-scale-3305926-FINAL-5bc4bf7ac9e77c00528fcecf.png)