Fetal membranes. The Placenta and Fetal Membranes 2022-12-08
Fetal membranes
Rating:
4,6/10
1570
reviews
Fetal membranes are structures that enclose and protect the developing fetus during pregnancy. These membranes are essential for the proper development and growth of the fetus, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the pregnancy. There are three main fetal membranes: the amnion, the chorion, and the placenta.
The amnion is a thin, transparent membrane that surrounds the fetus and is filled with amniotic fluid. The amniotic fluid acts as a cushion for the fetus, protecting it from injury and allowing it to move freely within the uterus. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus and maintains a constant environment for the developing baby. The amnion is continuous with the chorion, which is the outermost fetal membrane.
The chorion is a thicker membrane that encloses the amnion and the fetus. It is made up of cells from both the mother and the fetus, and it plays a vital role in the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. The chorion is also responsible for producing hormones that help to maintain the pregnancy.
The placenta is a complex organ that is formed during pregnancy and is responsible for exchanging nutrients, oxygen, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. It is attached to the inner wall of the uterus and is connected to the fetus by the umbilical cord. The placenta is made up of cells from both the mother and the fetus, and it is essential for the proper development and growth of the fetus.
In conclusion, the fetal membranes are essential for the proper development and growth of the fetus during pregnancy. They protect the fetus, maintain a constant environment, and facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the mother and the fetus. Understanding the structure and function of these membranes is crucial for the proper care and management of pregnant women and their developing fetuses.
Retained Fetal Membranes in Cows
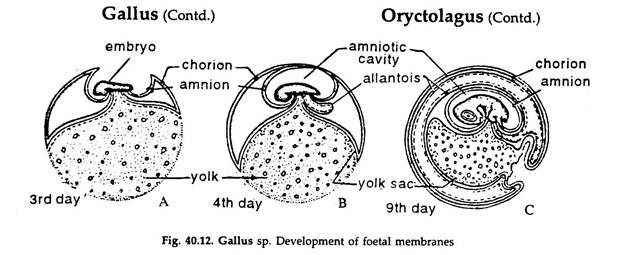
The other fetal membranes are the allantois and the secondary umbilical vesicle. The first membranes to form are the amnion and the yolk sac. It involves your doctor sweeping their gloved finger between the thin membranes of the amniotic sac in your uterus. The remains of the vitelline duct and yolk-sac may be sometimes observed beneath the amnion, close to the cord, the former as an attenuated thread, the latter as a minute sac. One subset of interstitial trophoblasts penetrates the walls of uterine spiral arteries and veins intramural trophoblast , finally reaching the vessel lumen endovascular trophoblast endoglandular trophoblast multinucleated trophoblast giant cells Fig. The trophoblast cells that start to invade maternal tissues are termed extravillous trophoblast. Ectoderm, blue; mesoderm, red; entoderm and notochord, black.
Next
The Role of the Fetal Membranes in Pregnancy and Birth
What is placenta and membranes? Around day 20—21 post conception, vascularization development of new vessels from haemangioblastic precursor cells within the villous mesenchyme gives rise to the formation of the first placental vessels tertiary villi. The variable flow pattern in humans has been termed multivillous flow Summary box 2. Separation of the Placenta. The pregnant uterus, showing the thickened mucous membrane and the altered condition of the uterine glands. This cavity is roofed in by a single stratum of flattened, ectodermal cells, the amniotic ectoderm, and its floor consists of the prismatic ectoderm of the embryonic disk—the continuity between the roof and floor being established at the margin of the embryonic disk. By the fifth month of pregnancy the decidua capsularis has practically disappeared, while during the succeeding months the decidua vera also undergoes atrophy, owing to the increased pressure.
Next
What is the membrane covering a fetus?
