Functionalism and gender inequality. Structural Functionalist Theory Of Gender Inequality Essay 2023-01-04
Functionalism and gender inequality
Rating:
9,2/10
871
reviews
Functionalism is a sociological theory that focuses on the ways in which different parts of society contribute to the stability and cohesion of the whole. According to functionalists, each aspect of society serves a specific function and performs a specific role in maintaining social order. While functionalism has been a useful tool for understanding the role of various social institutions in maintaining social stability, it has also been criticized for its inability to adequately address issues of social inequality, particularly with regard to gender.
One of the key criticisms of functionalism is that it tends to reproduce and reinforce existing social inequalities, rather than challenging them. For example, functionalists may argue that traditional gender roles, in which men are expected to be breadwinners and women are expected to be homemakers, serve a functional purpose in maintaining social stability and cohesion. However, this perspective ignores the ways in which these traditional gender roles contribute to gender inequality by limiting the opportunities and choices available to women and reinforcing male dominance.
Another criticism of functionalism is that it tends to view social phenomena as natural and inevitable, rather than as the result of historical and cultural influences. This can lead to the idea that social inequalities, such as gender inequality, are simply the way things are and cannot be changed. This can discourage attempts to challenge and address these inequalities, and may even serve to justify them.
Despite these criticisms, functionalism can be a useful perspective for understanding the role of social institutions in maintaining social stability. However, it is important to recognize that functionalism alone is not sufficient for understanding and addressing issues of social inequality. It is necessary to also consider the ways in which social inequalities are constructed and maintained, and to work towards creating more equitable and just societies. This may involve challenging and transforming traditional gender roles and other systems of power and privilege that contribute to social inequality. Overall, functionalism can provide a valuable perspective on the role of social institutions in maintaining social stability, but it is important to recognize its limitations and to consider other perspectives in order to fully understand and address issues of social inequality.
Gender Inequality According to Functionalist and Marxist...

This is, however, a gender inequality which has been much targeted by global activism to combat these diverse manifestations of violence and their unequal effects on women. For instance, a functionalist might say that gender inequalities have survived in order to keep both the workforce and the traditional family caregiver roles fulfilled to keep society functioning. There would be no incentive to work hard and do difficult educational courses. They may also be dysfunctional, which means that society will have negative consequences. In perspective, functionalism structures social influences by what is visible and in demand now. Functionalists looked less at what made up the mind and more at how purpose, or roles, drive behavior.
Next
Functionalist Perspective On Gender Inequality

What are the four theoretical perspectives on the origins of gender differences? Functionalism also postulates that all cultural or social phenomena have a positive function and that all are indispensable. Everyone has a role to fill in this functional society, in other words we need to have stratification so as everyone has a purpose. They believe that inequality is both inevitable and functional. Consequentially, the feminist movements fight for same opportunities and rights for women including economic, political, and social rights. Sen 2001 Women are not treated equally.
Next
Gender Differences: The Functionalist Theory Of Gender Roles

However different cultures interpret sexed bodies differently and project different norms on those bodies thereby creating feminine and masculine persons. These theories project the notion females disadvantage in gender issues and therefore coined to help publicised the topic. Those who are better off in society aren 't as willing to do dangerous or dirty jobs. Of all the major sociological perspectives, symbolic interactionism has probably developed the most detailed theory of socialization, Haralambos, Holborn. Gender has created a grand division between men and women. What is the functionalist perspective on gender? During the time that functionalists were writing, some dominant ideas and theories about women often assumed they were inferior when compared to men. To address the global issue of gendered inequality in more innovative ways, it would be useful to further the contemporary debate and emphasis on intersectionality in relation to gender inequality and to highlight the increasing academic focus on masculinity and gender relations and its link to feminism Further, he feels that to address the structural and institutional causes of inequality, one of the main factors for doing so is the recognition of many, interconnected inequalities, as well as having an openness to work with diverse kinds of partners in a variety of ways.
Next
Racial And Gender Inequality: Functionalist Theory

