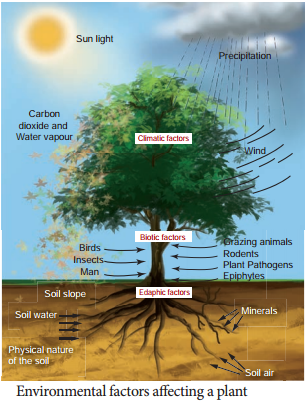
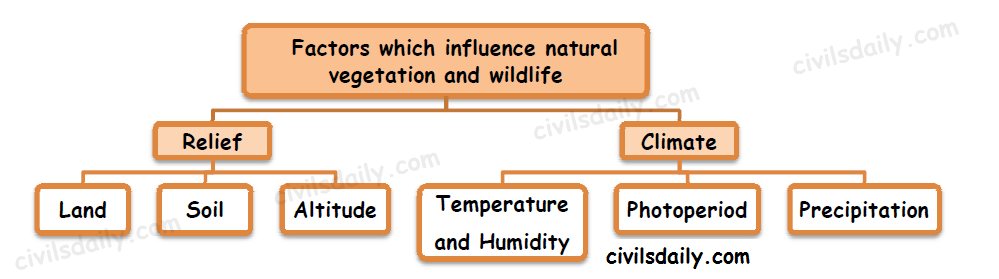
Vegetation is the plant life that grows in a particular area. It is a crucial component of ecosystems, as it provides habitat and food for animals, helps to regulate the climate, and plays a vital role in the water cycle. There are many factors that can affect the type and abundance of vegetation in an area, including climate, soil, topography, and human activities.
Climate is perhaps the most important factor influencing vegetation. Different types of plants are adapted to thrive in specific climatic conditions, such as certain temperature ranges, levels of rainfall, and patterns of sunlight. For example, tropical rainforests are characterized by high humidity, warm temperatures, and heavy rainfall, and are home to a diverse array of plant species, including towering trees, vines, and epiphytes. In contrast, deserts are characterized by low humidity, high temperatures, and little rainfall, and support plant species that are adapted to conserve water, such as cacti and succulents.
Soil is another important factor that affects vegetation. Different types of soil support different types of plants, due to differences in pH, nutrient availability, and structure. For example, plants that grow in acidic soils, such as pines and hemlocks, require different nutrients than plants that grow in alkaline soils, such as aspens and cottonwoods. In addition, soil structure and texture can affect the ability of plants to root and absorb water and nutrients.
Topography, or the physical features of the land, also plays a role in determining the type and abundance of vegetation in an area. Slopes and elevations can affect the amount of sunlight and moisture an area receives, which can in turn affect the types of plants that can grow there. For example, plants that grow on steep slopes may have deep roots to anchor them in place and prevent erosion, while plants that grow at high elevations may be adapted to withstand colder temperatures and less sunlight.
Human activities can also have a significant impact on vegetation. Land use practices, such as agriculture, urbanization, and logging, can alter the natural habitat of plants and disrupt ecological balances. Pollution, including air and water pollution, can also harm plant life and reduce biodiversity. Climate change, caused by the burning of fossil fuels and other human activities, is also having a major impact on vegetation worldwide, as rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affect the ability of plants to thrive.
In conclusion, vegetation is affected by a variety of factors, including climate, soil, topography, and human activities. Understanding these factors is important for preserving and protecting plant life, as well as for managing and utilizing the resources provided by vegetation.