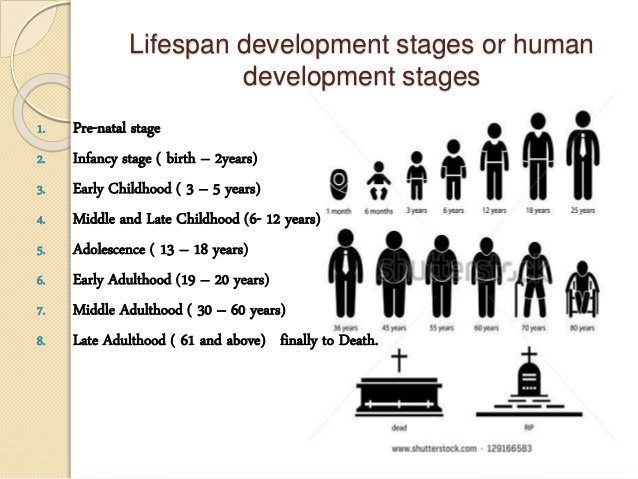
Human development is the process of growth and change that occurs throughout an individual's lifespan. There are several different stages of human development, including infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Each stage is characterized by unique physical, emotional, and cognitive milestones that mark the progress of an individual from one stage to the next.
The first stage of human development is infancy, which is typically defined as the first year of life. During this stage, infants are highly dependent on others for their basic needs, including feeding, dressing, and diaper changes. They are also learning how to explore their environment through their senses and movement. Physical milestones during infancy include the development of fine and gross motor skills, such as grasping objects, sitting upright, and crawling. Emotional milestones include the development of attachment to caregivers and the ability to express a range of emotions.
The second stage of human development is childhood, which is typically defined as the period from one to eleven years old. During this stage, children continue to grow and develop physically, emotionally, and cognitively. They learn to walk, run, and participate in a variety of activities that involve coordination and physical skill. They also learn to express their thoughts and feelings through language and communication. Emotional milestones during childhood include the development of self-esteem, self-control, and the ability to form friendships. Cognitive milestones include the development of problem-solving skills, attention and memory, and the ability to think abstractly.
The third stage of human development is adolescence, which is typically defined as the period from eleven to eighteen years old. During this stage, adolescents experience rapid physical, emotional, and cognitive changes as they transition from childhood to adulthood. Physical changes during adolescence include the onset of puberty, the development of secondary sexual characteristics, and the growth spurt. Emotional changes during adolescence include the development of a sense of identity and independence, as well as the ability to form close relationships with peers. Cognitive changes during adolescence include the development of logical reasoning skills and the ability to think abstractly and critically.
The fourth and final stage of human development is adulthood, which is typically defined as the period from eighteen years old and beyond. During this stage, individuals are considered fully grown and are expected to take on more responsibilities and roles in society. Physical changes during adulthood are generally slower and more gradual than in earlier stages of development. Emotional changes during adulthood may include the development of more stable and mature relationships, as well as the ability to handle stress and solve problems effectively. Cognitive changes during adulthood may include the development of more advanced problem-solving skills and the ability to think abstractly and critically.
In conclusion, human development is a complex and multifaceted process that occurs throughout an individual's lifespan. Understanding the four stages of human development can help us better understand the unique challenges and opportunities that individuals face at different stages of life, and can inform the ways in which we support and guide individuals as they grow and develop.