A stereotype is a widely held but fixed and oversimplified image or idea of a particular type of person or thing. Stereotypes are often based on appearances, culture, ethnicity, gender, and other characteristics, and they can be both positive and negative. While stereotypes may seem harmless, they can have serious consequences and can be harmful to those who are being stereotyped.
One of the main problems with stereotypes is that they often lead to prejudice and discrimination. When people hold stereotypes about certain groups of people, they may treat those individuals unfairly or unjustly. This can lead to negative consequences such as difficulty finding employment, housing, or even experiencing violence. Stereotypes also limit individuals by restricting their opportunities and limiting their ability to be seen as individuals rather than members of a group.
Another issue with stereotypes is that they often rely on incomplete or inaccurate information. People may base their stereotypes on a limited number of experiences or interactions with a particular group, rather than taking the time to understand the diversity and complexity of that group. This can lead to misunderstandings and further perpetuate negative stereotypes.
It is important to challenge and dismantle stereotypes in order to create a more inclusive and equitable society. This can be done by educating oneself about different cultures and groups, engaging in respectful dialogue with others, and speaking out against stereotypes when they are encountered. By actively working to combat stereotypes, we can create a more understanding and accepting world for everyone.
In conclusion, stereotypes are harmful and limiting beliefs that rely on incomplete or inaccurate information. It is important to challenge and dismantle stereotypes in order to create a more inclusive and equitable society. By educating ourselves and actively working to combat stereotypes, we can create a more understanding and accepting world for everyone.
Freezing Point Depression Lauric Acid Lab Report
Another beaker with the same amount of tap water will be placed on a hot plate. Lauric acid has a melting point of about 45°C and is easily melted in a test tube placed in a beaker of hot water. While the samples are melting, set up the temperature probe to the computer and have a beaker of room temperature water ready. Both rely on the weight of the solvent, solute, or solution. When it is fully melted, remove it from the water bath. Materials and Methods: By adding 300mL of tap water to a beaker with about 20 to 25°C to a beaker. In this case, for low solute concentrations, the freezing point depression depends solely on the concentration of solute particles, not on their individual properties.
What Is The Freezing Point of Lauric Acid? (Answered)

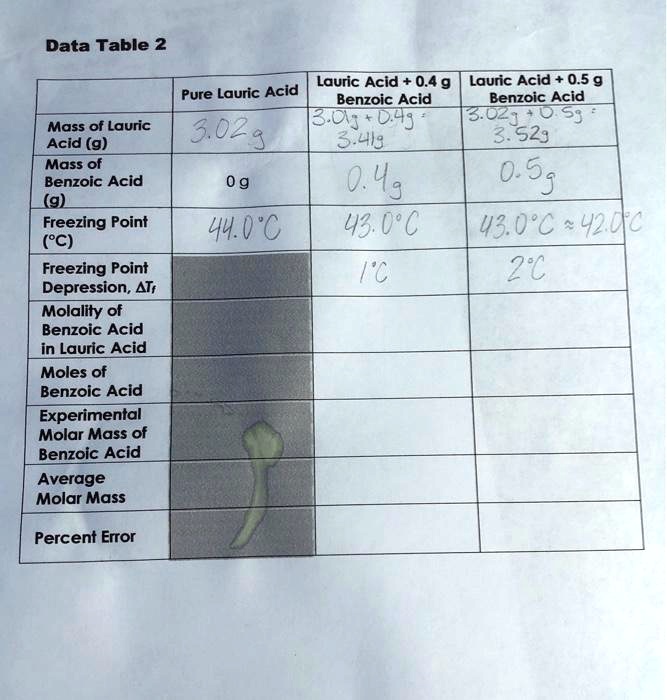
Is lauric acid a molecular or ionic compound? What is KF and KR? Another source of error could have came from the samples themselves and their molalities and molarities. This will allow you to calculate the colligative molality of the solution, mc. Put the temperature probe into the test tube and being stirring the molten lauric acid. The freezing point depression constant Kf of the solvent lauric acid is 3. Explanation: Kf is the molal freezing point depression constant of the solvent 1. This particular fatty acid has many benefits, including weight loss, improved mental clarity, and increased energy.
Freezing Point Depression Lauric Acid
The substances lauric acid and stearic acid are solid at room temperature. . Monolaurin is a compound that has antiviral, antibacterial, and antiprotozoal properties. The formula m is used to find the freezing point depression constant after figuring out the change in temperature and the molality of the samples Molality equals the moles of solute divided the mass of the solvent. Freezing Point Depression of Lauric Acid Intro: Molecules are required to be in a certain arrangement in order to freeze or solidify. This formation constant, Kf , describes the formation of a complex ion from its central ion and attached ligands. Lauric acid is a fatty acid, esters of which occur in natural substances such as coconut milk and palm kernel oil.
Lauric Acid Freezing Point Lab Writeup

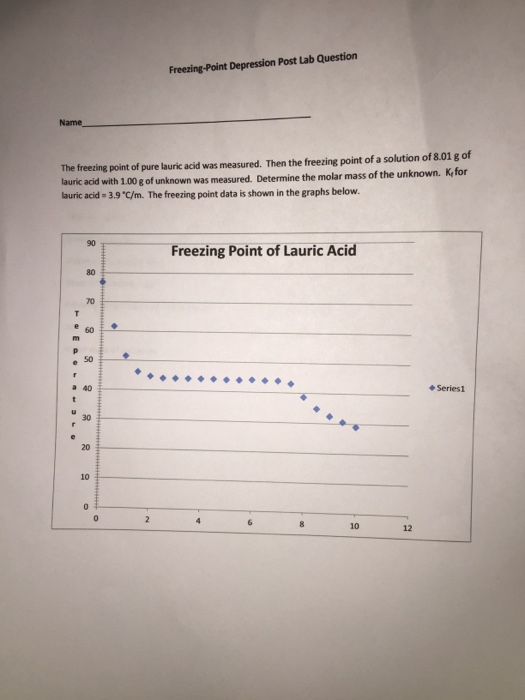
To perform this determination, you must know the mass of both the solvent and solute and the molecular mass of the solute. At what temperature does lauric acid become a liquid? In our experiment, we have Kf but need m molality of the benzoic acid. Wait 5 seconds then hit collect on the Lab Pro screen on the computer. The table below gives values of Kf for various solvents. After obtaining the data from the logging software, the freezing point of lauric acid is determined by plotting a line of best fit on the Logger Pro data and then calculating the y-intercept, or the point on the x-axis where it intersects with zero.
Using Freezing

The melting point of lauric acid and stearic acid is 44 °C and 69. The freezing point depression thus is called a colligative property. The freezing point of lauric acid is lower than room temperature, meaning that it is a solid at room temperature. For example, butter, oil, and margarine all contain high levels of lauric acid. Note:Freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent.