The Germanic group of languages is a subfamily of the Indo-European language family that includes languages such as English, German, Dutch, and the Scandinavian languages. These languages are spoken by approximately 500 million people worldwide and have a long and complex history.
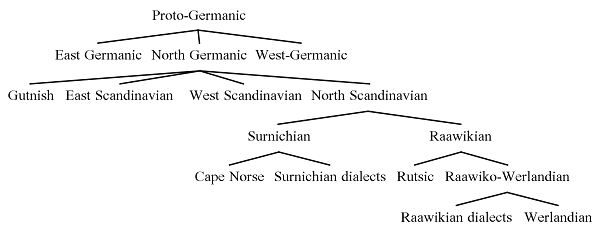
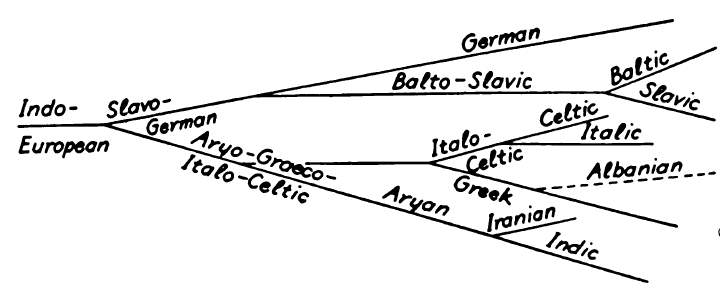
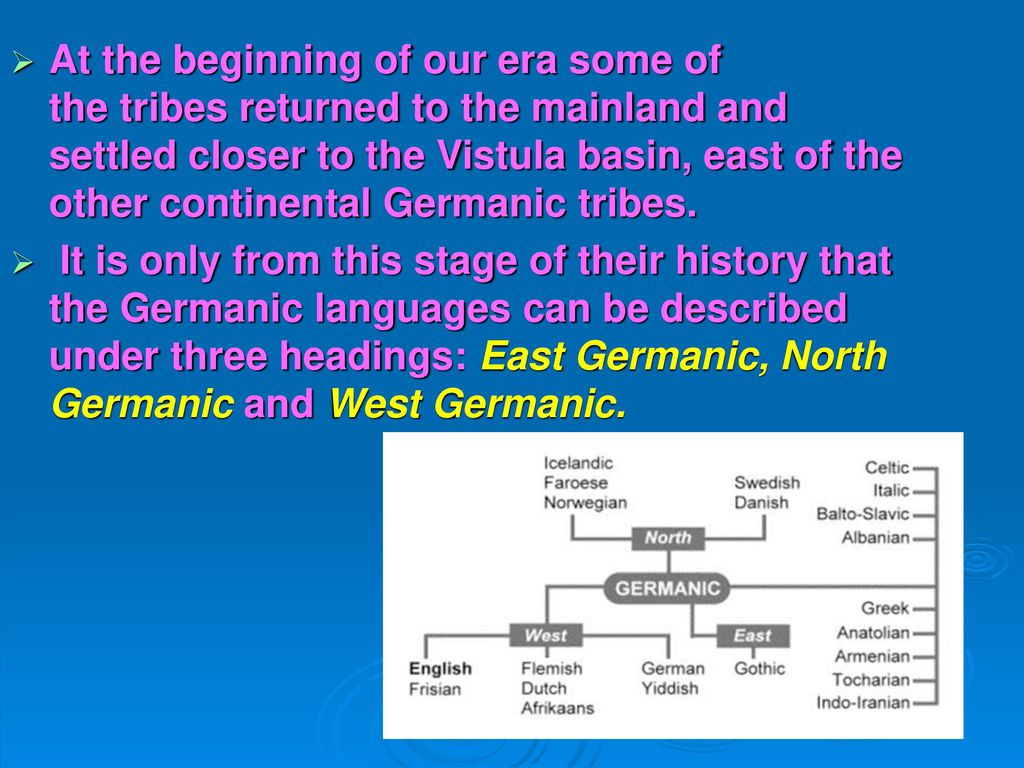
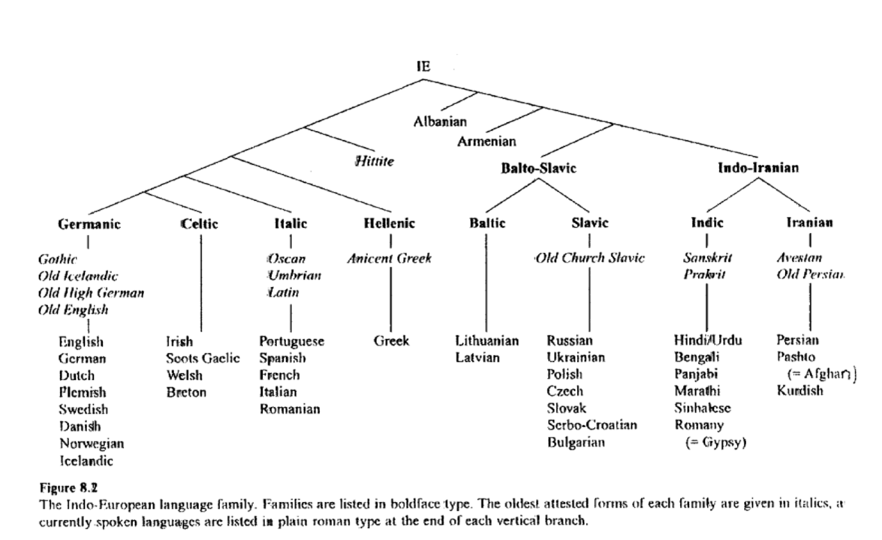
The Germanic languages are thought to have originated in the Nordic region of Europe, with the earliest written records dating back to the 1st century AD. The earliest Germanic language, known as Proto-Germanic, is believed to have split off from the Indo-European language family around the 3rd or 4th century BC. From Proto-Germanic, the various Germanic languages developed and evolved over time, with significant influence from other language groups such as the Celtic, Latin, and Slavic languages.
One of the most notable features of the Germanic languages is their use of inflection, which is the alteration of a word's form to indicate grammatical relationships such as tense, mood, or case. This is in contrast to languages like English, which rely more on word order and function words to convey meaning. The Germanic languages also have a rich vowel system and a complex system of consonants, including sounds that are not found in other language families.
One of the most widely spoken Germanic languages is English, which is the official language of many countries and is spoken as a second language by millions of people around the world. English has a rich history and has evolved over time, with significant influences from other language groups such as Latin, French, and Old Norse. English has also played a central role in the development of modern science, technology, and literature, and it is often considered the international language of business and communication.
Other major Germanic languages include German, which is spoken by more than 100 million people in Germany and Austria, and Dutch, which is spoken by more than 23 million people in the Netherlands and parts of Belgium. The Scandinavian languages, which include Swedish, Danish, and Norwegian, are also part of the Germanic group and are spoken by more than 20 million people in the Nordic region of Europe.
Overall, the Germanic group of languages is a diverse and influential language family that has had a significant impact on the development of modern communication and culture. From the earliest Proto-Germanic to the contemporary Germanic languages of today, these languages have evolved and adapted over time, reflecting the complex histories and cultures of the people who speak them.