Within the functionalist theory, …show more content… Families reproduce, nurture, and socialize children. This more comprehensive approach to combating violence can be seen in the example of the existence of the International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women, in 2016, which was then followed by Sixteen Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence. Despite the fact that population growth is slowing this decline, as population growth is more prevalent in countries where there is most evidence of gender inequality. According to the functionalist perspective society is viewed as a multifaceted system whose different parts work together to endorse harmony and stability. To round out the second wave, an example of sexuality was radical lesbian feminism Euler, 2016, 7b.
Next
Functionalism and gender inequalities

When both paid and unpaid work such as household chores and caring for children are taken into consideration, women work longer hours than men—an average of 30 minutes a day longer in developed countries and 50 minutes in developing countries. Marxism: Marxism: In the 19th century, Marxism was inspired by two men Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. There can be shown a difference of the way people expect to behave when drinking. Such campaigns are not without their critics; for example, there are diverse views on what can, or cannot, be defined as sexual abuse, and the problem of establishing consent. The third assumption is that culture is built upon connected parts and that you cannot change one part without changing another. Of course, poor men, men of color, gay men, to name just some of the groups other than women, are affected by economic, racial, and sexual discrimination. Traditional gender roles are carried out with the man being the financial and status provider in a family, and the woman performing household duties, providing emotional and sexual support, and raising the children.
Next
social inequality

