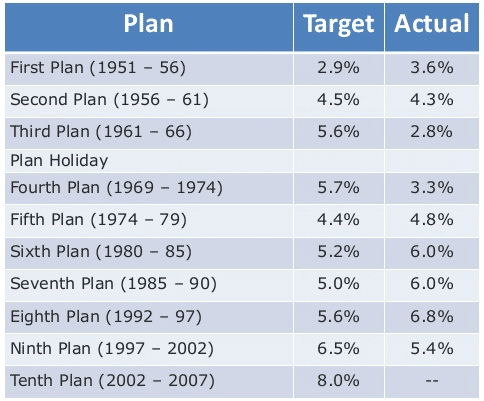
India has a long history of implementing Five-Year Plans as a means of economic development. The first Five-Year Plan was launched in 1951, just a few years after India gained independence from British rule. Since then, the country has implemented a total of twelve Five-Year Plans, with the most recent one being the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, which ran from 2012 to 2017.
The main objective of the Five-Year Plans in India is to promote balanced and rapid economic development by focusing on specific sectors and regions. The Planning Commission, an apex body responsible for the formulation and implementation of the Five-Year Plans, works closely with state governments and other stakeholders to identify priority areas and allocate resources accordingly.
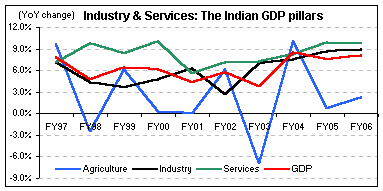
One of the main features of the Five-Year Plans in India is the emphasis on mixed economic development, which combines both public and private sector participation. The government plays a crucial role in providing infrastructure, such as roads, power, and irrigation facilities, while the private sector is encouraged to invest in areas such as industry, agriculture, and services.
Over the years, the focus of the Five-Year Plans in India has evolved to meet the changing needs of the country. The early plans were primarily geared towards achieving self-sufficiency in food production and improving basic infrastructure. The later plans, on the other hand, have focused more on issues such as employment generation, poverty reduction, and environmental sustainability.
Despite the overall success of the Five-Year Plans in India, there have been some criticisms as well. Some have argued that the planning process is too centralized and does not adequately take into account the needs and priorities of different states and regions. Others have pointed out that the implementation of the plans has not always been effective, due to issues such as inadequate resources, bureaucratic hurdles, and corruption.
In conclusion, the Five-Year Plans in India have played a crucial role in the country's economic development over the past seven decades. While there have been challenges and criticisms, the overall impact of the plans has been positive, and they continue to be an important tool for shaping the direction of the country's economic growth.