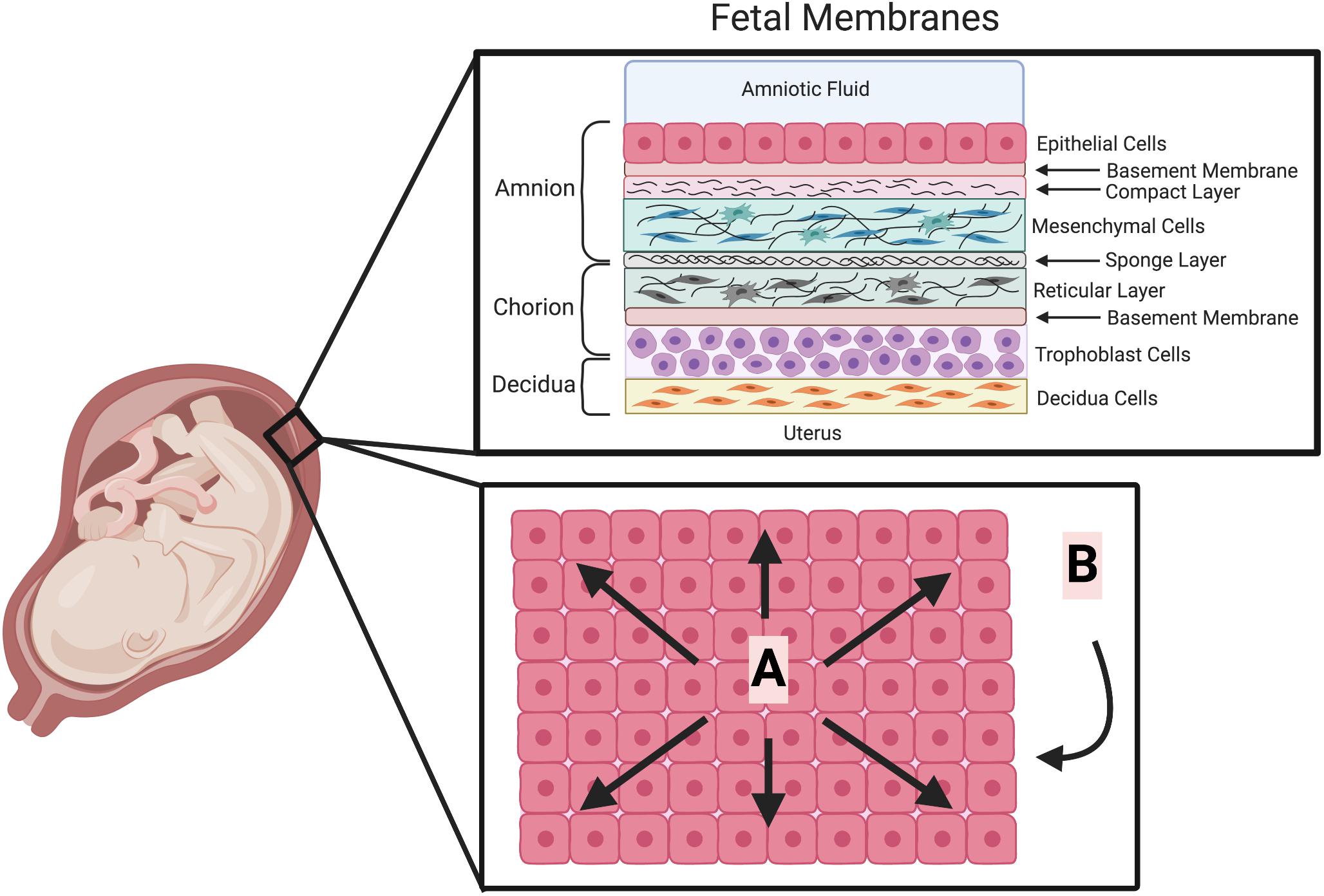
Its average thickness is about 3 cm. The placental membrane is where the exchange of substances happens between mother and fetus. At the end of this stage, at day 12 post conception, the process of implantation is completed. After the membrane sweep, you typically go home and wait for labor to start, usually within the next couple days. Although much is known about the histological structure, cellular composition and functional properties of the fetal membranes in normal and pathological pregnancies, the mechanisms that maintain the phenotype supporting pregnancy and cause the transition to a state promoting birth at the accurate time are poorly understood. The innermost layer is the amnion membrane, which is in contact with the amniotic fluid and maintains the structural integrity of the gestational sac by its mechanical strength. The amnion is the innermost membrane that encloses the embryo.
Next
Point of Care

Early villous stage Very early in pregnancy, specific types of villi develop as the forerunners of the placental villous tissues seen later in pregnancy primary villi. What is the fetal membrane called? The two chorioamniotic membranes are the amnion and the chorion, which make up the amniotic sac that surrounds and protects the fetus. Does Medicare cover amniotic membrane? The goal is not to break the water but to stimulate the prostaglandins in the uterus to trigger labor contractions. Oxygen is taken from, and carbonic acid is given up to the atmosphere through the egg-shell, while nutritive materials are at the same time absorbed by the blood from the yolk. The placenta is usually attached near the fundus uteri, and more frequently on the posterior than on the anterior wall of the uterus. Trophoblastic cell columns During penetration of the syncytial trabeculae, the cytotrophoblasts reach the maternal decidual tissues while the subsequently penetrating mesenchymal cells do not infiltrate to the tips of the trabeculae cell columns Fig. Outside the amniotic ectoderm is a thin layer of mesoderm, which is continuous with that of the somatopleure and is connected by the body-stalk with the mesodermal lining of the chorion.