Calkins would eventually become the first female president of the American Psychological Association in 1905. Race through the lens of interactionism provides a label of identity and relationships. Or, as Rahman 2014 argues, her iconic, global status afforded by the media, celebrities, and governments is actually very problematic, masking as it does the continued educational inequalities which have their roots in complex historical, geopolitical, and development aspects in an Internet age. Both of these together will create equilibrium among the society, which Feminism In The Workplace 1228 Words 5 Pages Women in the United States are expected to have a paying job to help pay for the families needs but at the same time they are expected to be there for their children and other family members as soon as possible when need. The functionalist perspective sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability.
Next
Functionalist Perspective, Gender Roles & Inequality
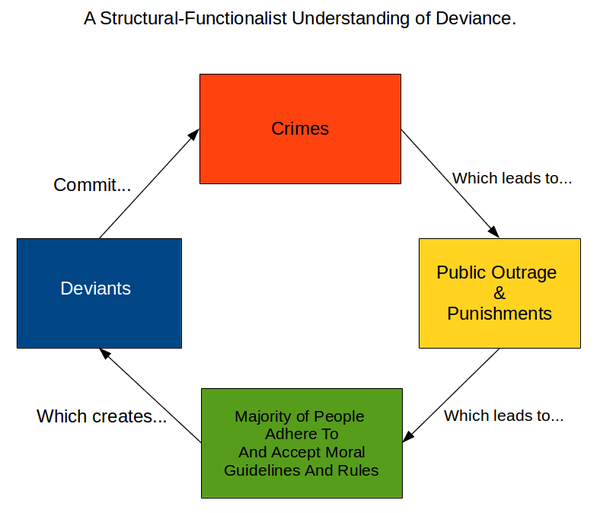
The gender division of labour happens in society so is therefore universal. Certain races or ethnicities are advantageous when obtaining power and privilege. The functionalist perspective views society as a complex system in which every part of that system contributes to its functioning. The functionalist view began as a response to structuralism, which instead looked at the composition of the mind. This is because functionalists believed that the point of understanding consciousness is to understand the behavior that a mental state produces. If people were all paid the same regardless of their work, they would take the easiest jobs and do as little training as possible.
Next
Functionalists and gender inequality Flashcards
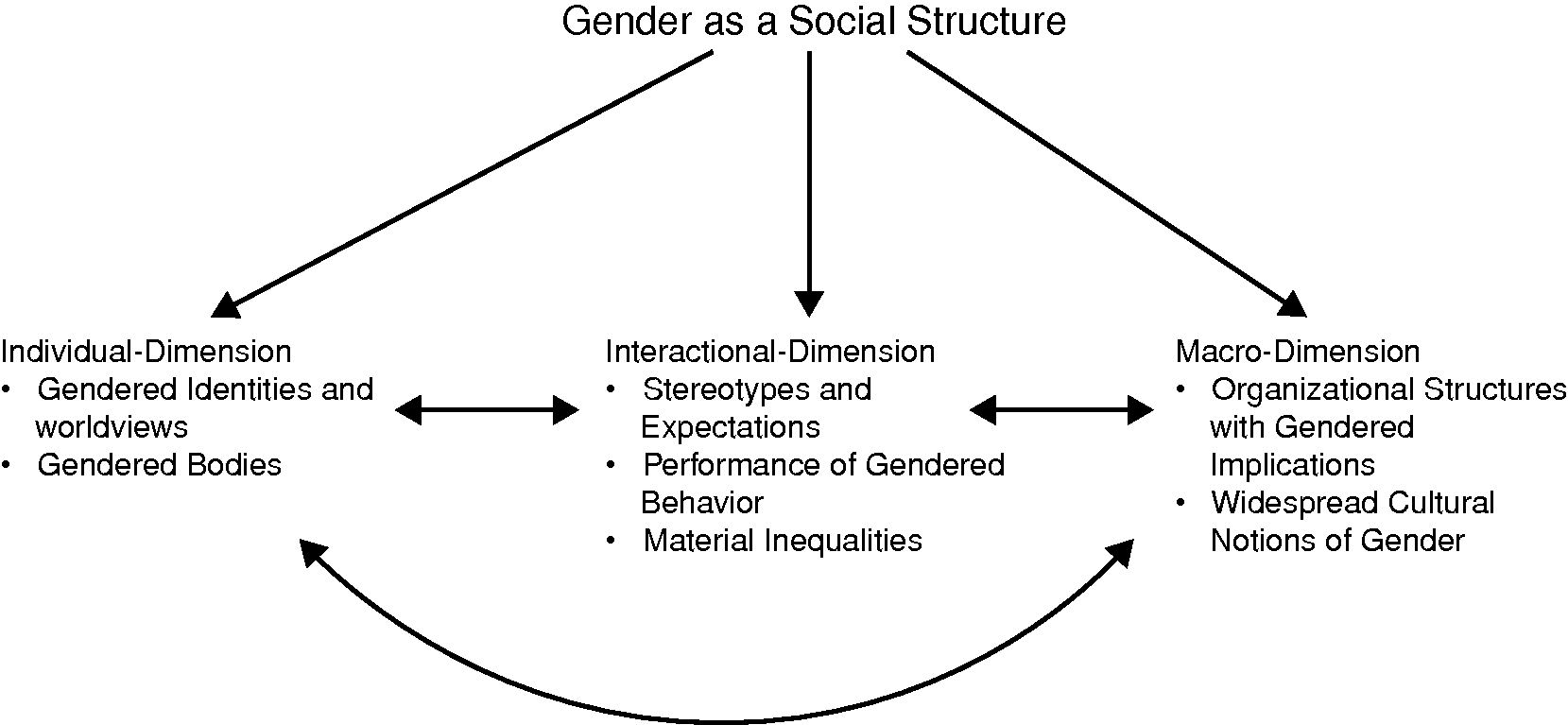
A structural functionalist view of gender inequality applies the division of labor to view predefined gender roles as complementary: women take care of the home while men provide for the family. This quote also talks about how gender is a big part of society that many people will emotionally hurt each other and talk about many gender stereotypes that are not relevant. Plato seems to have been very inconsistent on his views on women and their roles. Thesis Statement On Gender Inequality 919 Words 4 Pages The fact also arises that women not only suffer from lack of recognition for the work they do in households but also for their work in their jobs. Many men of a younger generation have no hesitation in calling themselves feminists and working with women on a range of issues and campaigns. The idealized images, stereotypes and archetypes have been studied from the female point of view. How is gender understood in a sociological perspective? The theory suggests, as an effective means of dividing labor or as a social system, that gender inequalities exist in which specific segments of labor are clearly responsible for certain respective acts.
Next





