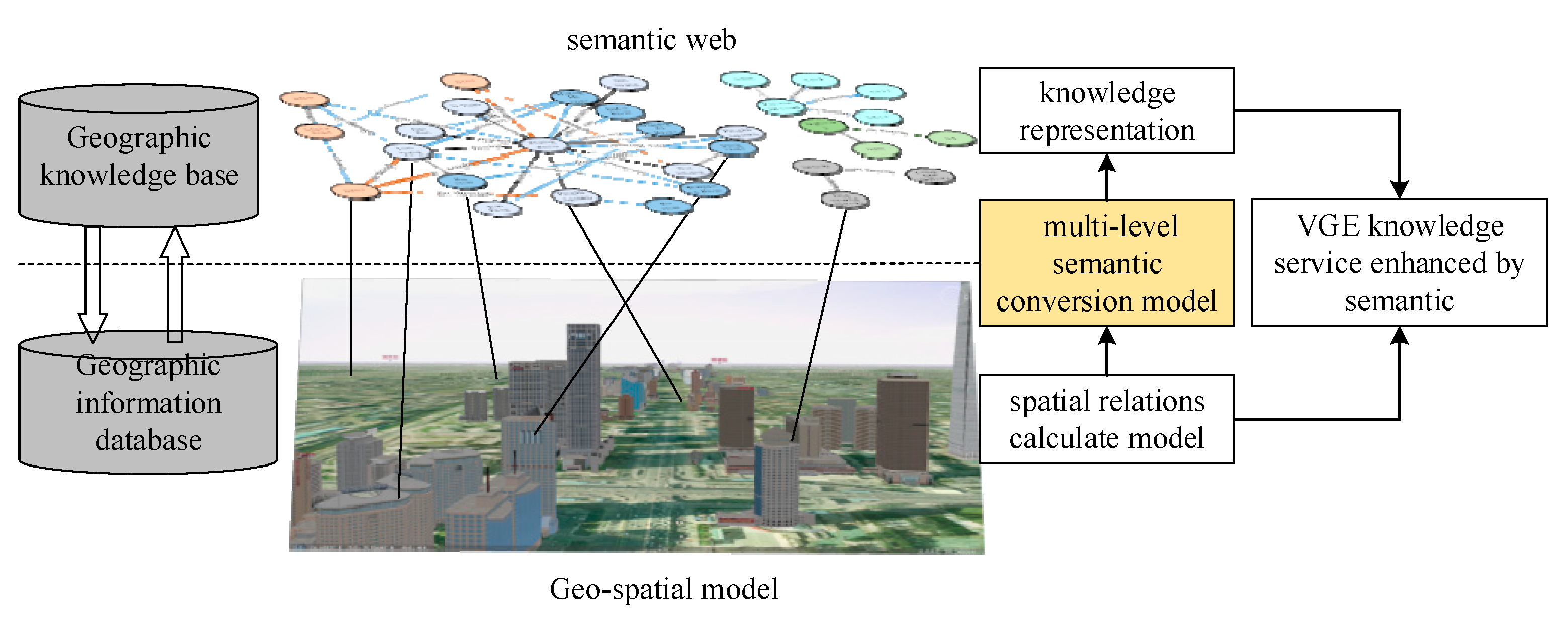
A geographical database, also known as a spatial database, is a type of database management system (DBMS) specifically designed to store and manage spatial data. Spatial data refers to information about the location and shape of objects on the earth's surface, such as roads, buildings, and geographical features.
Geographical databases are often used in applications such as mapping, land management, and transportation. They enable users to store and analyze large amounts of spatial data, and to generate maps and other visualizations that display this data in a meaningful way.
One of the key features of a geographical database is its ability to store and manage data in a way that reflects the spatial relationships between objects. For example, a geographical database can store information about the location of a road in relation to a city, or the shape of a lake in relation to a mountain range. This allows users to perform spatial queries, such as finding all the roads within a certain distance of a city, or all the lakes that are located within a certain mountain range.
Geographical databases also often include tools for data analysis and visualization. These tools can be used to create maps and other graphical representations of the data, which can help users understand the spatial relationships between objects and identify patterns and trends.
There are several types of geographical databases, including vector-based databases and raster-based databases. Vector-based databases store data as points, lines, and polygons, and are often used for storing data about discrete objects, such as roads and buildings. Raster-based databases, on the other hand, store data as a grid of cells, and are often used for storing data about continuous phenomena, such as elevation or temperature.
In summary, a geographical database is a specialized type of DBMS that is designed to store and manage spatial data. It enables users to perform spatial queries and generate maps and other visualizations to help them understand the spatial relationships between objects. Geographical databases are widely used in a variety of applications, including mapping, land management, and transportation.