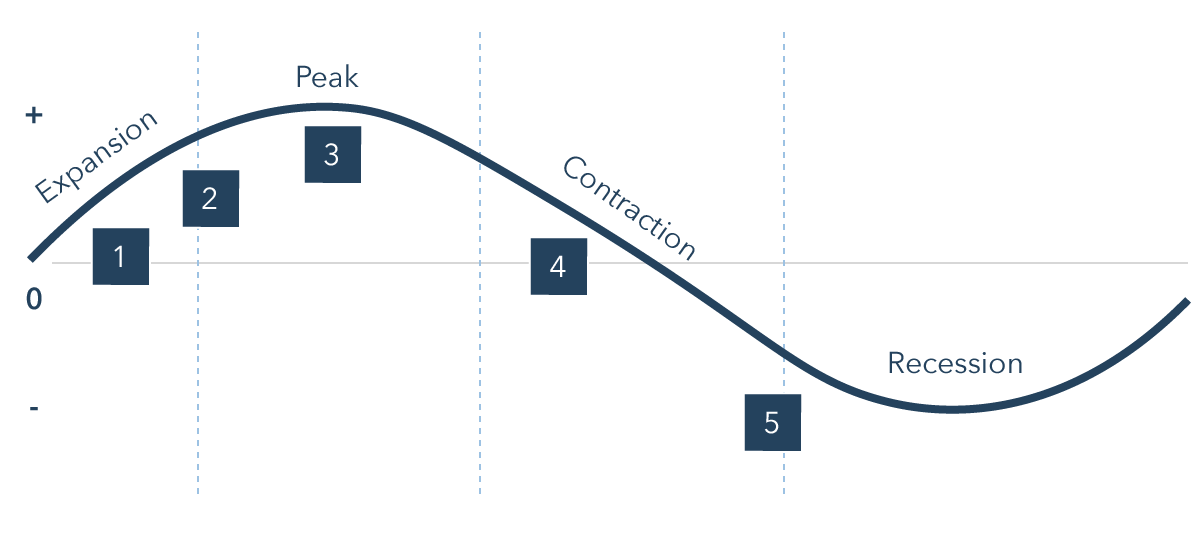
An economic recession is a period of economic downturn, during which an economy experiences negative growth in GDP (gross domestic product) for two or more consecutive quarters. It is characterized by declining economic activity, high unemployment, and declining consumer and business confidence.
One of the most prominent features of an economic recession is a decline in economic activity. This can manifest itself in various ways, such as a decrease in consumer spending, a decrease in business investment, and a decline in exports. As economic activity slows down, businesses may struggle to generate profits, leading to layoffs and an increase in unemployment.
Another feature of an economic recession is a decline in consumer and business confidence. When people and businesses are uncertain about the future, they are less likely to make large purchases or investments. This can further fuel the decline in economic activity, as businesses struggle to sell their products and services and consumers cut back on their spending.
A third feature of an economic recession is a decline in asset prices, such as stocks and real estate. When economic activity slows down, businesses may struggle to generate profits, leading to a decline in stock prices. Similarly, a decline in consumer spending can lead to a decrease in real estate values.
In addition to these economic effects, recessions can also have social and political consequences. High unemployment can lead to social unrest and political instability, as people struggle to make ends meet. Governments may also be forced to implement austerity measures in an effort to reduce their budget deficits, which can further negatively impact the economy.
Overall, economic recessions are characterized by declining economic activity, high unemployment, and declining consumer and business confidence. They can have significant negative consequences for individuals, businesses, and societies, and can take years to fully recover from.
