Voluntary simplicity, also known as simple living, is a lifestyle choice that involves intentionally simplifying one's life in order to prioritize personal values and reduce the negative impact on the environment. There are many different examples of voluntary simplicity, including minimizing material possessions, living in a smaller home, consuming less energy, and reducing one's environmental footprint.
One example of voluntary simplicity is minimalism, which involves intentionally reducing the number of possessions one owns in order to live a simpler, more organized life. This can involve decluttering and getting rid of unnecessary items, as well as being mindful about what new items are brought into the home. Minimalism can also involve simplifying one's wardrobe, choosing quality over quantity, and only buying items that are truly needed or bring joy.
Another example of voluntary simplicity is living in a smaller home, such as a tiny house or an apartment. This can involve downsizing from a larger, more traditional home in order to reduce the environmental impact of heating, cooling, and maintaining a larger space. It can also involve choosing a home that is closer to work, reducing the need for long commutes and the associated energy use.
Consuming less energy is another way that people can practice voluntary simplicity. This can involve reducing electricity use by turning off lights and appliances when they are not in use, using energy-efficient products, and investing in renewable energy sources. It can also involve reducing the use of fossil fuels by using public transportation, carpooling, or cycling instead of driving a car, or by choosing to walk or use an electric scooter for short trips.
Reducing one's environmental footprint is another aspect of voluntary simplicity. This can involve choosing to live a low-waste lifestyle by reducing the amount of disposable products used, such as single-use plastics, and by composting food waste and other organic materials. It can also involve choosing environmentally-friendly products, such as those made from recycled materials or that are produced using sustainable manufacturing practices.
In conclusion, voluntary simplicity is a lifestyle choice that involves intentionally simplifying one's life in order to prioritize personal values and reduce the negative impact on the environment. There are many different examples of voluntary simplicity, including minimalism, living in a smaller home, consuming less energy, and reducing one's environmental footprint. Adopting a simpler lifestyle can bring a sense of peace and contentment, as well as helping to preserve the planet for future generations.
General Motors (GM) is a leading global automaker that has been in operation for over 100 years. The company designs, builds, and sells a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and SUVs, under various brands such as Chevrolet, Buick, GMC, and Cadillac. GM also operates a financial services division that provides financing and insurance to customers and dealers.
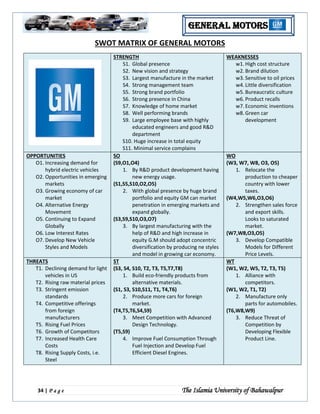
One way to analyze a company's position and potential for growth is through a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis. This analysis looks at a company's internal and external factors that can impact its performance.
Strengths:
Strong brand recognition: GM is a well-known and respected brand with a long history of producing high-quality vehicles. This strong brand recognition can help the company attract and retain customers, as well as negotiate favorable terms with suppliers and partners.
Diverse product portfolio: GM offers a wide range of vehicles across various segments, including cars, trucks, SUVs, and commercial vehicles. This diversification helps the company mitigate the risk of relying on any one particular product or market.
Global presence: GM has a strong global presence, with operations in six continents and a strong presence in key markets such as the United States, China, and Brazil. This global reach allows the company to tap into a wider customer base and benefit from economies of scale.
Weaknesses:
Dependence on the automotive industry: GM's business is heavily reliant on the automotive industry, which can be vulnerable to economic downturns and shifts in consumer preferences.
High debt levels: GM has a significant amount of debt on its balance sheet, which can limit its financial flexibility and increase its financial risk.
Pension obligations: GM has a large number of retired employees and significant pension obligations, which can be a financial burden for the company.
Opportunities:
Growing demand for electric vehicles: There is increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) due to concerns about climate change and the need to reduce emissions. GM has made significant investments in EV technology and has a strong presence in this market with its Chevrolet Bolt EV.
Partnerships and collaborations: GM has formed partnerships and collaborations with other companies in the automotive industry and beyond, such as its partnership with Nikola to develop fuel cell technology for heavy-duty trucks. These partnerships can help the company access new technologies and markets.
Emerging markets: GM has a strong presence in emerging markets such as China and India, which are expected to see strong growth in vehicle sales in the coming years.
Threats:
Competition: GM faces intense competition from other global automakers as well as newer entrants to the market, such as Tesla.
Government regulations: The automotive industry is subject to a variety of government regulations, including emissions standards, safety standards, and fuel efficiency standards. These regulations can impact the company's ability to produce and sell its products.
Trade tensions: GM's global operations make it vulnerable to trade tensions and tariffs, which can impact the cost and availability of raw materials and finished goods.
Overall, GM has a number of strengths, including a strong brand, diverse product portfolio, and global presence. However, the company also faces challenges such as high debt levels, pension obligations, and competition. GM has opportunities to tap into growing demand for EVs and partnerships and collaborations, as well as emerging markets. It also faces threats from government regulations and trade tensions. By carefully considering these factors, GM can make strategic decisions to position itself for success in the future.