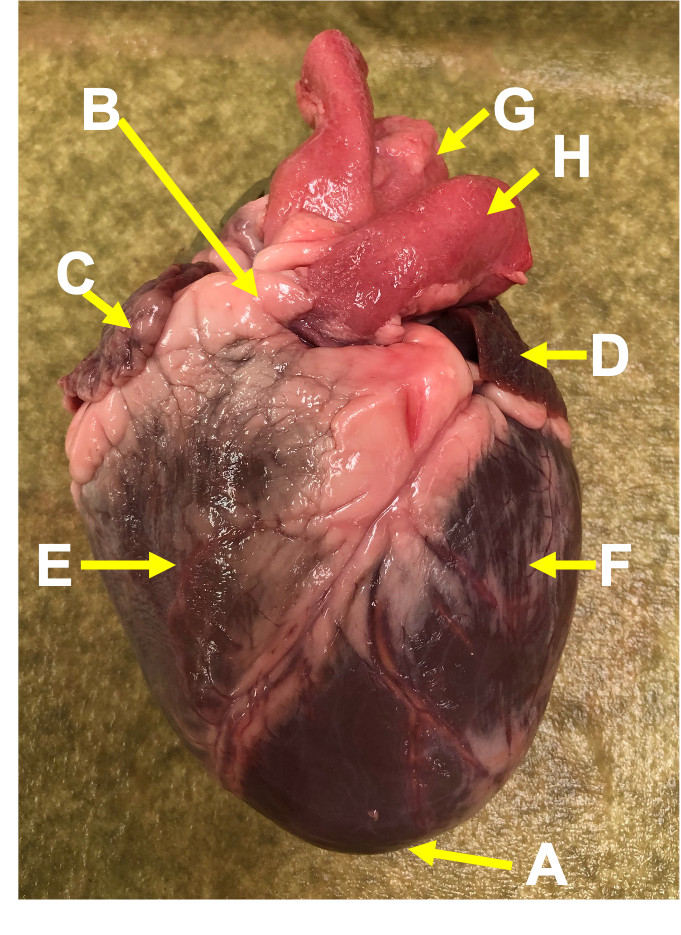
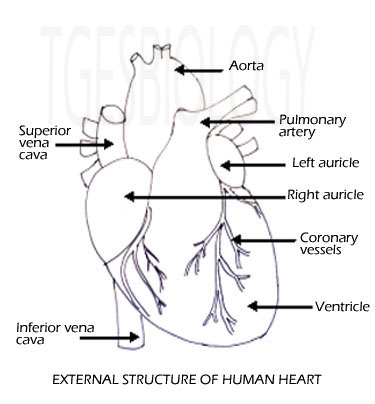
The human heart is a complex and vital organ that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, and is protected by the ribcage. The heart is divided into four chambers: the left and right atria, and the left and right ventricles. The atria are the upper chambers of the heart, while the ventricles are the lower chambers.
The heart has a unique external structure that helps it to function effectively. The outer layer of the heart is known as the epicardium, which is a thin layer of tissue that covers the surface of the heart. The middle layer of the heart is known as the myocardium, which is a thick layer of muscle tissue that is responsible for contracting and relaxing to pump blood through the heart. The inner layer of the heart is known as the endocardium, which is a thin layer of tissue that lines the inside of the heart and helps to prevent damage to the heart muscle.
The heart is also surrounded by a network of blood vessels, including the aorta, the vena cava, and the pulmonary artery and vein. These blood vessels transport oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to and from the heart, respectively.
The heart has a unique system of electrical conduction that helps to coordinate the contraction of the heart muscle. This system includes the sinoatrial (SA) node, the atrioventricular (AV) node, and the Purkinje fibers. The SA node is located in the right atrium and acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, sending electrical impulses that stimulate the contraction of the heart muscle. The AV node is located in the interatrial septum and helps to coordinate the contraction of the atria and ventricles. The Purkinje fibers are located in the ventricles and help to transmit the electrical impulses throughout the heart muscle.
In summary, the human heart has a complex external structure that is essential for its function. It is made up of three layers of tissue, is surrounded by a network of blood vessels, and has a unique system of electrical conduction. All of these components work together to ensure that the heart is able to pump blood efficiently and effectively throughout the body.