Features of Recession

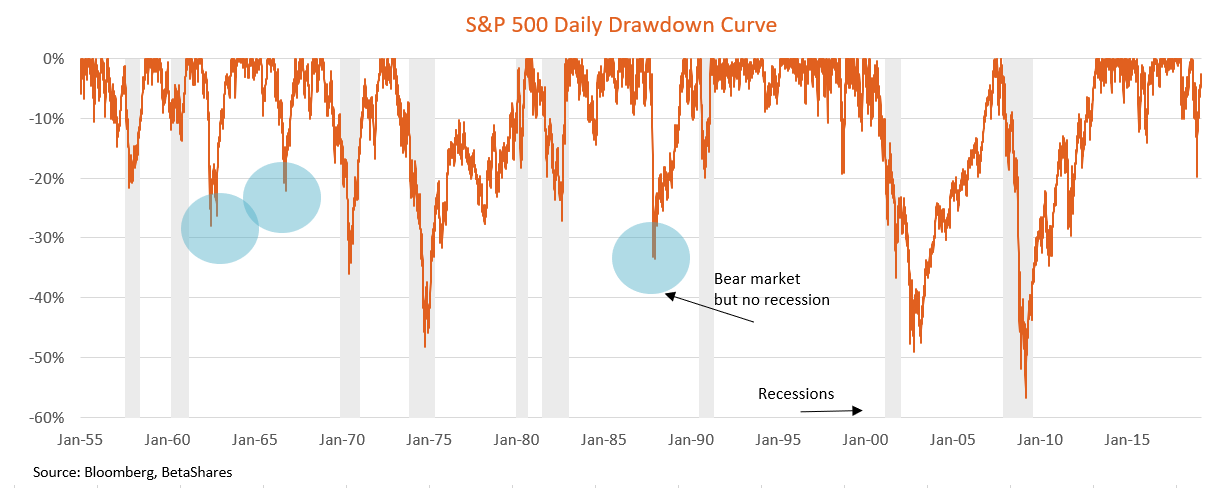
They come around, on average, once every six or seven years. But sometimes the economy feels like it was hit by an asteroid, such as in the Great Recession of 2008. But recessions come in many shapes and sizes. In the second week of October, a massive stock market crash wiped out the savings of millions of Americans. When the Asset Bubble Explodes Market Bubble An asset bubble occurs when the price of an item such as gold, stocks, or housing soars beyond its sustainable value. Thus, rising unemployment may not be seen early in the economic downturn.
Recession Primer, Part Two: Features of a Recession

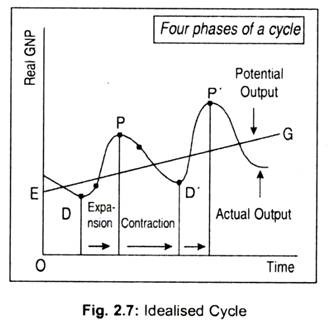
Lesson Summary A recession is a decline of economic activity, more specifically, a decline in gross domestic product GDP for two or more consecutive quarters. Depending on political orientation by current government, the worsening public balance becomes at the forefront of attention and restrictive fiscal policies worsen the crisis. As a result, interest rates rose. Although this was not as sharp a rise as occurred in previous recessions, it drove inflation higher and contributed to a fall in GDP growth. The actual gap between recessions can be as little as a year, or it can be a decade or more. All Answers ltd, 'Characteristics Of Recession And Financial Crisis Economics Essay' UKEssays.
U.S. Economic Recessions: Causes, Impacts & History
Beyond its duration, the Great Recession was notably a Economic Crisis in Europe: The European economy is in the midst of the deepest recession since the 1930s, with real GDP projected to shrink by some 4% in 2009, the sharpest contraction in the history of the European Union. Instead, the prevalence of high inflation rate and a high unemployment rate makes the situation worse. Recession The economy slows down, and the level of sales and production orders start declining. The private mortgage market is practically nonexistent; 96-97% of mortgages are flowing through Fannie and Freddie now. This is when goods and services are difficult to sell when consumers' purchasing power is reduced. So the latter is a more pronounced degree of recession , in which the economy tends not to slow down, but to paralysis or, worse, collapse.
Features of economic recession pdf
This resulted in low real wages which meant lower savings and a decline in the investment of the country. The Fed funds rate rose to 19% in January 1981, slipped to 15% in March, then rose back to 19% by June. Production facilities become underutilized, and companies respond by reducing the work rate. The background to this recession was the war that started in September 1980, when the oil-producing state Iraq invaded its oil-producing neighbor, the newly established Islamic state of Iran. Leading Economic Indicators: Definition, Examples, Index The Treasury yield curve is the most important indicator for the average person. However, interest rates continued to rise: The Fed funds rate touched 17. The virus variant spreads faster than the previous BA2.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/recession-df34d60052364265828adb59917f12a8.png)
