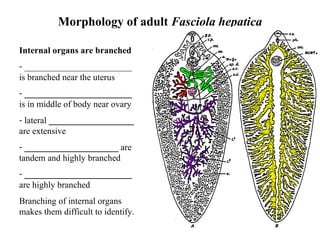
Fasciola hepatica, also known as the liver fluke, is a parasitic flatworm that infects the liver of mammals, including humans. It is a member of the class Trematoda, which includes all parasitic flatworms. The adult F. hepatica is small, measuring about 0.5 to 1.5 inches in length and 0.2 to 0.4 inches in width. It has a flat, elongated body with a triangular shape and a rounded anterior end. The body is covered in a tough, protective cuticle that is made up of chitin and other structural proteins.
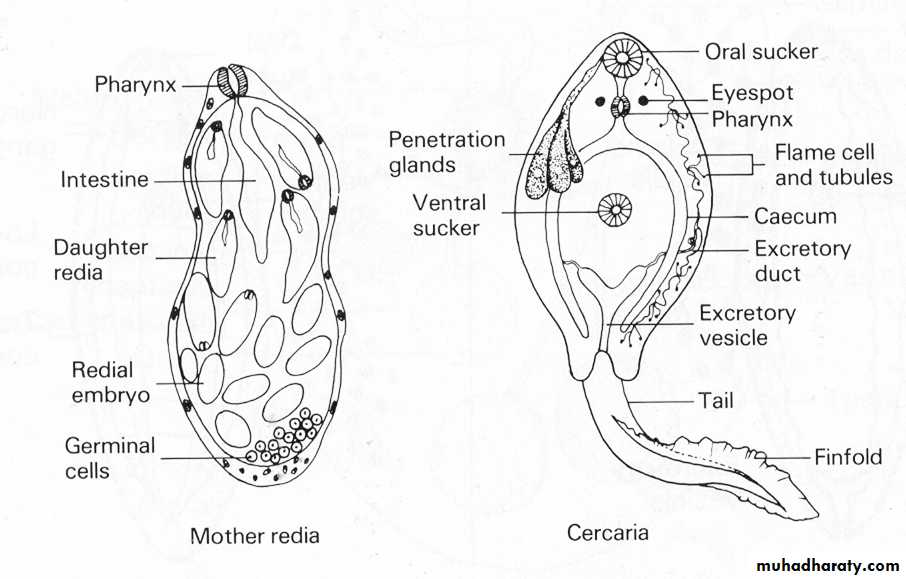
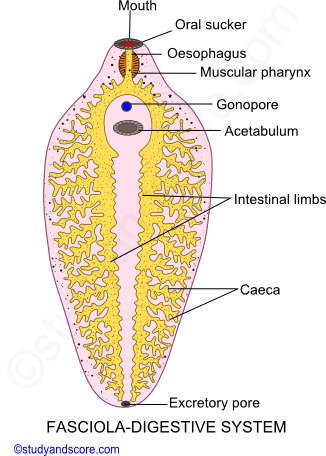
The digestive system of F. hepatica consists of a simple tubular gut with a mouth and an anus. The mouth is located on the ventral surface of the anterior end, and it is surrounded by a muscular pharynx that helps the fluke to attach to the host's intestinal wall. The anus is located on the posterior end of the body, and it is used to excrete waste products.
F. hepatica has a simple nervous system consisting of a small brain and a pair of ganglia, which are clusters of nerve cells. The brain is located at the anterior end of the body, and it controls the fluke's basic functions such as movement and feeding. The ganglia are located near the pharynx and control the pharynx's muscle movements.
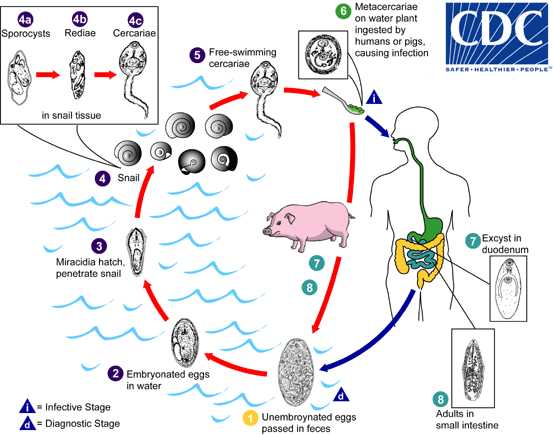
F. hepatica reproduces sexually, with both male and female flukes present in the same host. The female fluke lays eggs that are passed out of the host in the feces. The eggs hatch into ciliated larvae called miracidia, which swim through water and seek out suitable snail hosts. Inside the snail, the miracidia develop into sporocysts, which then produce cercariae. The cercariae are released from the snail and swim through water until they find a suitable host, such as a cow or a sheep. Once inside the host, the cercariae burrow into the liver and transform into adult flukes.
In conclusion, F. hepatica is a small, flatworm that infects the liver of mammals and reproduces sexually. It has a simple anatomy, with a tubular gut, a small brain, and a pair of ganglia. The fluke's body is covered in a tough cuticle, and it has a mouth and an anus for feeding and excretion. Understanding the morphology of F. hepatica is important for understanding its life cycle and developing effective control and treatment measures.