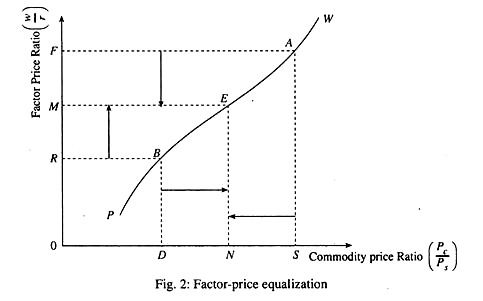
The factor price equalization theorem is a theory in economics that suggests that, under certain conditions, the price of a particular factor of production (such as labor or capital) will tend to be equalized across different countries. This means that, for example, the wage rate for a particular type of labor will tend to be similar across countries, even if the cost of living or other economic conditions differ significantly.
The idea behind the factor price equalization theorem is that international trade can lead to a convergence of prices for factors of production. This occurs because, as countries trade with each other, they can specialize in the production of certain goods or services and import other goods or services that they do not produce. This specialization can lead to a more efficient allocation of resources, which can in turn lead to lower prices for the goods and services that are being traded.
One of the key assumptions underlying the factor price equalization theorem is that there are no barriers to international trade. This means that countries are able to freely exchange goods and services with each other, and that there are no tariffs, quotas, or other barriers that would limit the flow of trade. In addition, the theorem assumes that there are no significant differences in the productivity of the factors of production between countries. For example, if the productivity of labor is significantly higher in one country compared to another, this could lead to differences in wage rates between the two countries, despite the presence of international trade.
Another important assumption of the factor price equalization theorem is that there are no transport costs associated with international trade. In other words, it is assumed that it is just as easy and cost-effective to ship goods and services between countries as it is to produce them within a single country. This assumption allows for a more efficient allocation of resources and helps to ensure that prices are equalized across countries.
There are a number of factors that can impact the degree to which the factor price equalization theorem holds true in the real world. For example, if there are barriers to international trade or significant differences in productivity between countries, this could lead to differences in prices for factors of production. In addition, transport costs and other logistical issues can also impact the equalization of prices across countries.
Overall, the factor price equalization theorem is an important theory in economics that helps to explain how international trade can lead to the convergence of prices for factors of production. While there are a number of factors that can impact the degree to which this theorem holds true in the real world, it remains an important concept for understanding the impact of international trade on economic conditions around the world.