Next
Placenta and Fetal Membranes Flashcards

What is the inner membrane of an embryo? The diverticulum is lined by entoderm and covered by mesoderm, and in the latter are carried the allantoic or umbilical vessels. Incidence is lower in beef cows than in dairy cows. The amniotic sac protects the fetus from injury and helps to regulate his temperature. Seen through the latter, the chorion presents a mottled appearance, consisting of gray, purple, or yellowish areas. From the interstitital trophoblast all other subtypes of extravillous trophoblast develop. On the outer side, the amniotic sac is connected to the yolk sac, the allantois, and via the umbilical cord, the placenta. Remove all the contents from the ROM Plus foil pouch.
Next
The Placenta and Fetal Membranes
The fetal membranes, sometimes called extraembryonic membranes, are tissues that form in the uterus during the first few weeks of development and develop along with the growing embryo. Nevertheless, the fetal blood is able to absorb, through the walls of the villi, oxygen and nutritive materials from the maternal blood, and give up to the latter its waste products. NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. The amnion is in contact with the amniotic fluid and ensures structural integrity of the sac due to its mechanical strength. In favor of the view that the placenta possesses certain selective powers may be mentioned the fact that glucose is more plentiful in the maternal than in the fetal blood. Fetal membranes consist of three layers: the amnion and the chorion, issued from fetal tissues and the decidua issued from maternal tissue.
Next
Fetal membranes
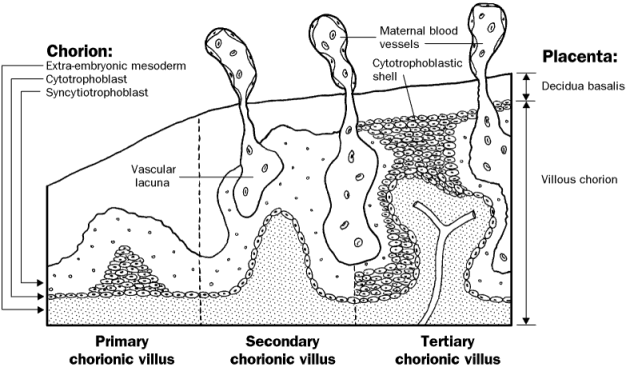
In this way the allantoic circulation, which is of the utmost importance in connection with the respiration and nutrition of the chick, is established. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review. The developing embryo is completely surrounded by the growing placenta, which at that stage consists of the two fundamental subtypes of the trophoblast. The interglandular tissue is also increased in quantity, and is crowded with large round, oval, or polygonal cells, termed decidual cells. Coincidently with the growth of the embryo, the decidua capsularis is thinned and extended Fig.
Next
Development of the fetal membranes

It is composed of fetal and maternal portions. It undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic villi, which invade and destroy the uterine decidua and at the same time absorb from it nutritive materials for the growth of the embryo. In reptiles, birds, and many mammals the allantois becomes expanded into a vesicle which projects into the extra-embryonic celom. The villous trees are connected via a major trunk stem villus to the chorionic plate and display multiple sites of branching, finally ending in terminal villi. The thickness and vascularity of the mucous membrane are greatly increased; its glands are elongated and open on its free surface by funnel-shaped orifices, while their deeper portions are tortuous and dilated into irregular spaces. Early and accurate detection of the PROM or PPROM increases the chances for the patient to have a positive outcome with fewer complications.
Next
Retained Fetal Membranes in Mares

Contributions describing clinical observations, cellular and molecular changes, in vitro mechanistic studies, new concepts and methodologies are sought. Which is the innermost layer of the fetal membrane? In the stratum spongiosum the glands are compressed and appear as slit-like fissures, while their epithelium undergoes degeneration. A branch of an umbilical artery enters each villus and ends in a capillary plexus from which the blood is drained by a tributary of the umbilical vein. Although advocated at various times, oxytocin, estradiol, prostaglandin F2alpha, and oral calcium preparations have not been shown to hasten expulsion of retained membranes or to prevent complications. After a sweep you will most likely lose some or all of your mucous plug. Median section through the horse digit. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Next








